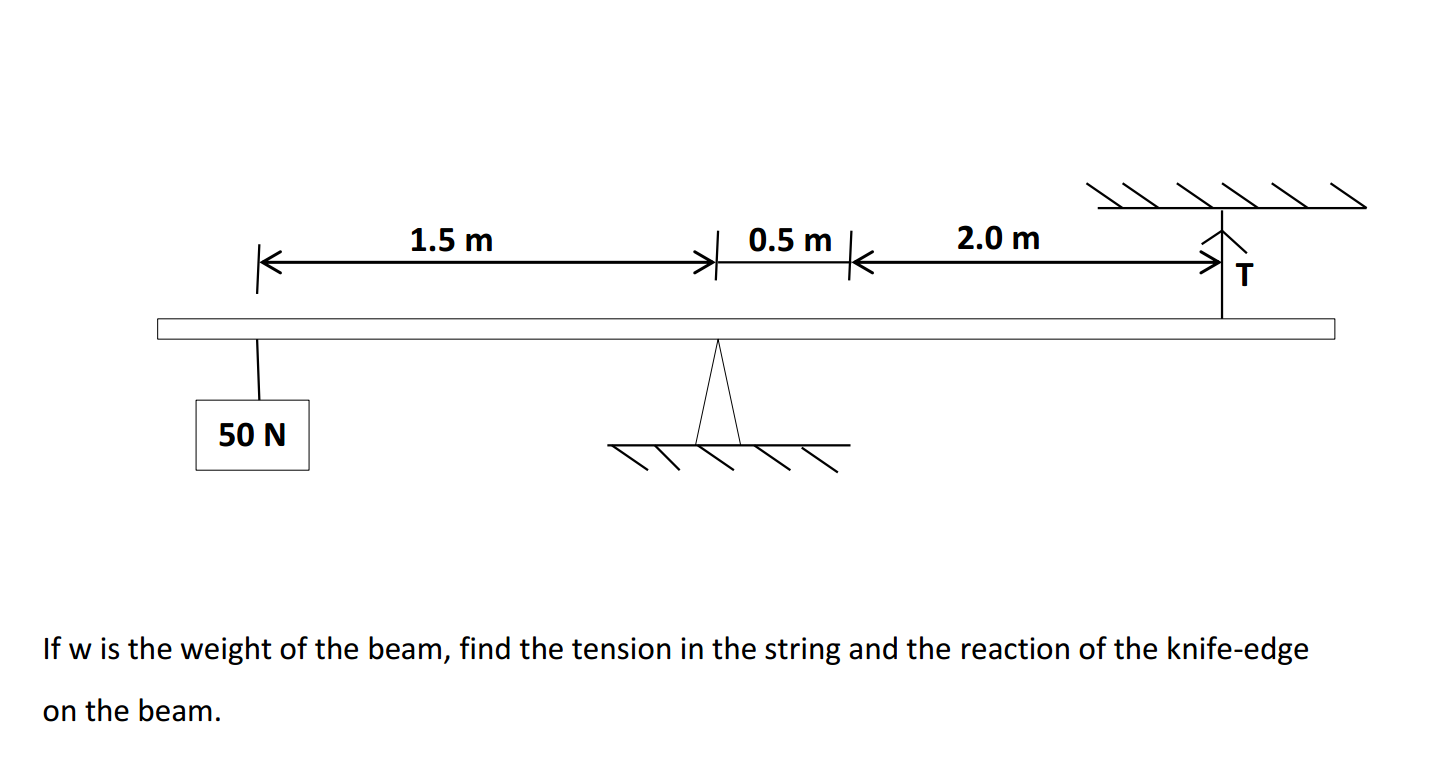
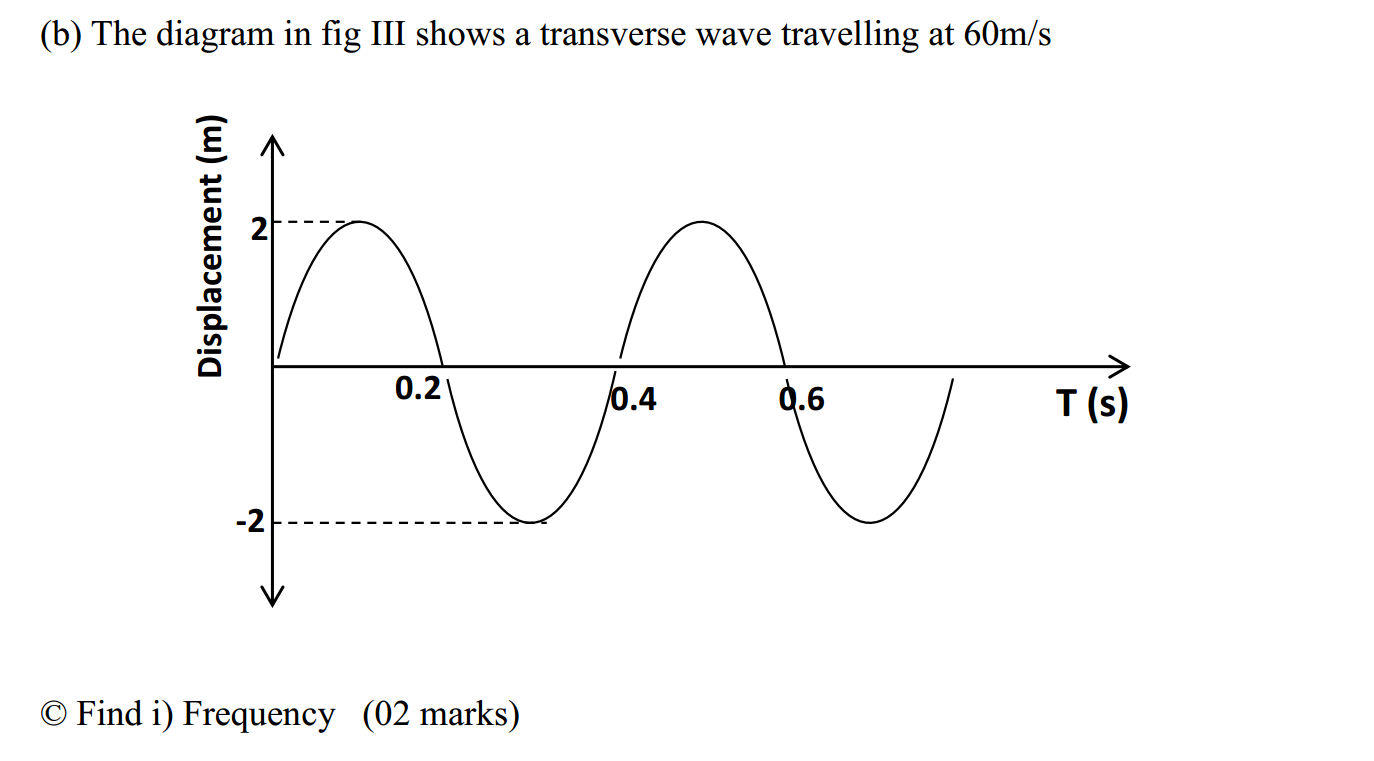
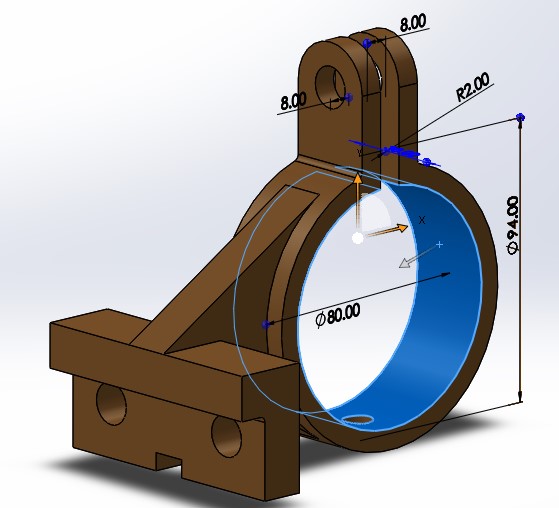
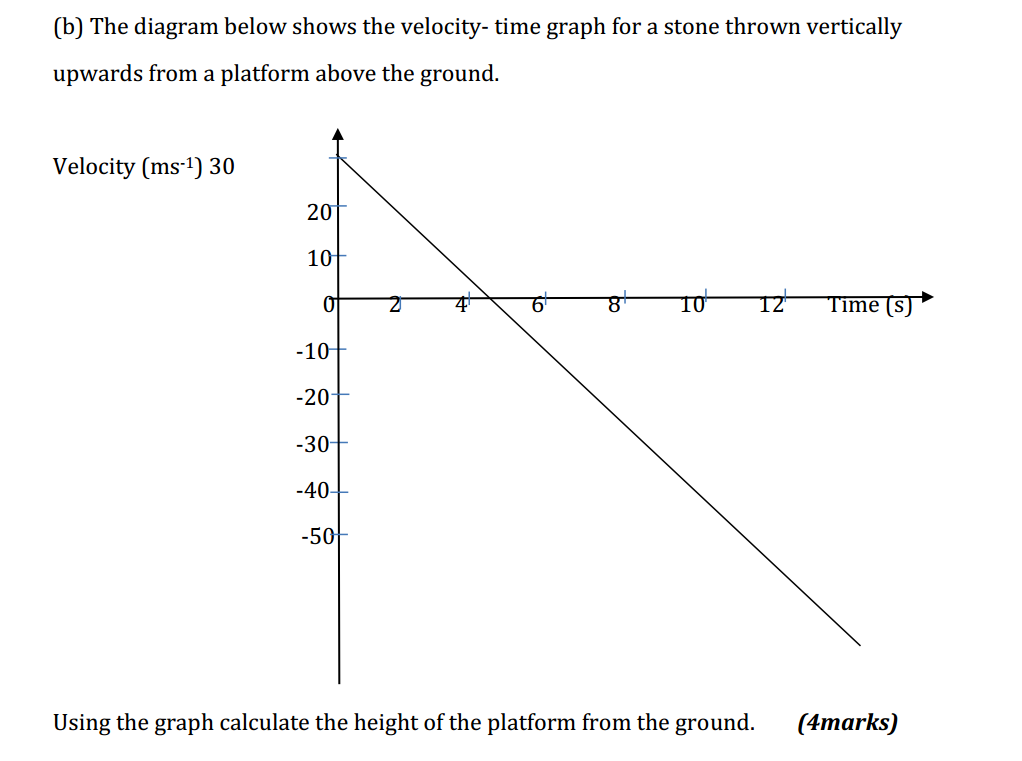
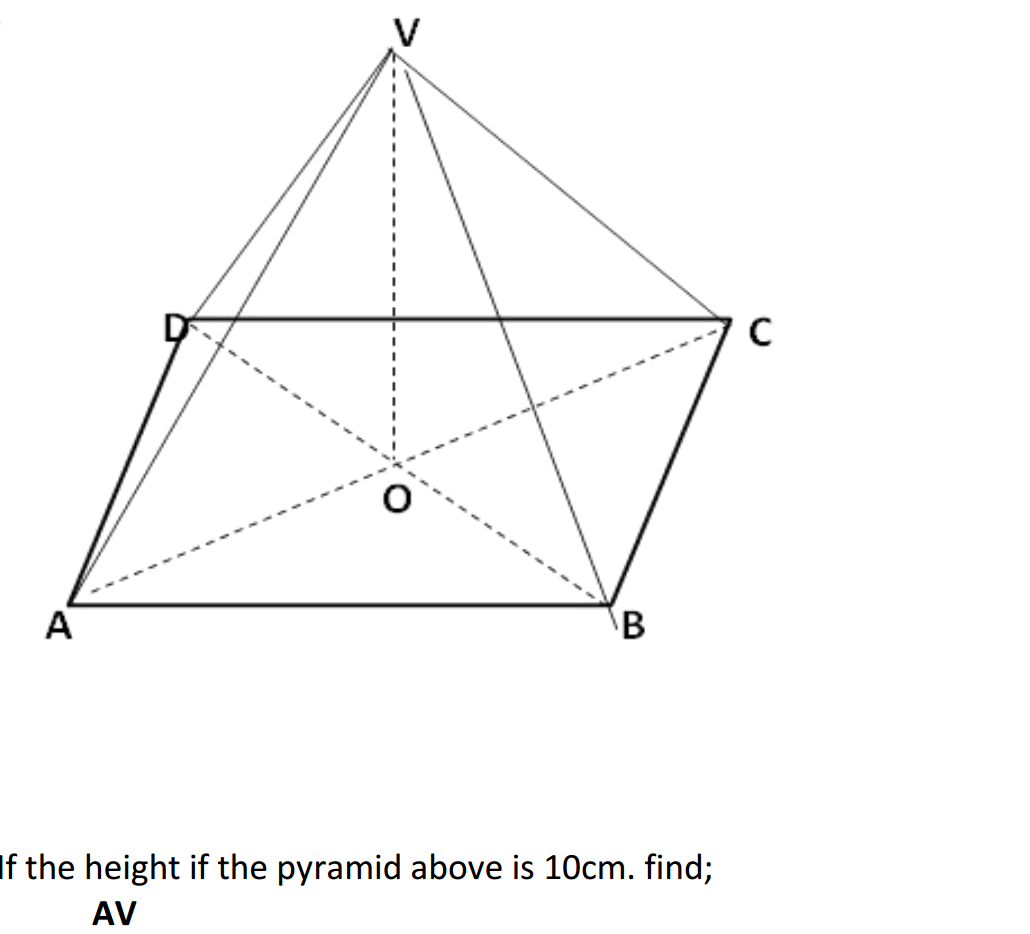
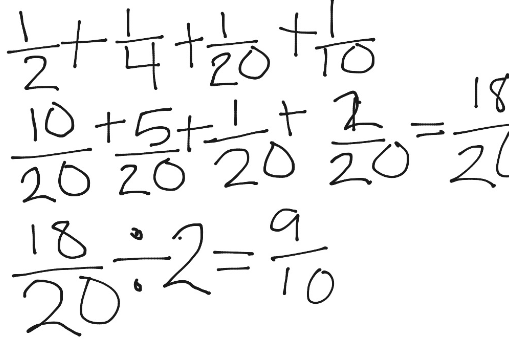- Subject-Verb Agreement: Ensure that the subject and the verb in a sentence agree in number. For example:
- Incorrect: “The team are playing well.”
- Correct: “The team is playing well.”
- Punctuation: Use punctuation marks correctly. This includes periods, commas, question marks, exclamation points, colons, semicolons, apostrophes, and quotation marks.
- Sentence Structure: Form sentences with a clear structure that includes a subject, verb, and, where necessary, an object. For example:
- “She (subject) reads (verb) a book (object).”
- Tense Consistency: Maintain consistency in verb tenses within a sentence or paragraph. For example:
- “She works hard and achieved success.”
- Use of Articles (a, an, the): Understand when to use indefinite articles (a, an) and the definite article (the) based on whether you are referring to something specific or nonspecific.
- Correct Pronoun Usage: Use the correct pronouns for subjects and objects. For example:
- “He (subject pronoun) likes it.”
- “Give it to her (object pronoun).”
- Avoiding Double Negatives: Avoid using double negatives in a sentence, as they can create confusion. For example:
- Incorrect: “I don’t need no help.”
- Correct: “I don’t need any help.”
- Word Order: Adhere to the standard word order in English sentences, which typically follows the pattern subject-verb-object (SVO). For example:
- “The cat (subject) chased (verb) the mouse (object).”
- Use of Prepositions: Use prepositions correctly to indicate relationships between words in a sentence. For example:
- “He is sitting on the chair.”
- Avoiding Run-On Sentences: Ensure that sentences are not overly long or run-on. Use appropriate punctuation or conjunctions to separate ideas.
These basic rules provide a foundation for clear and effective communication in English. As you become more comfortable with these fundamentals, you can explore more advanced grammatical concepts and nuances in the language.