1.What is the SI unit of electric charge? a) Ampere b) Coulomb c) Volt d) Ohm 2.What does Gauss's Law in electrostatics describe? a) Electric flux through a closed surface b) Magnetic field around a wire c) Electric field due to a point charge d) Voltage drop across a resistor 3.According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, what induces an electromotive force (EMF)? a) Electric charge b) Magnetic field c) Motion of a conductor relative to a magnetic field d) Voltage drop 4.What is the direction of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying wire? a) Away from the wire b) Towards the wire c) Parallel to the wire d) Perpendicular to the wire 5.What is the relationship between the strength of an electromagnet and the number of turns in the coil? a) Inversely proportional b) Directly proportional c) No relationship d) Exponential 6.Which law states that the induced electromotive force (EMF) in a closed loop is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the loop? a) Ohm's Law b) Gauss's Law c) Ampere's Law d) Faraday's Law 7.What is the relationship between the magnetic field strength and the distance from a current-carrying wire? a) Inversely proportional b) Directly proportional c) No relationship d) Exponential 8.What property of a material determines its susceptibility to magnetization when placed in an external magnetic field? a) Permittivity b) Conductivity c) Permeability d) Resistivity 9.What is the unit of magnetic flux density? a) Tesla b) Weber c) Gauss d) Henry 10.What happens to the force between two electric charges when the distance between them is doubled? a) It doubles b) It quadruples c) It is halved d) It is quartered 11.What law states that like magnetic poles repel each other, and unlike magnetic poles attract each other? a) Coulomb's Law b) Ohm's Law c) Ampere's Law d) Gauss's Law 12.What is the SI unit of magnetic flux? a) Weber b) Tesla c) Henry d) Ampere-turn 13.What determines the direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor? a) Fleming's Left-Hand Rule b) Fleming's Right-Hand Rule c) Lenz's Law d) Newton's Third Law 14.Which electromagnetic wave has the shortest wavelength? a) Radio waves b) Microwaves c) X-rays d) Gamma rays 15.Which device is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy? a) Transformer b) Generator c) Motor d) Capacitor 16.What is the SI unit of inductance? a) Volt b) Ohm c) Ampere d) Henry 17.What law describes the relationship between the electric current flowing through a conductor and the voltage across it? a) Ohm's Law b) Ampere's Law c) Faraday's Law d) Lenz's Law 18.What type of material exhibits zero resistance to the flow of electric current at low temperatures? a) Superconductor b) Insulator c) Semiconductor d) Conductor 19.Which electromagnetic wave has the longest wavelength? a) Radio waves b) Microwaves c) X-rays d) Gamma rays 20.What is the relationship between the magnetic field strength and the current flowing through a wire? a) Inversely proportional b) Directly proportional c) No relationship d) Exponential 21.What is the SI unit of capacitance? a) Volt b) Farad c) Ohm d) Ampere 22.What law states that the induced current in a circuit is in the direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux that produces it? a) Coulomb's Law b) Ohm's Law c) Lenz's Law d) Ampere's Law 23.Which electromagnetic wave has the highest frequency? a) Radio waves b) Microwaves c) X-rays d) Gamma rays 24.What is the function of a rectifier in an electrical circuit? a) To convert DC to AC b) To convert AC to DC c) To regulate voltage d) To amplify signals 25.What determines the direction of the induced current in a loop of wire according to Lenz's Law? a) The direction of the external magnetic field b) The direction of the induced magnetic field c) The direction of the change in magnetic flux d) The direction of the electric field 26.What property of a capacitor determines its ability to store electrical charge? a) Inductance b) Capacitance c) Resistance d) Conductance 27.What is the relationship between the voltage and current in a purely resistive circuit? a) Voltage leads current by 90 degrees b) Voltage lags current by 90 degrees c) Voltage and current are in phase d) Voltage and current are out of phase 28.What is the relationship between the voltage and current in an ideal inductor? a) Voltage leads current by 90 degrees b) Voltage lags current by 90 degrees c) Voltage and current are in phase d) Voltage and current are out of phase 29.What is the function of a transformer in an electrical circuit? a) To store electrical energy b) To convert electrical energy into mechanical energy c) To change the voltage of an alternating current d) To amplify signals 30.What is the relationship between the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of a transformer and the voltage across them? a) Inversely proportional b) Directly proportional c) No relationship d) Exponential These questions cover various concepts in electromagnetism and can be used for testing understanding or as study material.

30 objective questions related to electromagnetism with answers.
Shares:


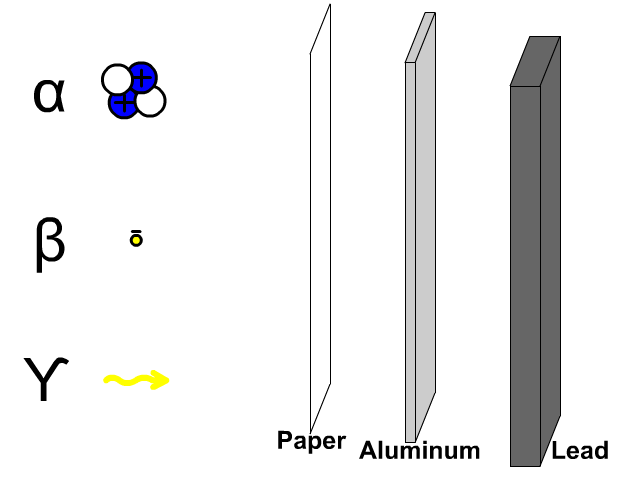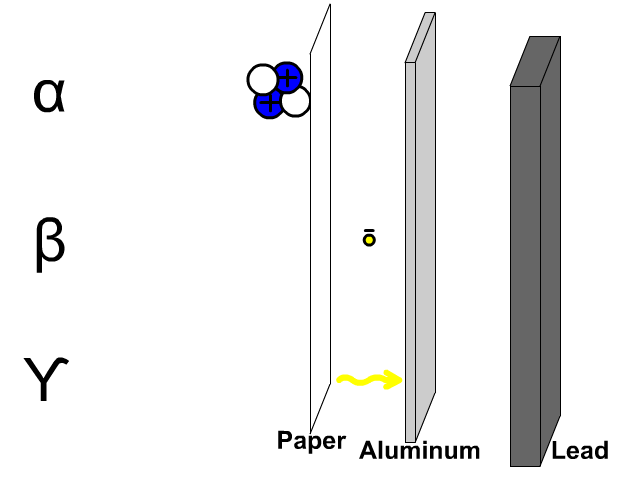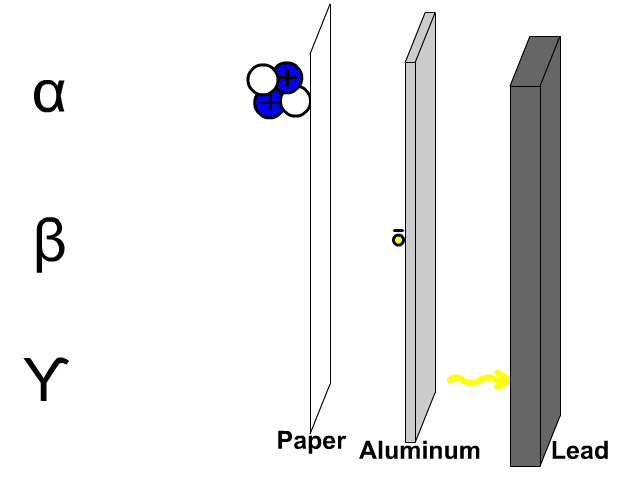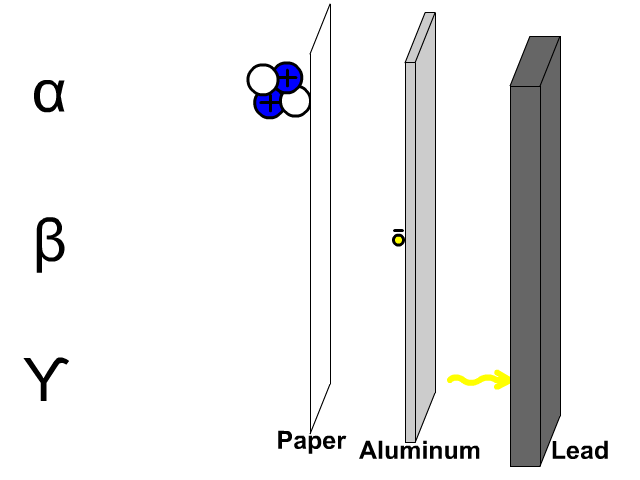









































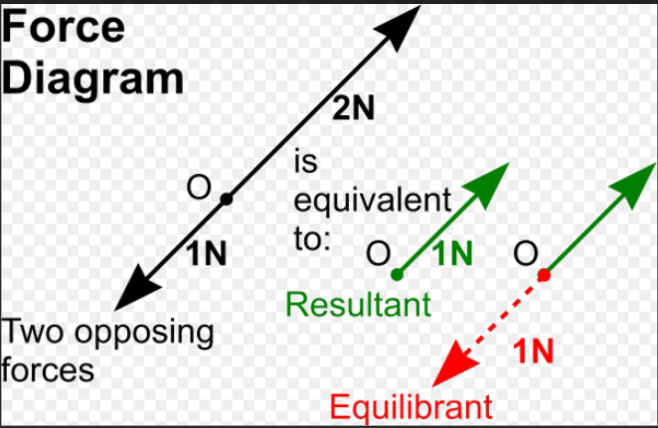




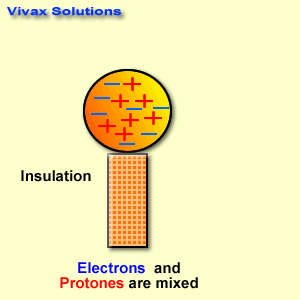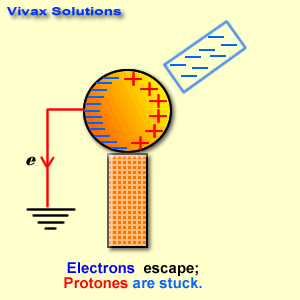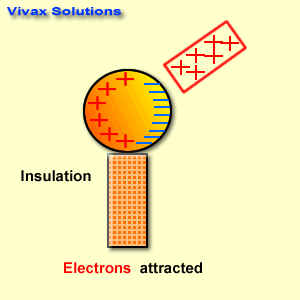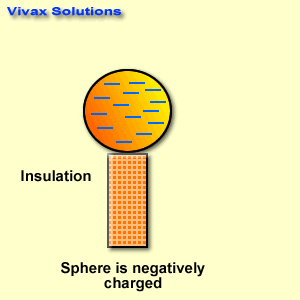



[…] 30 objective questions related to electromagnetism with answers. […]