A photon is a fundamental particle of light and electromagnetic radiation. It is the smallest discrete unit or quantum of electromagnetic energy. Photons are the carriers of the electromagnetic force and are responsible for transmitting and interacting with electromagnetic fields, including visible light, radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays. Here are some key characteristics and properties of photons:
- Wave-Particle Duality: Photons exhibit both particle-like and wave-like properties. This duality is a fundamental concept in quantum physics, known as wave-particle duality. While photons are particles, they also display wave-like behaviors, such as interference and diffraction.
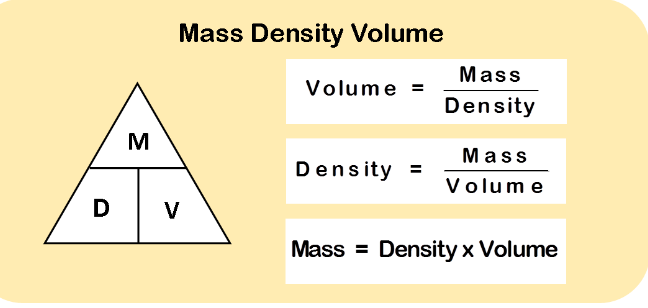
- Energy Quantum: Photons carry energy in discrete packets. The energy of a photon is directly proportional to its frequency or inversely proportional to its wavelength, as described by the Planck-Einstein relation, E = hf, where E is energy, h is Planck’s constant, and f is the frequency.
- Zero Rest Mass: Photons are massless particles, which means they do not have rest mass. They always travel at the speed of light in a vacuum (approximately 299,792,458 meters per second) and are never at rest.
- Quantization of Electromagnetic Fields: The concept of photons is crucial for understanding the quantization of electromagnetic fields, as described by quantum electrodynamics (QED). In this theory, electromagnetic fields consist of discrete packets of energy called photons.
- Emission and Absorption: Photons are emitted when charged particles (such as electrons) transition between energy levels in atoms or molecules. Conversely, photons are absorbed when particles gain energy and move to higher energy states.
- Visible and Beyond: While photons are commonly associated with visible light, they exist across the entire electromagnetic spectrum. They can have various wavelengths and frequencies, which determine their properties and the type of electromagnetic radiation they constitute. This includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
- Quantum of Action: The quantization of energy carried by photons is intimately tied to the fundamental concept of quantization in quantum mechanics. This quantization is expressed in Planck’s constant, h, and is a cornerstone of quantum physics.
In summary, photons are the discrete units of electromagnetic radiation, carrying energy and transmitting the electromagnetic force. They play a central role in the understanding of light, electromagnetic waves, and the behavior of particles in quantum physics.