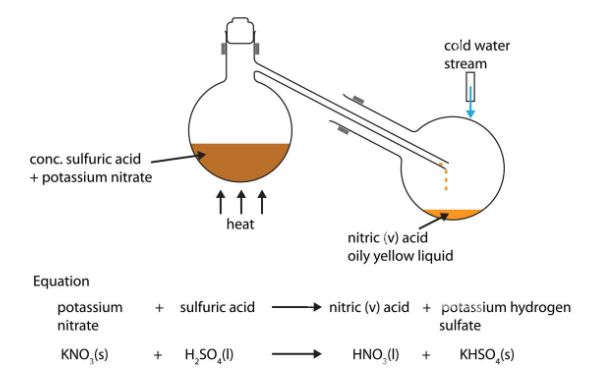
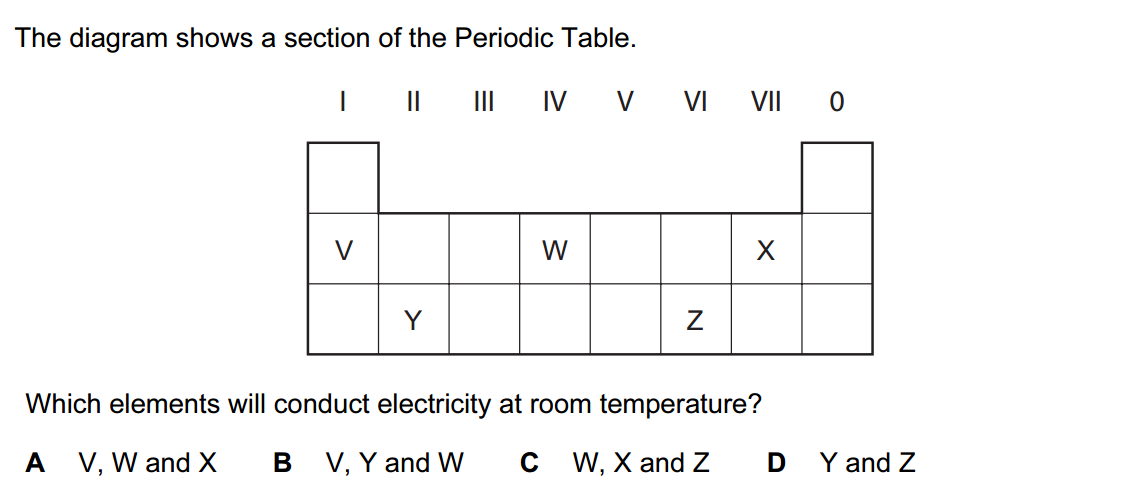
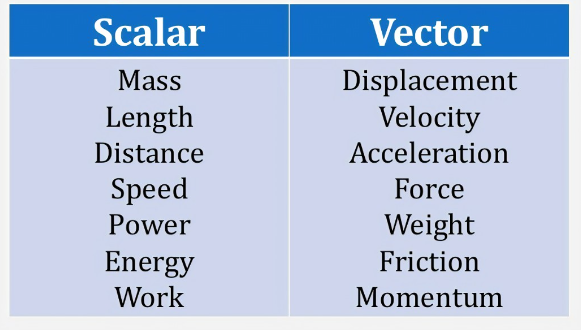
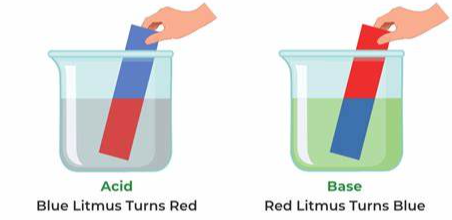
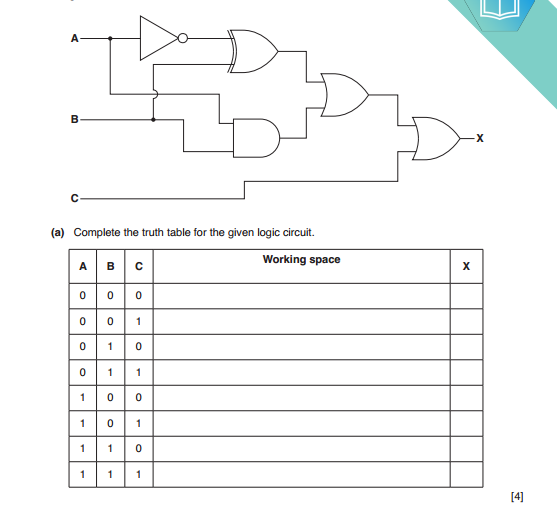
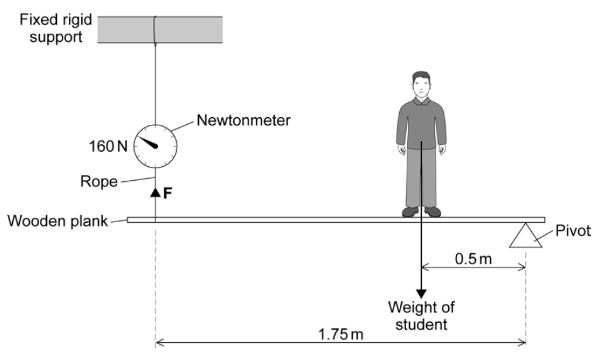
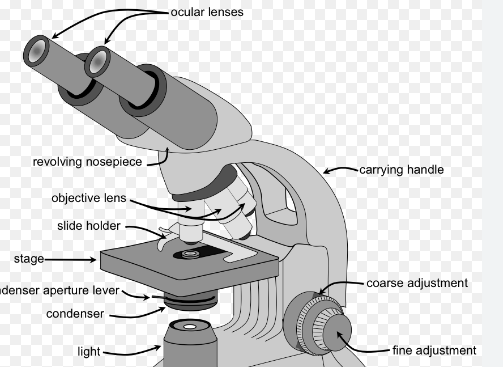
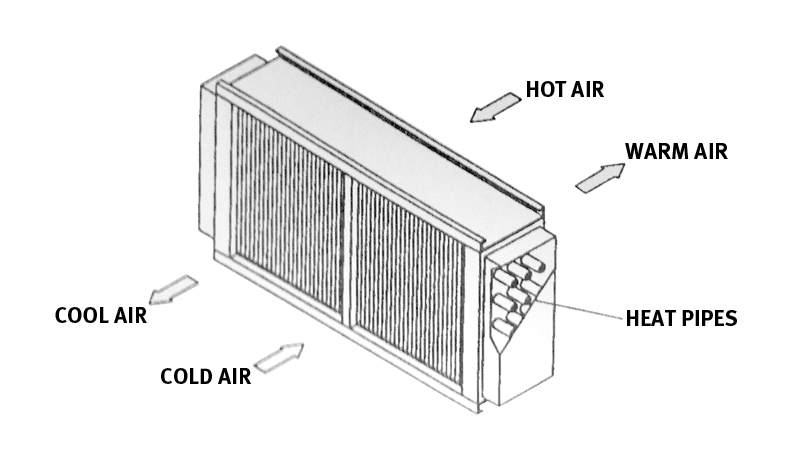
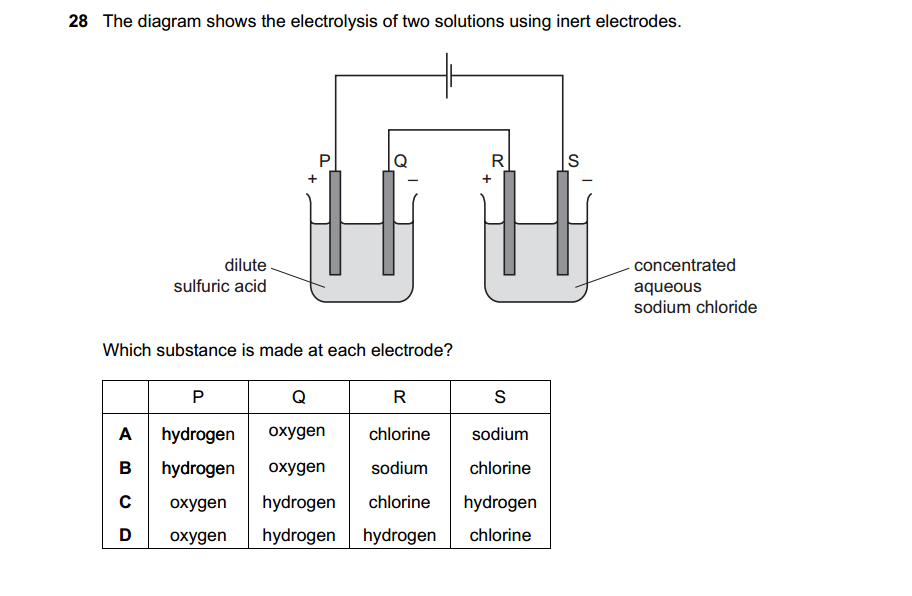
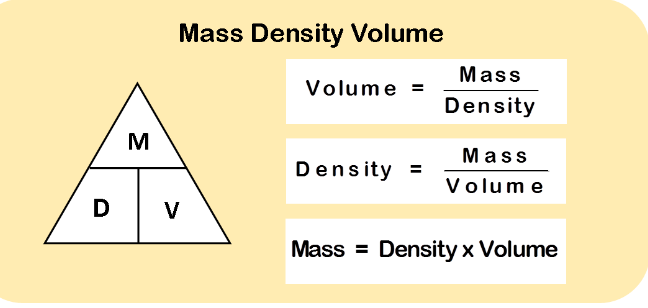
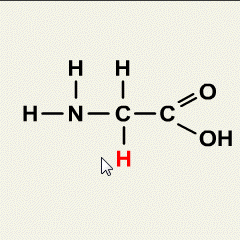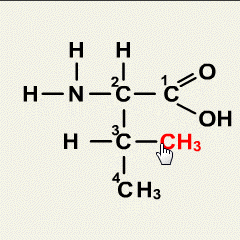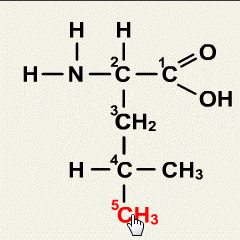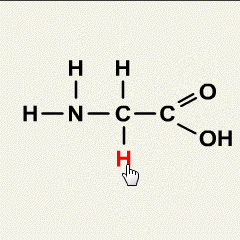
Here’s an expanded list featuring 40 famous scientists, their notable discoveries, and their countries of origin:
- Isaac Newton (England): Laws of motion and universal gravitation.
- Albert Einstein (Germany/Switzerland/USA): Theory of relativity (special and general), E=mc^2.
- Marie Curie (Poland/France): Radioactivity, discovery of polonium and radium.
- Charles Darwin (England): Theory of evolution by natural selection.
- Galileo Galilei (Italy): Telescope observations, laws of motion, and planetary motion.
- Louis Pasteur (France): Germ theory of disease, pasteurization.
- Nikola Tesla (Serbia/Croatia/USA): Alternating current (AC) electricity, Tesla coil.
- Alexander Fleming (Scotland/UK): Discovery of penicillin, antibiotics.
- Gregor Mendel (Austria-Hungary/Czech Republic): Laws of inheritance, genetics.
- Thomas Edison (USA): Phonograph, electric light bulb, motion picture camera.
- James Clerk Maxwell (Scotland/UK): Maxwell’s equations, electromagnetic theory.
- Michael Faraday (England): Electromagnetic induction, electrolysis.
- Erwin Schrödinger (Austria/Germany): Schrödinger equation, quantum mechanics.
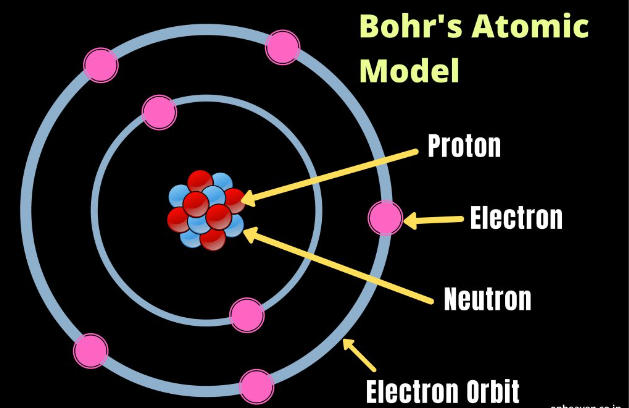
- Niels Bohr (Denmark): Bohr model of the atom, quantum theory.
- Max Planck (Germany): Quantum theory, Planck’s constant.
- Werner Heisenberg (Germany): Uncertainty principle, quantum mechanics.
- Enrico Fermi (Italy): Nuclear reactions, Fermi–Dirac statistics.
- Richard Feynman (USA): Quantum electrodynamics, Feynman diagrams.
- James Watson and Francis Crick (USA/UK): DNA structure, double helix model.
- Rosalind Franklin (England): X-ray diffraction of DNA, contributions to DNA structure.
- Aristotle (Ancient Greece): Foundations of biology, philosophy, and logic.
- Archimedes (Ancient Greece): Archimedes’ principle, hydrostatics, geometry.
- Hippocrates (Ancient Greece): Father of medicine, Hippocratic Oath.
- Pythagoras (Ancient Greece): Pythagorean theorem, mathematics, philosophy.
- Euclid (Ancient Greece): Euclidean geometry, “Elements.”
- Ptolemy (Ancient Greece): Geocentric model of the universe.
- Leonardo da Vinci (Italy): Scientific drawings, anatomical studies, engineering.
- Johannes Kepler (Germany): Laws of planetary motion, Kepler’s laws.
- Antoine Lavoisier (France): Law of conservation of mass, chemistry.
- André-Marie Ampère (France): Ampère’s law, electromagnetism.
- Hans Christian Ørsted (Denmark): Discovery of electromagnetism.
- Wilhelm Röntgen (Germany): Discovery of X-rays.
- Louis de Broglie (France): Wave-particle duality, quantum mechanics.
- Linus Pauling (USA): Molecular biology, quantum chemistry.
- Robert Hooke (England): Cell theory, microscopy.
- Antoine Lavoisier (France): Father of modern chemistry, oxygen discovery.
- Gottfried Leibniz (Germany): Calculus, philosophy.
- John Dalton (England): Atomic theory, Dalton’s law.
- William Harvey (England): Circulation of blood, anatomy.
- Carl Linnaeus (Sweden): Taxonomy, binomial nomenclature.
These scientists have made significant contributions across a wide range of scientific disciplines, shaping our understanding of the natural world and advancing human knowledge.