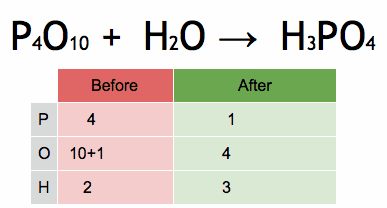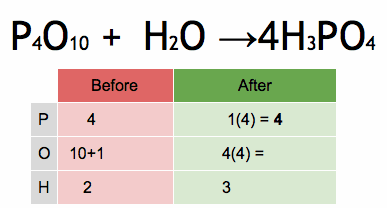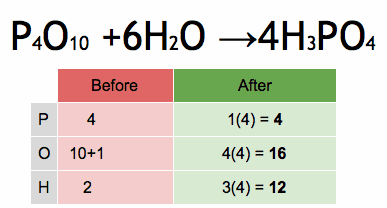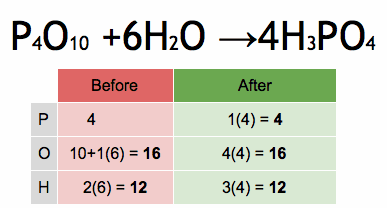
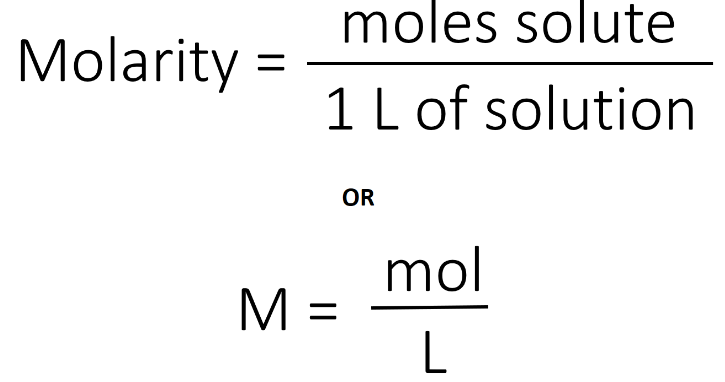Physical chemistry and organic chemistry are two distinct subfields within the broader discipline of chemistry, and they focus on different aspects of the subject. Here are the key differences between physical chemistry and organic chemistry:
Physical Chemistry:
- Focus: Physical chemistry primarily deals with the study of the physical and chemical properties of matter, as well as the principles and theories that govern chemical behavior and reactions.
- Topics: It covers a wide range of topics, including thermodynamics, kinetics, quantum mechanics, spectroscopy, electrochemistry, statistical mechanics, and the behavior of gases and liquids.
- Theoretical Emphasis: Physical chemistry places a significant emphasis on mathematical and theoretical concepts. It involves the use of mathematical models and equations to explain and predict chemical phenomena.
- Quantitative Analysis: Physical chemists often perform quantitative analyses and measurements to understand and describe the behavior of matter at the molecular and atomic levels.
- Interdisciplinary: It is an interdisciplinary field that bridges the gap between chemistry and physics. Physical chemists often work on topics that have applications in both chemistry and physics.
- Example Questions: Questions in physical chemistry might include the study of reaction mechanisms, the behavior of chemical compounds under different conditions, and the study of energy changes in chemical reactions.
Organic Chemistry:
- Focus: Organic chemistry focuses on the study of the structure, properties, reactions, and synthesis of organic compounds, which are primarily composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- Topics: It covers a wide range of topics, including the structure of organic molecules, functional groups, reaction mechanisms, synthesis of organic compounds, and the identification of organic compounds.
- Laboratory Work: Organic chemistry involves extensive laboratory work, with a strong emphasis on experimental techniques and chemical reactions. Organic chemists synthesize and analyze organic compounds in the lab.
- Nomenclature: Organic chemistry places a significant emphasis on the nomenclature of organic compounds, including the systematic naming of chemical structures.
- Applications: Organic chemistry has a wide range of applications, including drug discovery, the development of materials, the study of natural products, and the design of new molecules with specific properties.
- Example Questions: Questions in organic chemistry might include the synthesis of organic compounds, the mechanisms of chemical reactions, the structure-activity relationships in pharmaceuticals, and the identification of unknown compounds.
In summary, physical chemistry is focused on the fundamental principles and theories that govern chemical behavior and reactions, often involving mathematical and theoretical concepts. Organic chemistry, on the other hand, is concerned with the study of carbon-containing compounds, their structure, reactions, and synthesis, with a strong emphasis on experimental work. Both subfields are essential within the field of chemistry and serve different purposes and applications.