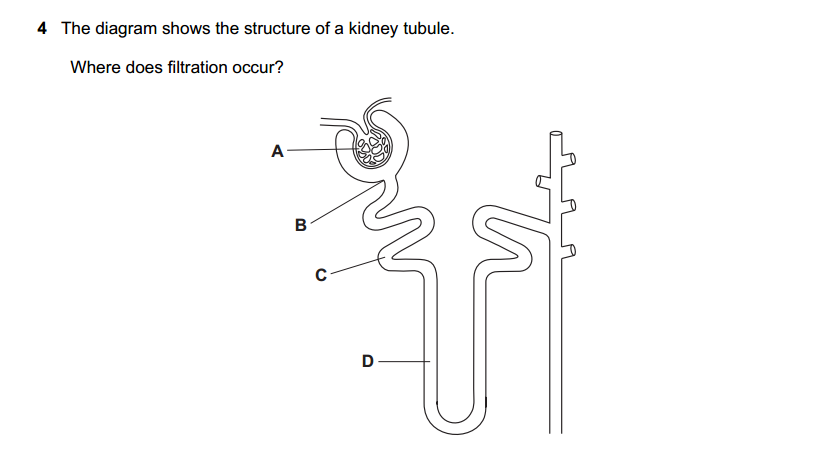
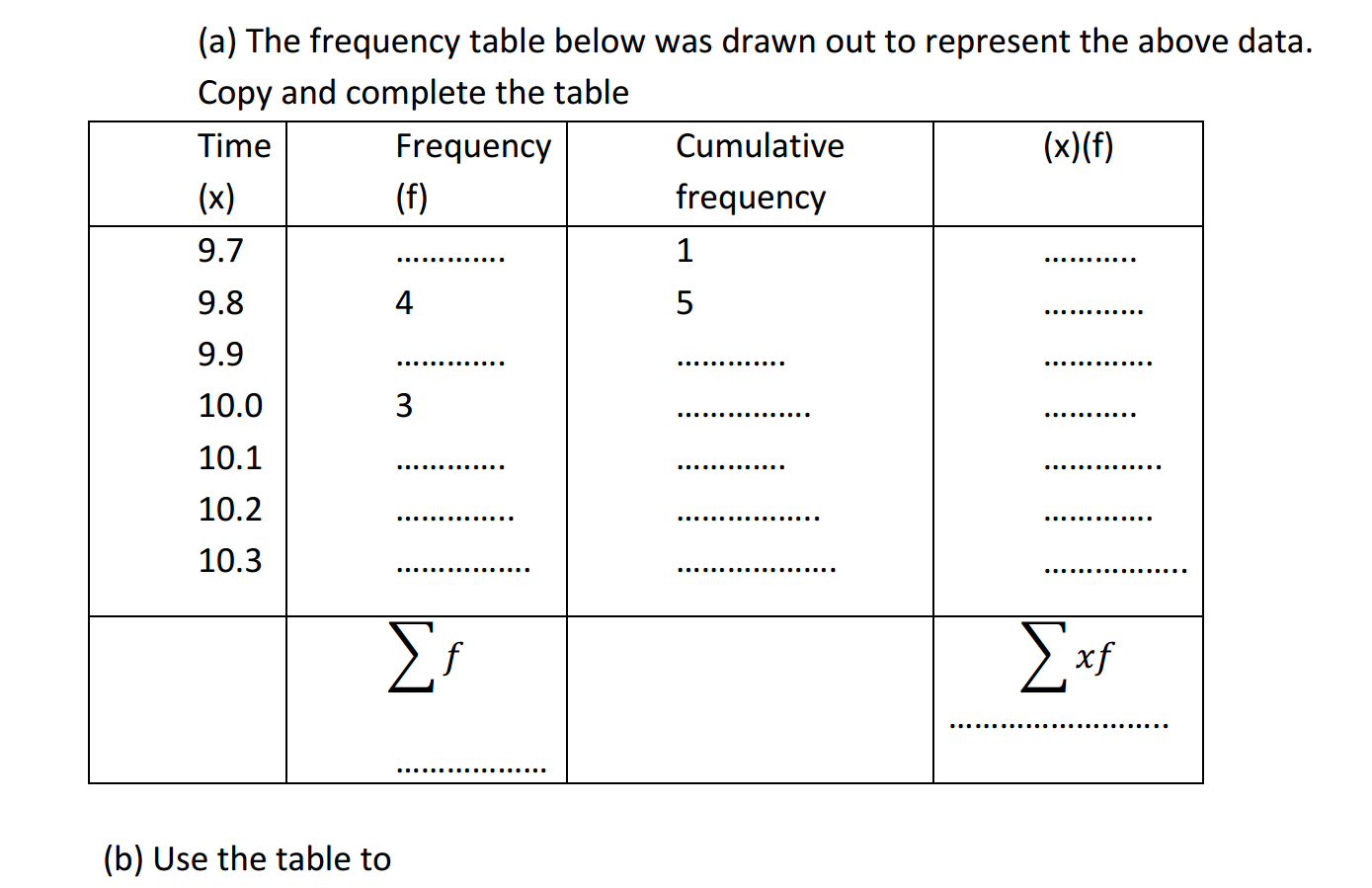
Economics is a complex field with many terms and concepts. Here are some common terms and their definitions.
- Scarcity:
- Definition: Scarcity is the fundamental economic problem of having seemingly unlimited human wants in a world of limited resources.
- Supply and Demand:
- Definition: Supply refers to the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing to offer for sale, while demand is the quantity that consumers are willing to purchase.
- Opportunity Cost:
- Definition: Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative forgone when a decision is made to allocate resources to a particular choice.
- Inflation:
- Definition: Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, causing purchasing power to fall.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
- Definition: GDP is the total monetary or market value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period.
- Monopoly:
- Definition: A monopoly is a market structure in which a single seller or producer supplies a given product, dominating the market and controlling prices.
- Elasticity:
- Definition: Elasticity measures how sensitive the quantity demanded or supplied is to changes in price or income.
- Fiscal Policy:
- Definition: Fiscal policy is the use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy.
- Market Equilibrium:
- Definition: Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity of a good that buyers are willing and able to buy equals the quantity that sellers are willing and able to produce.
- Labor Force:
- Definition: The labor force consists of people who are either employed or actively seeking employment.
These are just a few fundamental economics terms and their explanations. Economics is a vast field with many more concepts, theories, and principles.