Here are 40 objective questions related to nuclear physics: 1.What is the smallest component of an atom's nucleus? a) Proton b) Neutron c) Electron d) Quark 2.What force holds the nucleus of an atom together? a) Electromagnetic force b) Gravitational force c) Weak nuclear force d) Strong nuclear force 3.What is the charge of a neutron? a) Positive b) Negative c) Neutral d) Variable 4.Which particle is emitted during radioactive decay? a) Photon b) Neutrino c) Electron d) All of the above 5.What is the process by which an unstable nucleus emits radiation? a) Fusion b) Fission c) Radioactivity d) Transmutation 6.What is the SI unit of radioactivity? a) Joule b) Tesla c) Becquerel d) Curie 7.Which type of radiation has the highest penetrating power? a) Alpha b) Beta c) Gamma d) Neutron 8.What is the charge of an alpha particle? a) Positive b) Negative c) Neutral d) Variable 9.Which type of decay results in the emission of an electron from the nucleus? a) Alpha decay b) Beta decay c) Gamma decay d) Positron emission 10.What is the term for the time it takes for half of the radioactive nuclei in a sample to decay? a) Half-life b) Decay constant c) Activity d) Fission rate 11.What element is commonly used as fuel in nuclear reactors? a) Uranium b) Oxygen c) Carbon d) Hydrogen 12.What is the process by which a heavy nucleus splits into two or more lighter nuclei? a) Fusion b) Fission c) Decay d) Transmutation 13.What is the main product of nuclear fission reactions in nuclear reactors? a) Helium b) Uranium c) Neutrons d) Energy 14.Which type of radiation consists of high-energy photons? a) Alpha b) Beta c) Gamma d) Neutron 15.What is the term for the capture of a neutron by a nucleus, resulting in the formation of a heavier nucleus? a) Fusion b) Fission c) Neutron activation d) Neutron capture 16.Which particle has the smallest mass? a) Proton b) Neutron c) Electron d) Photon 17.What is the term for the process by which an unstable nucleus spontaneously emits an alpha particle? a) Alpha decay b) Beta decay c) Gamma decay d) Positron emission 18.What is the approximate mass of a neutron in atomic mass units (amu)? a) 1 amu b) 0.5 amu c) 1.008 amu d) 1.67 amu 19.Which type of radiation consists of high-speed electrons? a) Alpha b) Beta c) Gamma d) Neutron 20.What is the term for the process by which a heavy nucleus captures a neutron and then undergoes beta decay? a) Fusion b) Fission c) Neutron activation d) Neutron capture 21.What is the energy released per unit mass in a nuclear reaction? a) Momentum b) Kinetic energy c) Binding energy d) Potential energy 22.What is the term for the process by which a neutron splits into a proton and an electron? a) Neutron capture b) Neutron decay c) Beta decay d) Positron emission 23.Which type of radiation can be stopped by a sheet of paper? a) Alpha b) Beta c) Gamma d) Neutron 24.What is the term for the process by which a nucleus undergoes spontaneous decay by emitting a gamma ray? a) Alpha decay b) Beta decay c) Gamma decay d) Positron emission 25.What is the approximate mass of a proton in atomic mass units (amu)? a) 1 amu b) 0.5 amu c) 1.008 amu d) 1.67 amu 26.Which element is commonly used as a moderator in nuclear reactors? a) Uranium b) Carbon c) Boron d) Water 27.What is the term for the process by which a proton splits into a neutron and a positron? a) Neutron capture b) Neutron decay c) Beta decay d) Positron emission 28.Which type of radiation consists of a high-energy helium nucleus? a) Alpha b) Beta c) Gamma d) Neutron 29.What is the term for the process by which an unstable nucleus undergoes spontaneous decay by emitting a positron? a) Alpha decay b) Beta decay c) Gamma decay d) Positron emission 30.Which particle has the same mass as an electron but carries a positive charge? a) Proton b) Neutron c) Positron d) Photon 31.What is the term for the energy required to completely separate the nucleons in a nucleus? a) Momentum b) Kinetic energy c) Binding energy d) Potential energy 32.Which element is commonly used as a coolant in nuclear reactors? a) Uranium b) Carbon c) Boron d) Water 33.What is the term for the process by which a nucleus gains energy by absorbing a photon? a) Fusion b) Fission c) Neutron activation d) Photon absorption 34.Which type of radiation consists of a high-energy neutron? a) Alpha b) Beta c) Gamma d) Neutron 35.What is the term for the spontaneous decay of a proton into a neutron and a positron? a) Neutron capture b) Neutron decay c) Beta decay d) Positron emission 36.Which type of radiation consists of a high-energy electron? a) Alpha b) Beta c) Gamma d) Neutron 37.What is the term for the process by which a nucleus gains energy by absorbing a neutron? a) Fusion b) Fission c) Neutron activation d) Photon absorption 38.Which element is commonly used as a shield to absorb gamma radiation? a) Lead b) Aluminum c) Copper d) Iron 39.What is the term for the process by which a nucleus loses energy by emitting a photon? a) Fusion b) Fission c) Neutron activation d) Photon emission 40.Which type of radiation consists of a high-energy proton? a) Alpha b) Beta c) Gamma d) Neutron These questions cover various concepts in nuclear physics and can be used for testing understanding or as study material.

40 Objective Questions in Nuclear Physics with Solutions.
Shares:


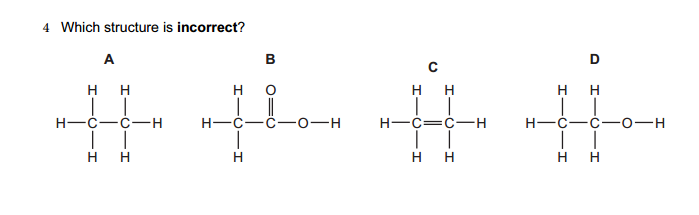
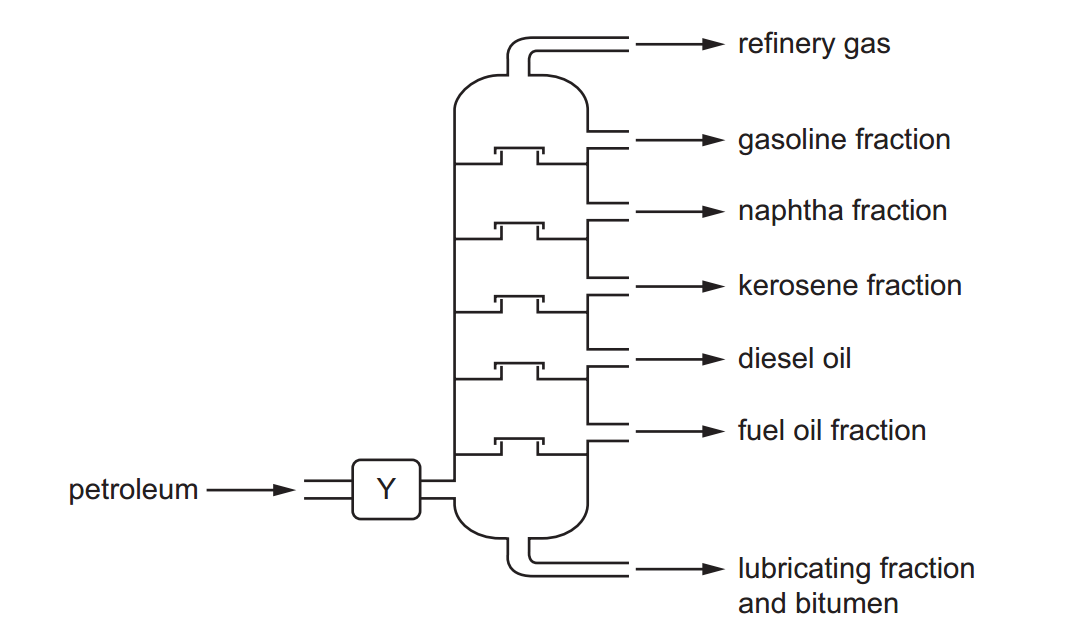
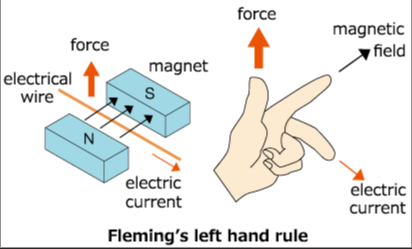



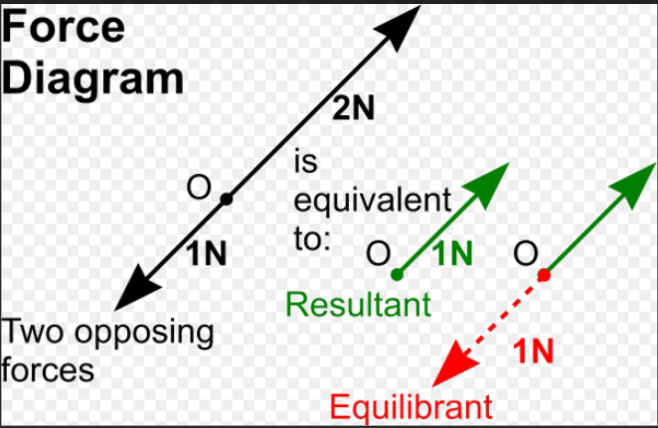



















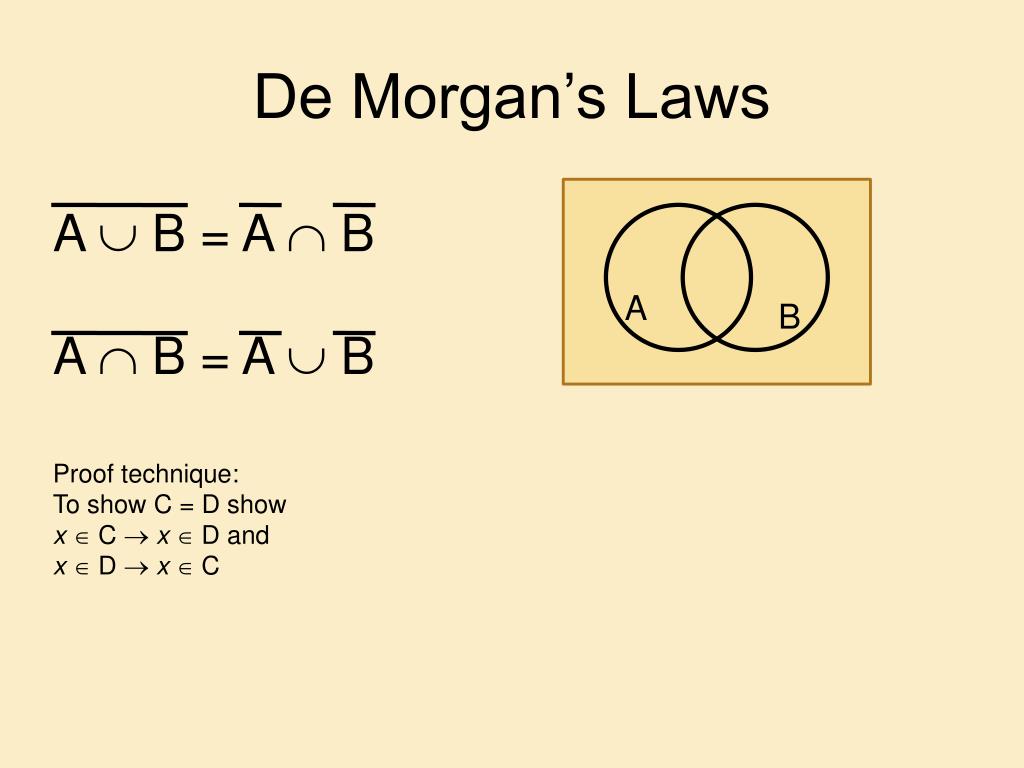

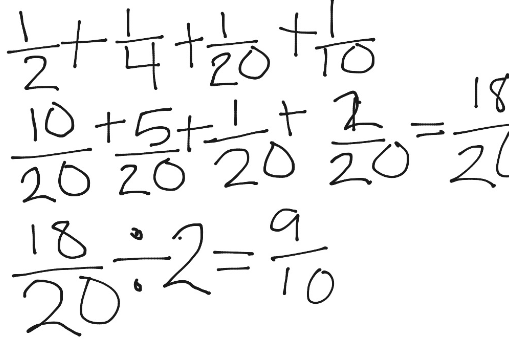

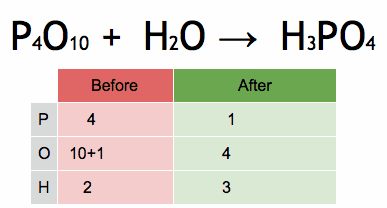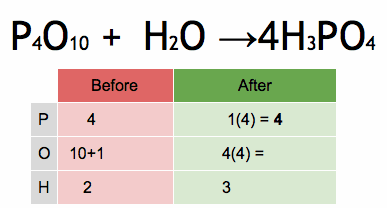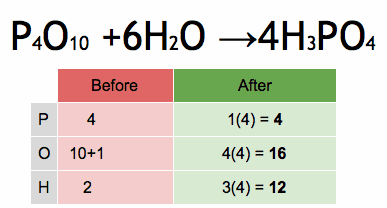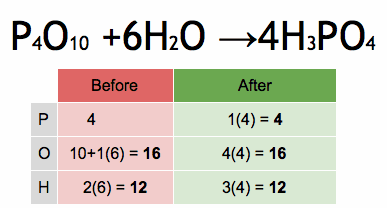






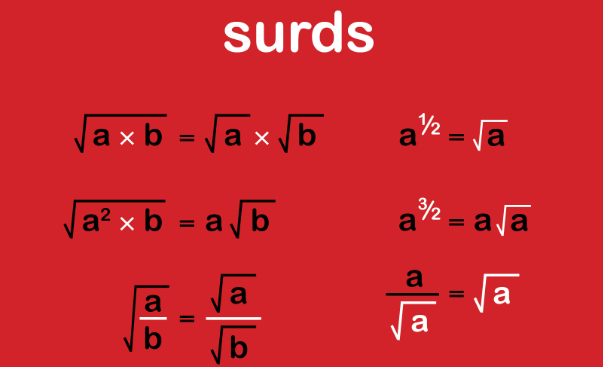









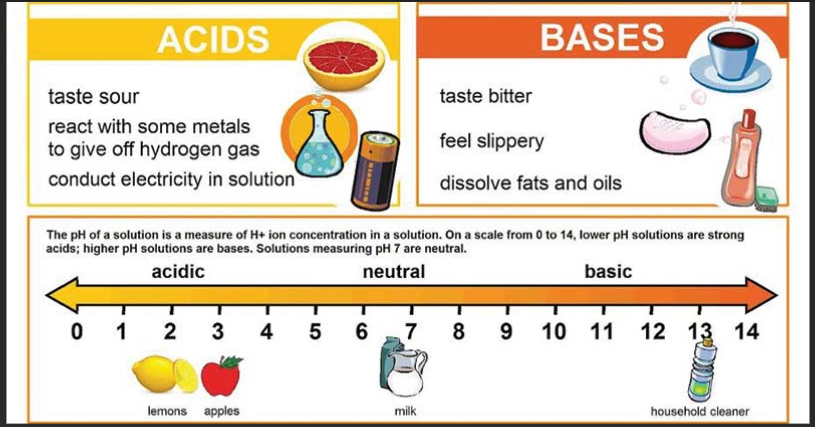















[…] 40 Objective Questions in Nuclear Physics with Solutions. […]