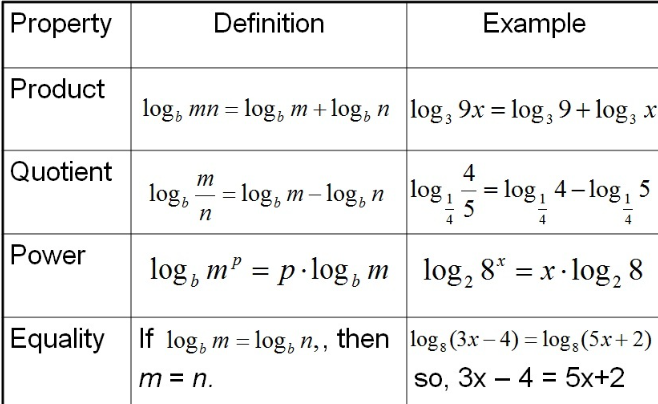
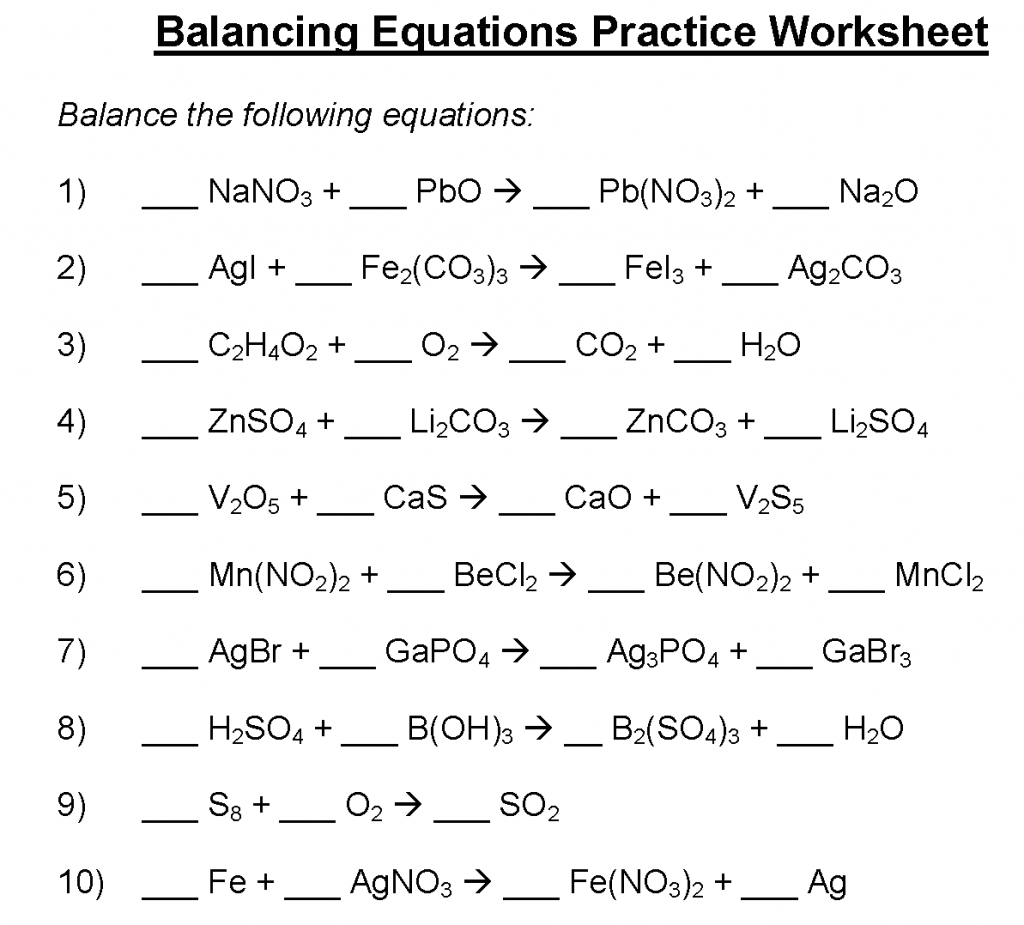
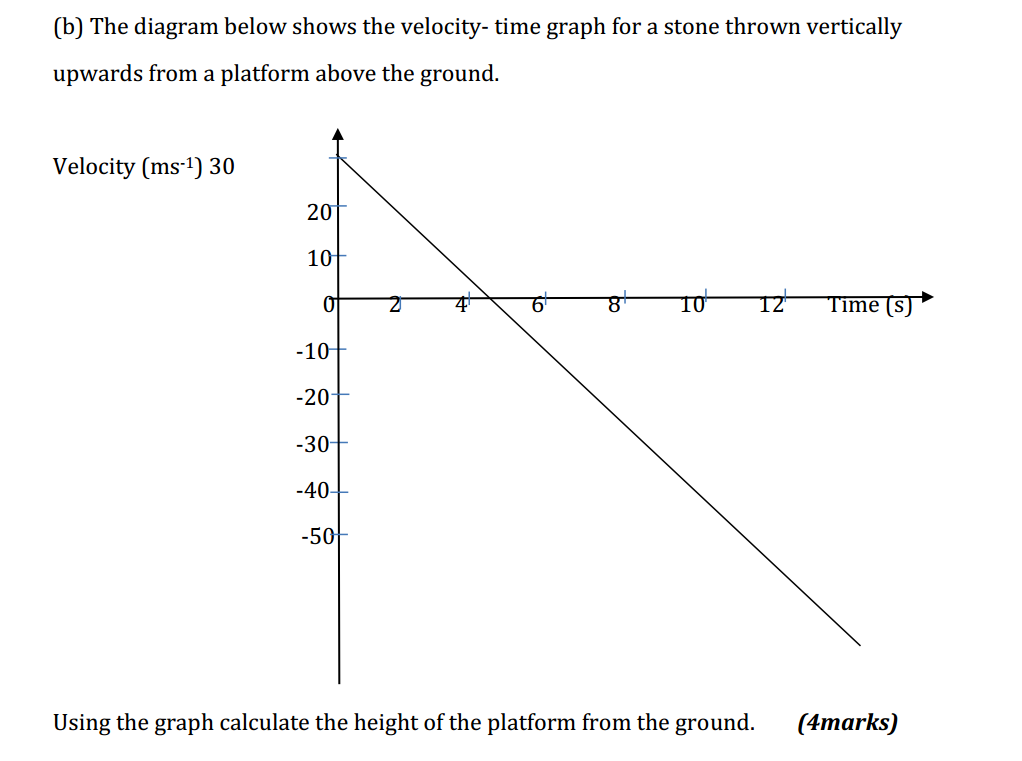
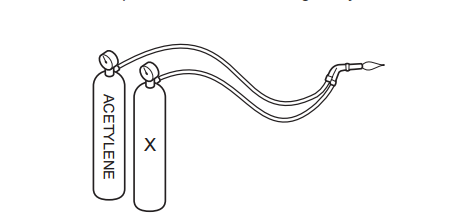
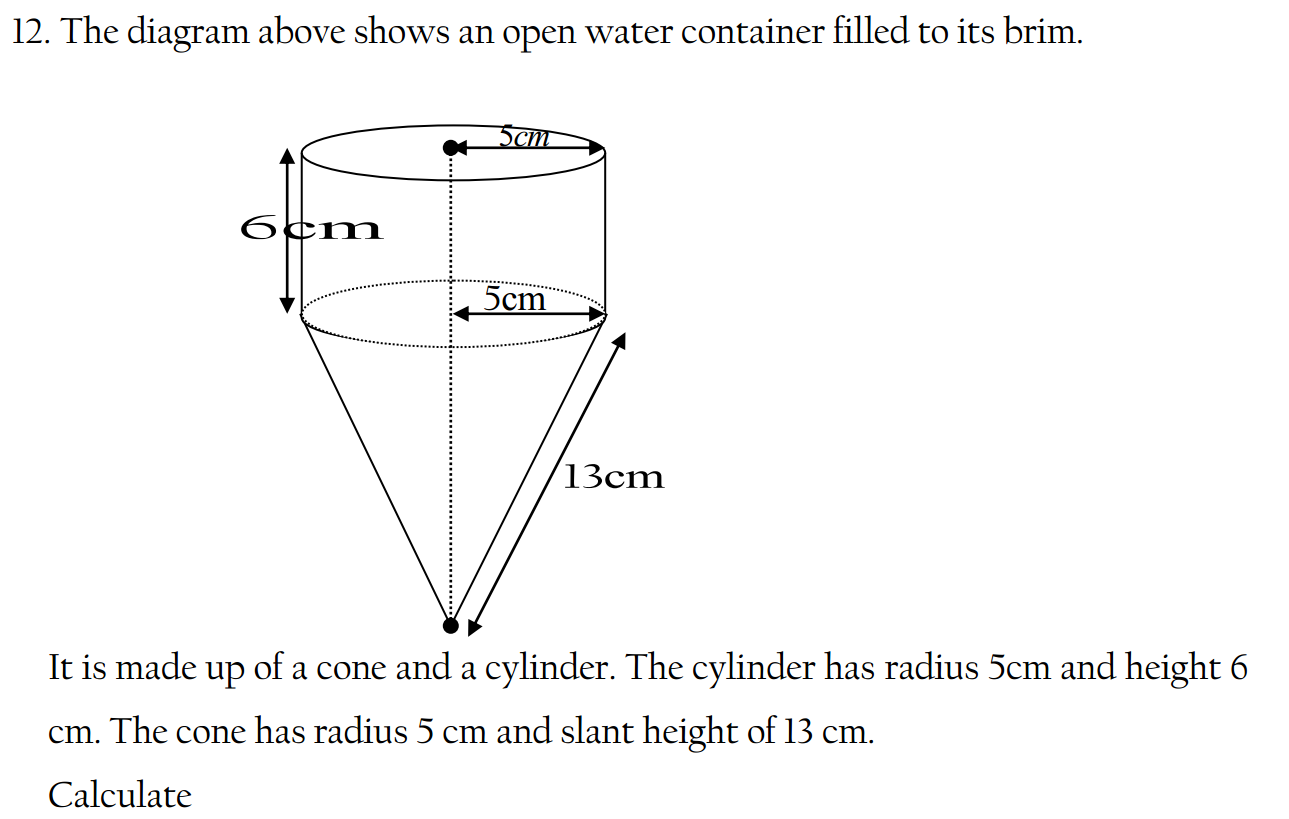
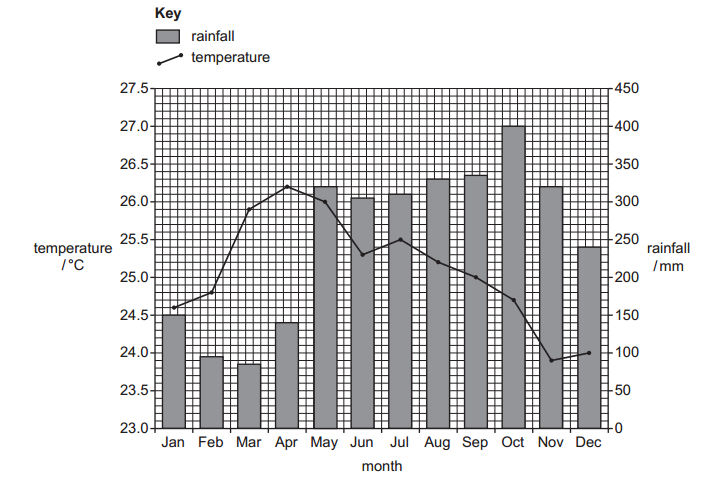
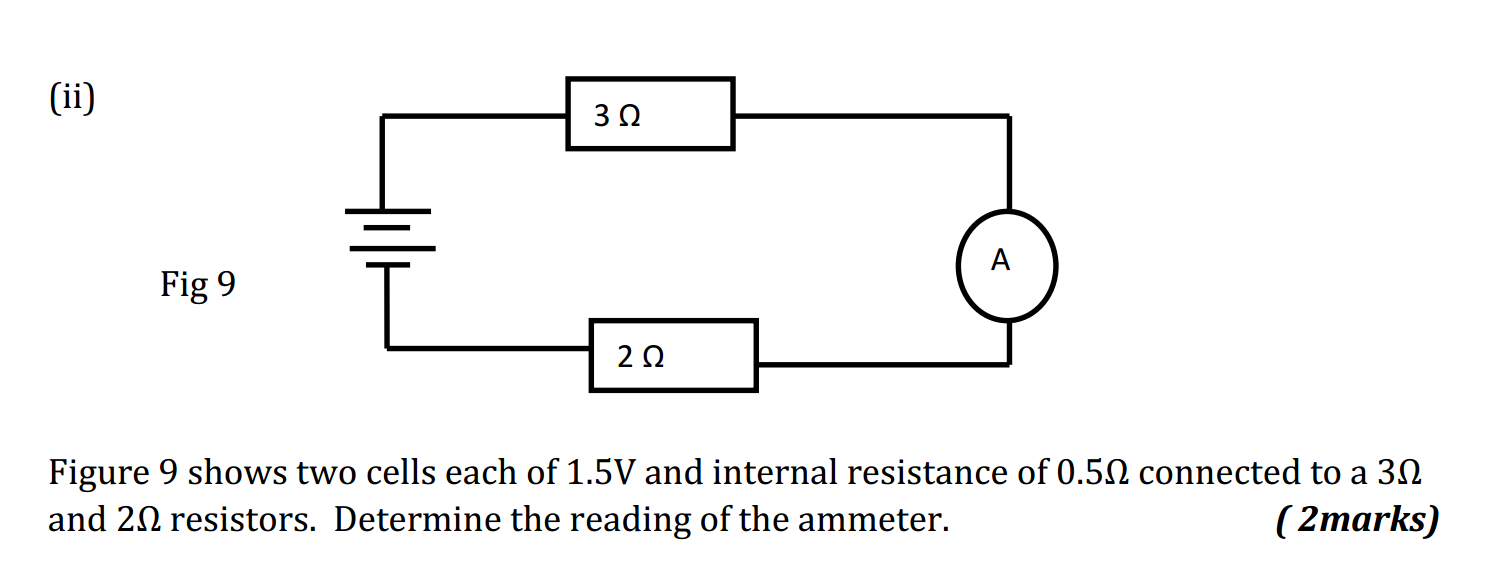
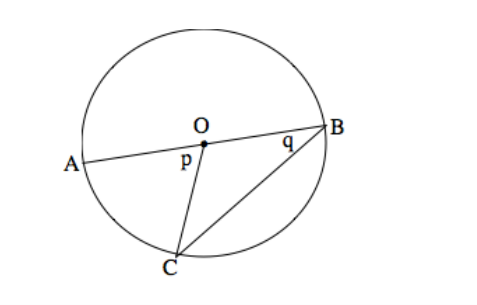
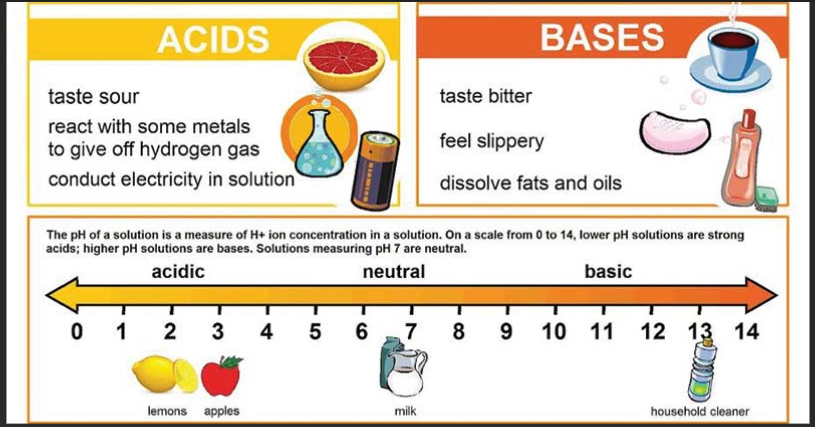
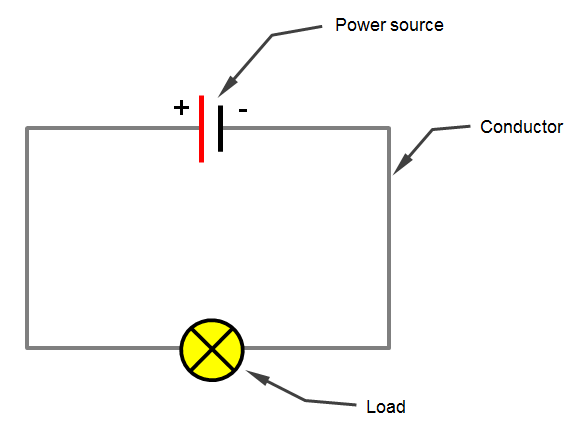
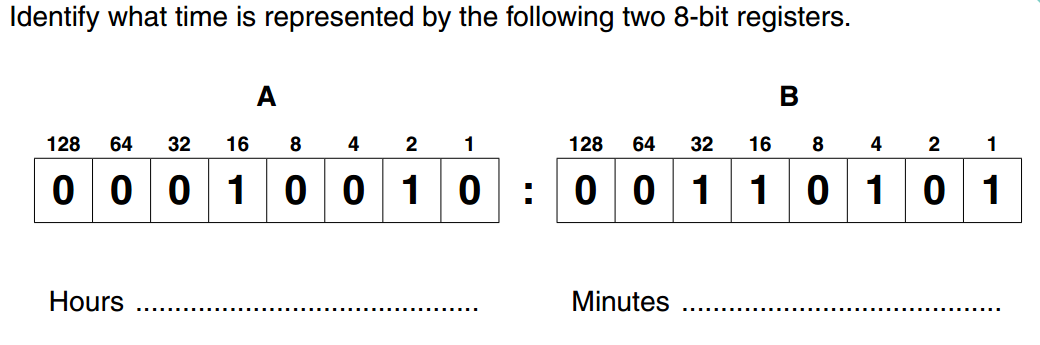
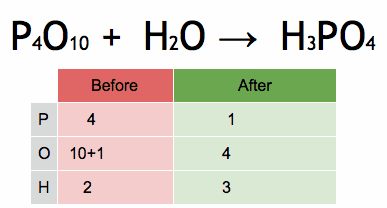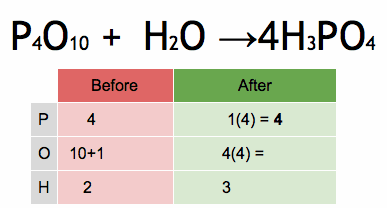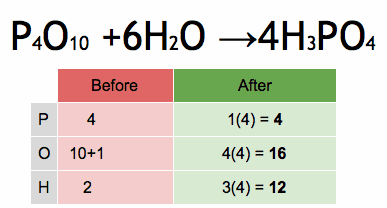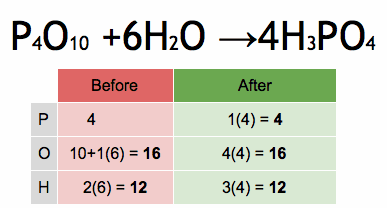
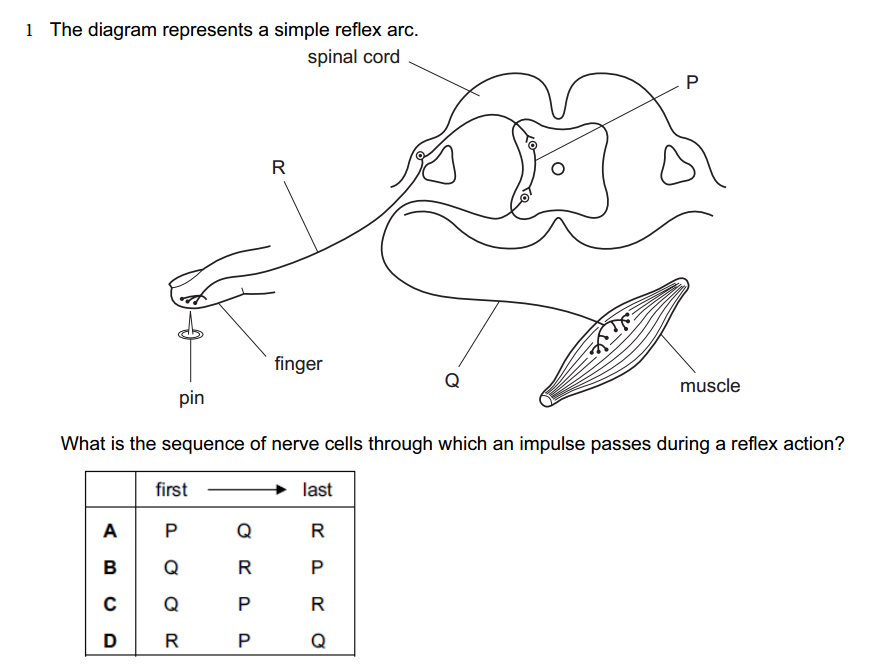
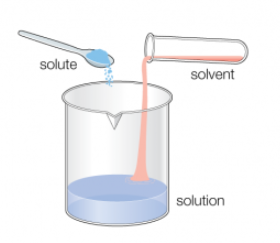
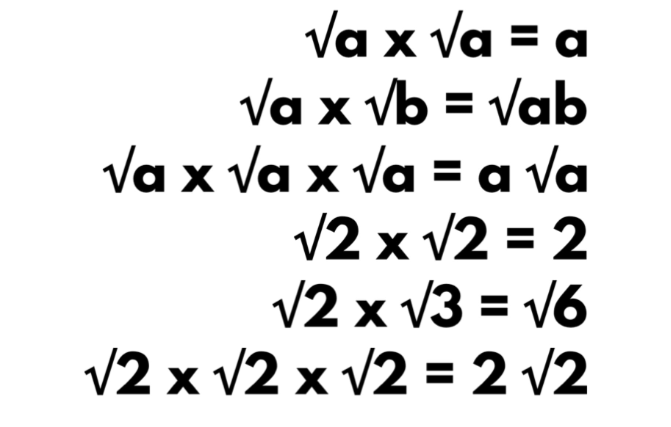- Find the derivative of the function f(x) = 3x^2 + 2x – 5.
- Calculate the indefinite integral of the function f(x) = 4x^3 – 2x^2 + 3x – 1.
- Determine the derivative of the function f(x) = sin(2x).
- Find the limit of the function f(x) = (x^2 + 3x – 4) / (x – 1) as x approaches 1.
- Calculate the definite integral of the function f(x) = 2x over the interval [1, 3].
- Determine the critical points of the function f(x) = x^3 – 6x^2 + 9x.
- Find the second derivative of the function f(x) = e^x cos(x).
- Evaluate the limit as x approaches infinity of the function f(x) = (3x^2 + 2x) / (4x^2 + 5).
- Determine the area between the curves y = x^2 and y = 2x – 1.
- Find the equation of the tangent line to the curve y = 4x^2 – 2x + 1 at the point (2, 13).
- Calculate the antiderivative of the function f(x) = 3 / (x^2 + 4x + 3).
- Find the maximum value of the function f(x) = x^3 – 12x^2 + 36x + 5 over the interval [0, 6].
- Determine the derivative of the function f(x) = ln(2x – 1).
- Find the limit as x approaches 0 of the function f(x) = (sin(3x)) / x.
- Calculate the definite integral of the function f(x) = 5 / (x^2 + 4) over the interval [-2, 2].
- Determine the points of inflection of the function f(x) = x^3 – 6x^2 + 9x.
- Find the derivative of the function f(x) = 3^(2x + 1).
- Evaluate the limit as x approaches negative infinity of the function f(x) = (2x^3 – 4x^2 + 3) / (5x^3 + 2).
- Determine the area enclosed by the curve y = x^2 and the line y = 2x – 3.
- Find the equation of the normal line to the curve y = e^x sin(x) at the point where x = π/4.
These questions cover various topics in calculus, including differentiation, integration, limits, curve sketching, and optimization.