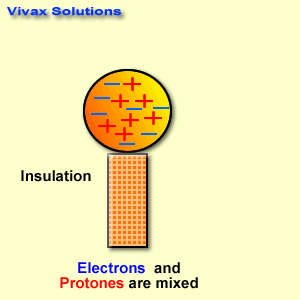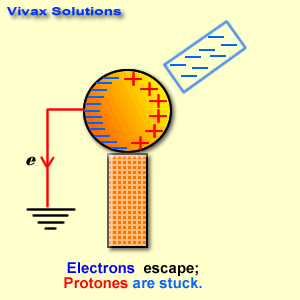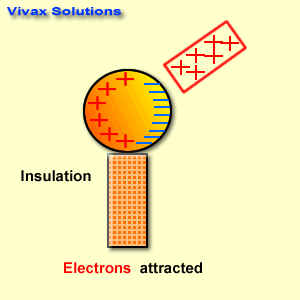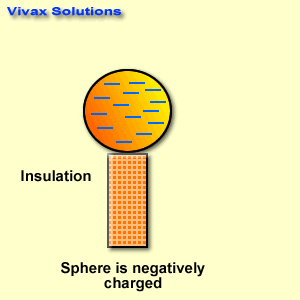
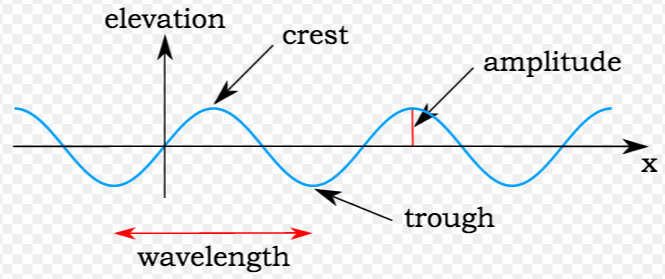
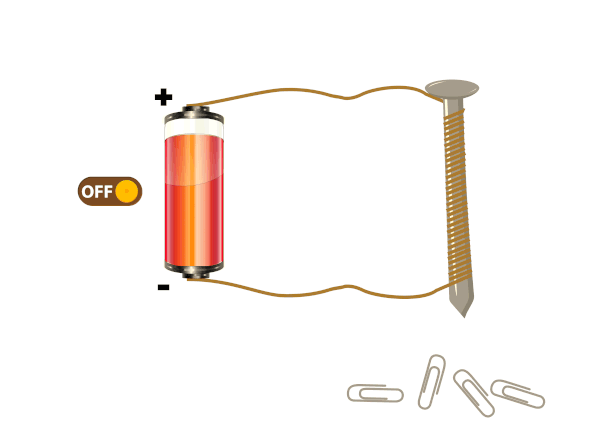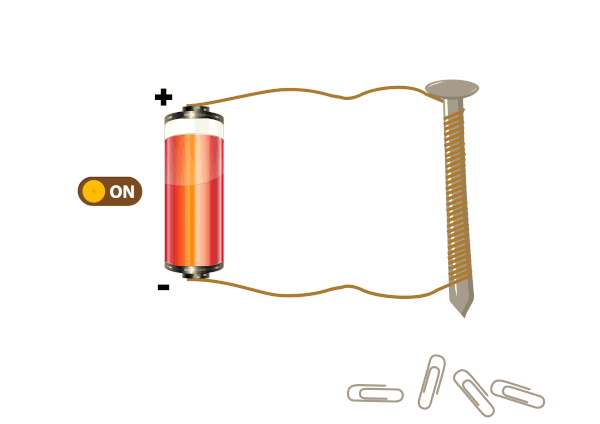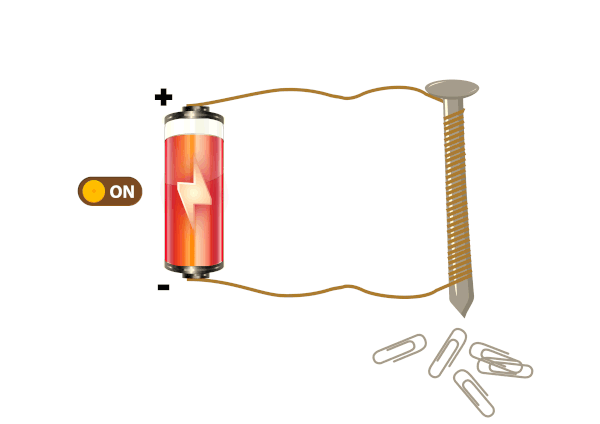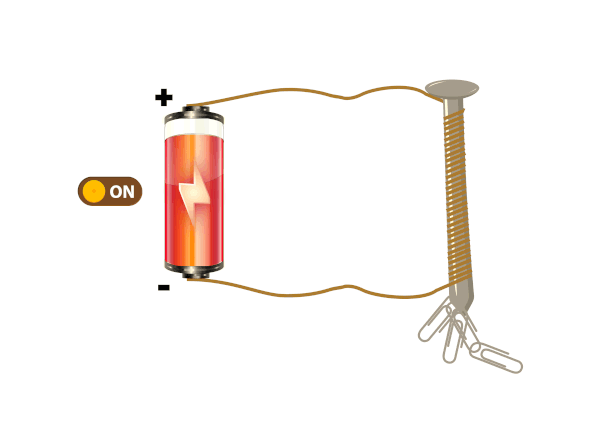
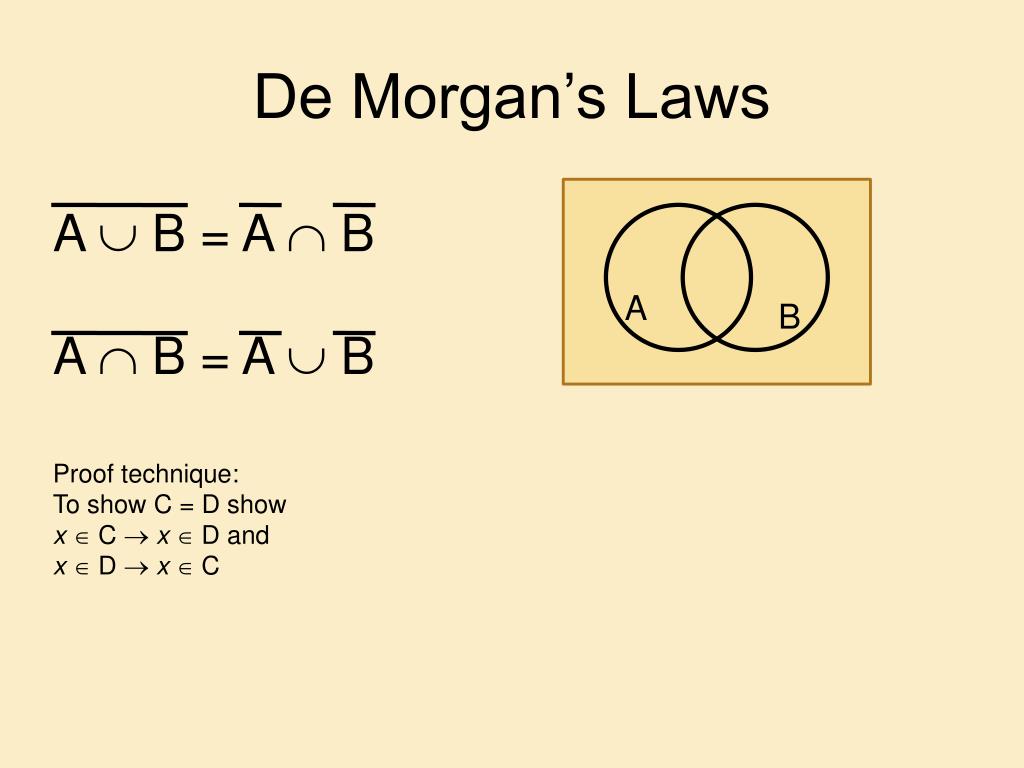
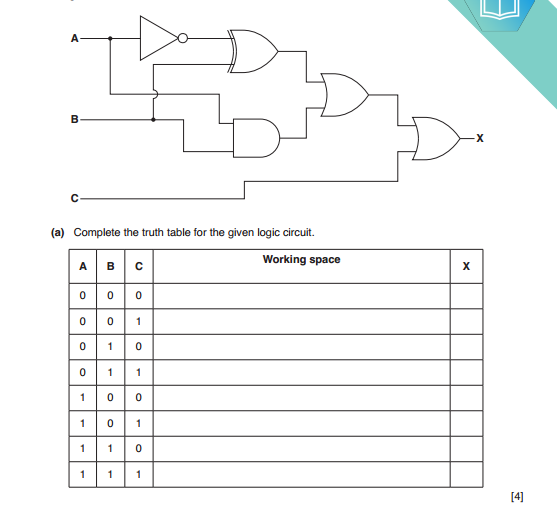
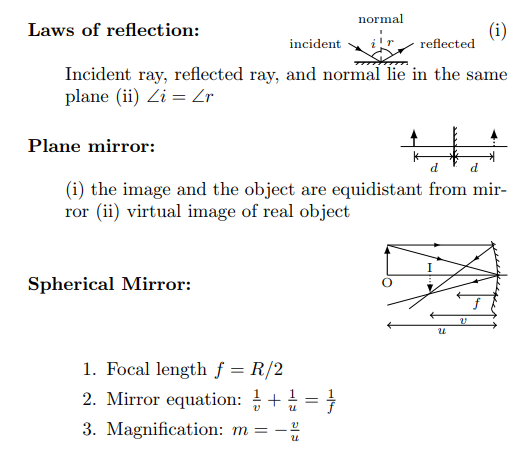
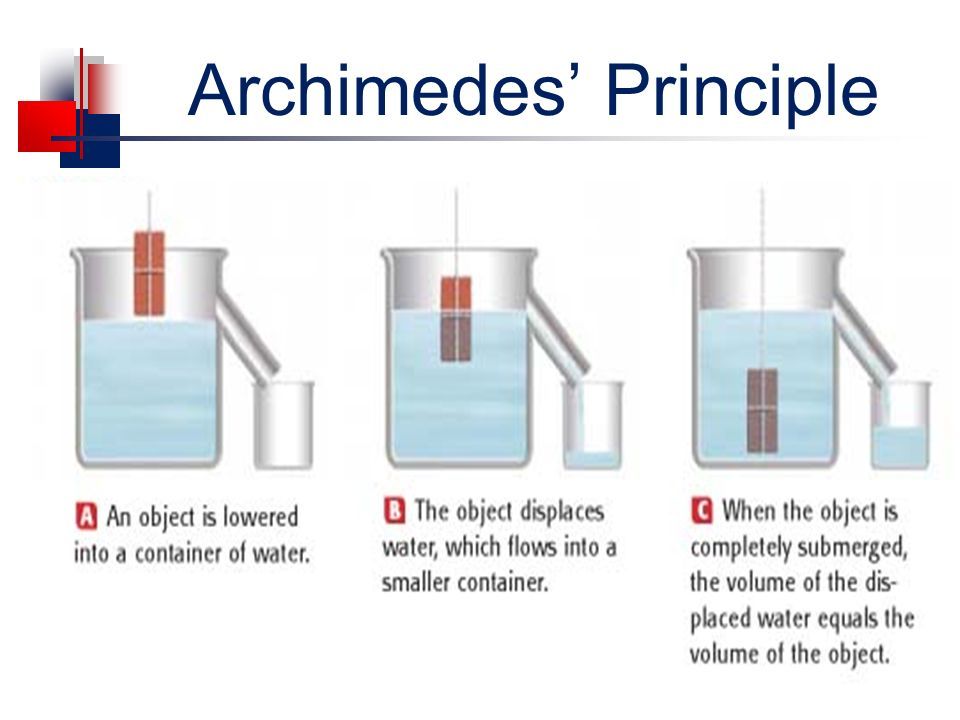
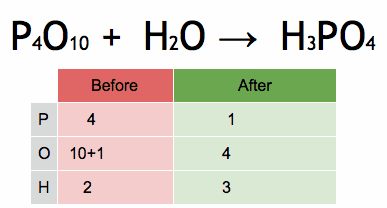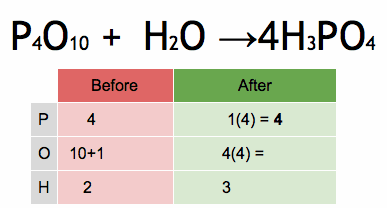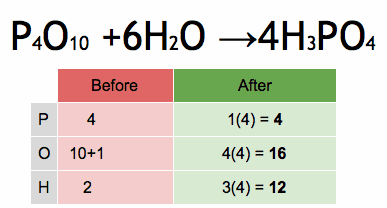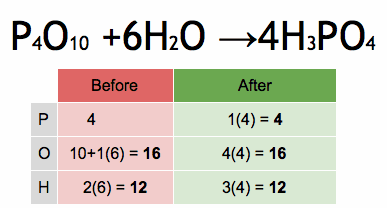
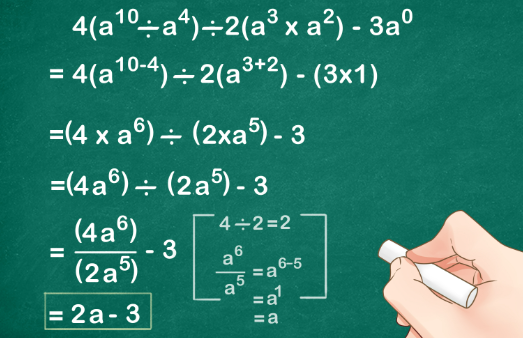Electrical conductors are materials that allow electric current to flow through them with relative ease. They have a high conductivity, meaning their atoms and electrons are arranged in such a way that electrons can move freely in response to an electric field. Here are some common electrical conductors and examples:
- Copper (Cu):
- Copper is one of the most widely used electrical conductors. It’s found in electrical wiring, power cables, and in components like motors and transformers.
- Aluminum (Al):
- Aluminum is commonly used for power transmission lines because it is lightweight and has good conductivity. It’s also used in electrical wiring.
- Silver (Ag):
- Silver has the highest electrical conductivity of all elements. It’s used in applications where the highest level of conductivity is required, such as in high-end audio connectors and some specialized electrical equipment.
- Gold (Au):
- Gold is highly conductive and, like silver, is used in specialized applications. It’s often used in high-quality connectors and switches due to its resistance to corrosion.
- Brass:
- Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. It’s used for various electrical connectors and fittings because of its good conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Bronze:
- Bronze is another copper alloy, consisting mainly of copper and tin. It’s used in electrical components like connectors, springs, and switches.
- Iron (Fe):
- Iron is used in some electrical applications, especially in electromagnetic components like transformers and inductors.
- Steel:
- Certain types of steel are used in electrical applications where durability and magnetic properties are required. Examples include electrical appliances and power transformers.
- Tungsten (W):
- Tungsten has high melting and boiling points and is used in electrical applications where extreme temperatures are a concern, such as in light bulb filaments.
- Nickel (Ni):
- Nickel is used as a conductor in some electrical wires and components, as well as in batteries.
- Graphite:
- Graphite is a form of carbon that can conduct electricity due to its unique structure. It’s used in items like pencils, where the graphite core conducts electricity, as well as in certain types of batteries.
- Carbon (in the form of carbon black or carbon fiber):
- Carbon, in various forms, can conduct electricity. It’s used in applications like resistors, where its resistance properties are essential.
- Semi-conductors (e.g., Silicon):
- While not as conductive as metals, semiconductors like silicon are essential in the electronics industry for making transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits.
- Ionic Solutions (e.g., Saltwater):
- Some solutions, like saltwater, can conduct electricity due to the presence of ions (charged particles). These solutions are used in electrochemical processes, such as in batteries and electrolysis.
These are just a few examples of electrical conductors. The choice of conductor depends on factors like electrical conductivity, cost, durability, and the specific requirements of the application.