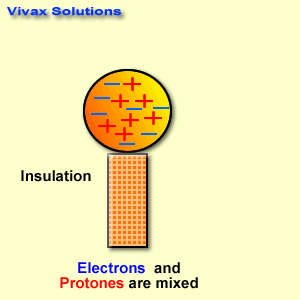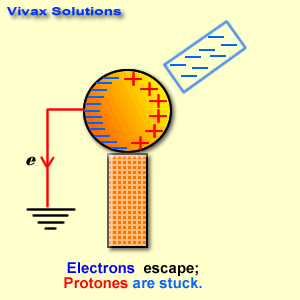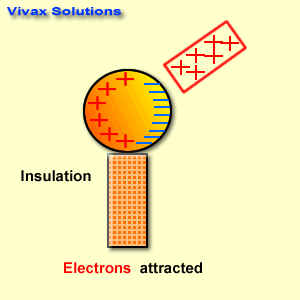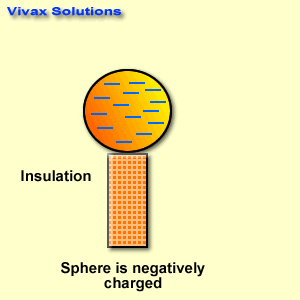
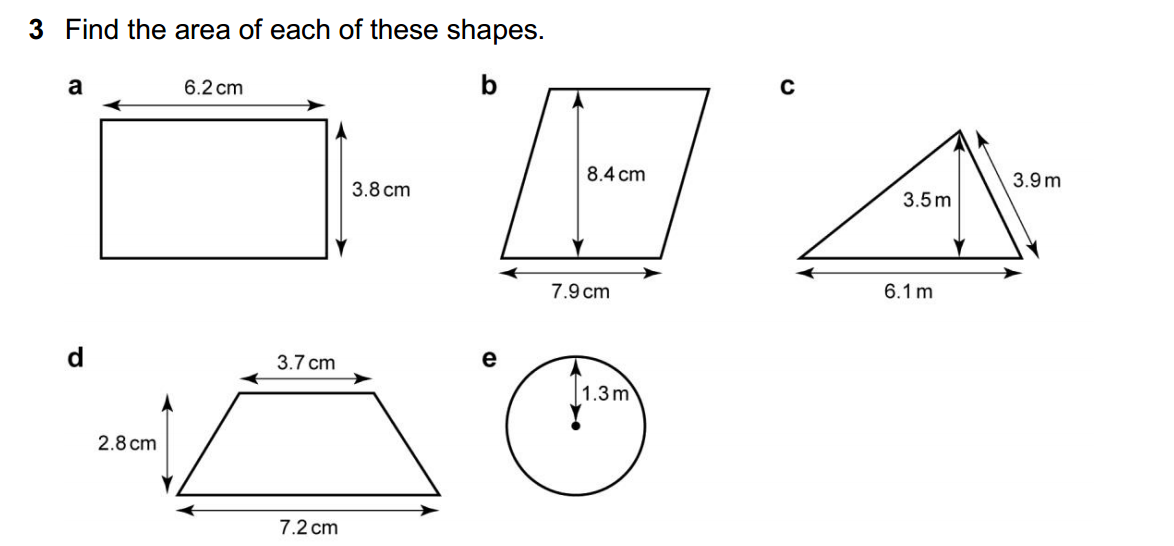
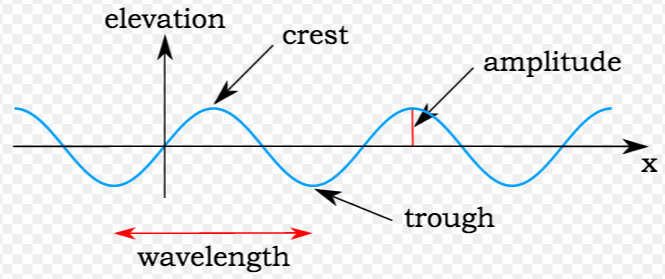
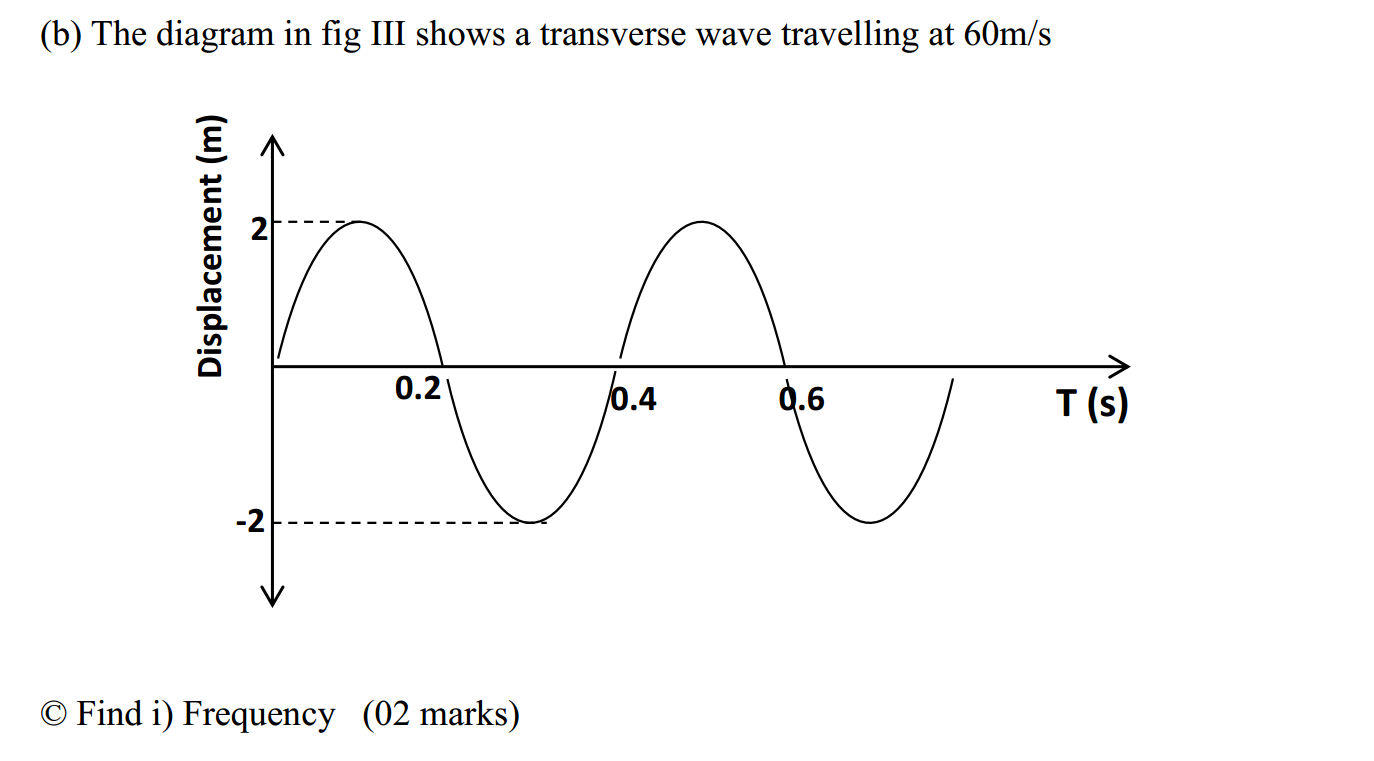
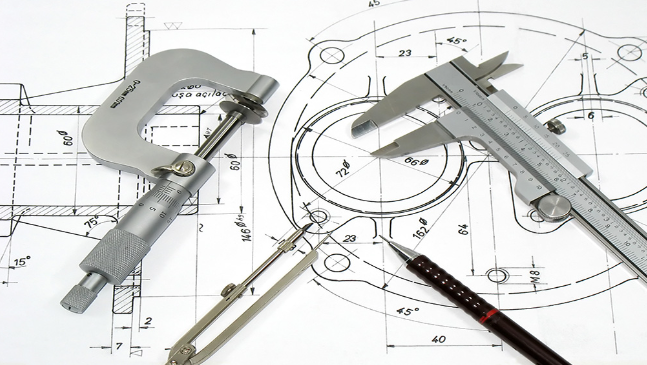
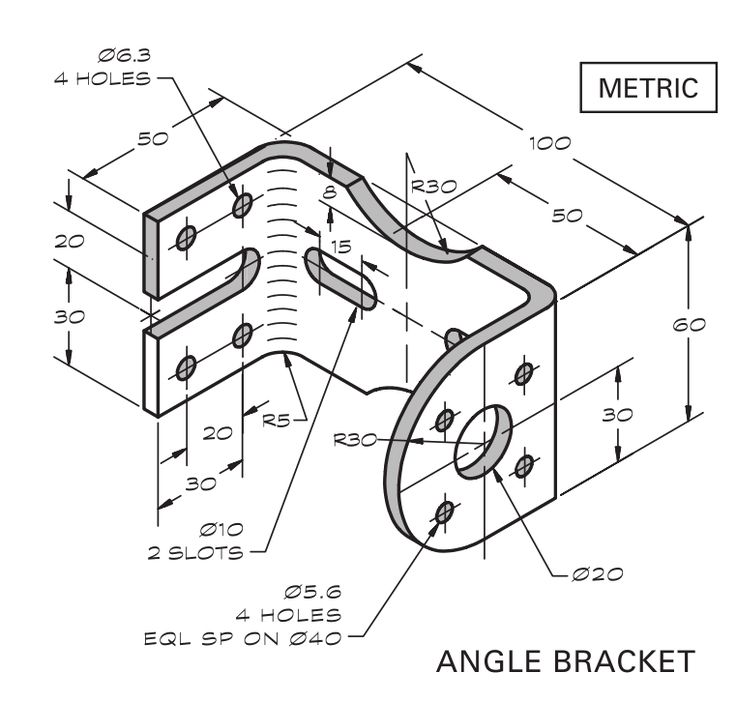
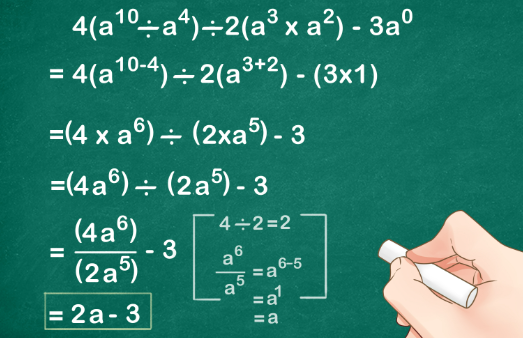Measuring tools are essential in various fields, from construction and engineering to cooking and crafting. Here are some basic measuring tools and their applications:
- Ruler or Tape Measure:
- Applications: Measuring length, width, and height of objects, distances, or dimensions in construction, crafting, and design projects.
- Calipers:
- Applications: Precisely measuring the diameter or thickness of objects, including pipes, holes, and components in mechanical and technical work.
- Micrometer:
- Applications: Extremely precise measurements of small objects, such as machine parts, screws, and other mechanical components.
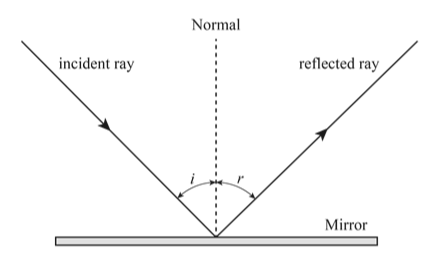
- Protractor:
- Applications: Measuring and setting angles for design, engineering, and mathematical purposes.
- Measuring Tape:
- Applications: Measuring long distances or circumferences, such as in construction, tailoring, and surveying.
- Level:
- Applications: Determining if a surface is level or plumb in construction and DIY projects.
- Spirit Level (Bubble Level):
- Applications: Checking the horizontal and vertical alignment of objects, like picture frames, shelves, and appliances.
- Scale:
- Applications: Weighing objects for various purposes, including cooking, shipping, and scientific experiments.
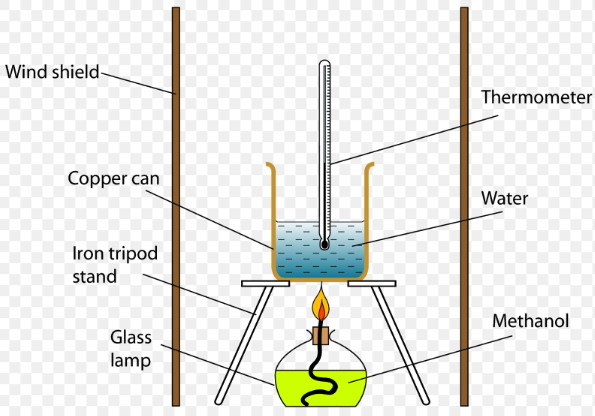
- Thermometer:
- Applications: Measuring temperature in various settings, from weather forecasting to cooking and medical applications.
- Hygrometer:
- Applications: Measuring humidity levels in the air, essential for climate control and meteorological studies.
- Multimeter:
- Applications: Measuring electrical properties like voltage, current, and resistance in electronics and electrical systems.
- Gauge Blocks:
- Applications: Precision measurement and calibration in engineering and manufacturing to ensure the accuracy of machines and tools.
- Dial Indicator:
- Applications: Measuring small distances, often used in manufacturing and machining processes.
- Feeler Gauge:
- Applications: Measuring the clearance or gap between two objects, often used in automotive maintenance.
- Angle Gauge:
- Applications: Measuring angles and checking angular relationships, important in carpentry and metalworking.
- Bore Gauge:
- Applications: Measuring the inside diameter of holes or cylinders, commonly used in engineering and machining.
- Thread Gauge:
- Applications: Checking the pitch and size of screw threads, crucial for fastening and assembly.
- Depth Gauge:
- Applications: Measuring the depth or thickness of a hole or recess, used in carpentry, metalworking, and machining.
These are just a few examples of basic measuring tools and their applications. The choice of measuring tool depends on the specific task and the level of precision required. Using the right measuring tool ensures accurate and reliable results in a wide range of applications.