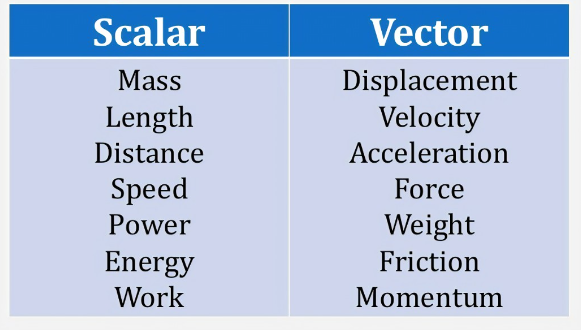
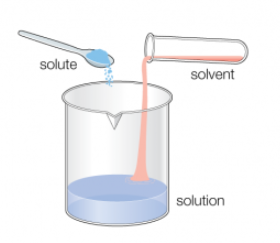
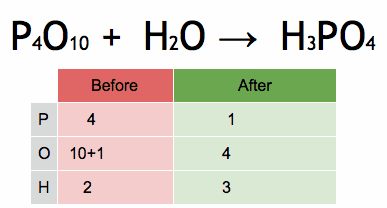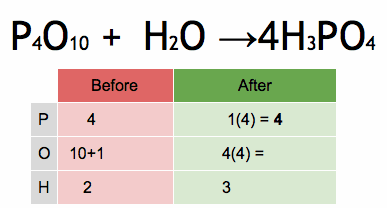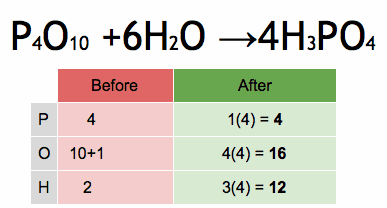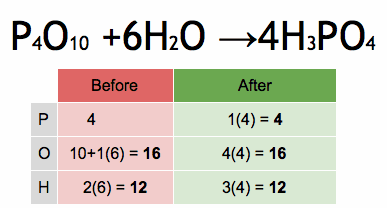
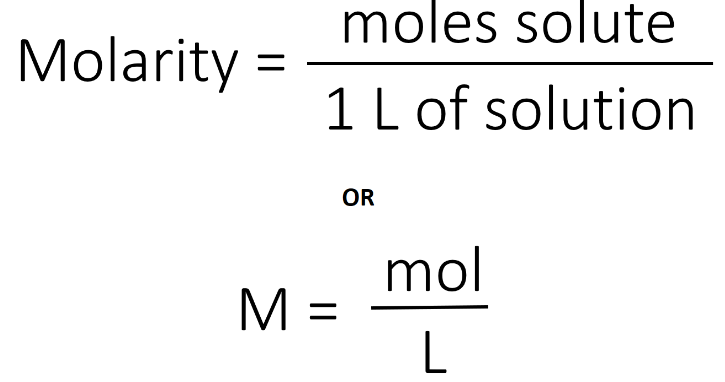Acids and bases are two distinct types of chemical substances with contrasting properties. Here are the main differences between acids and bases:
- Definition:
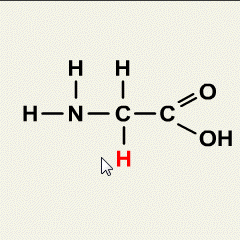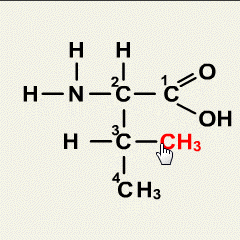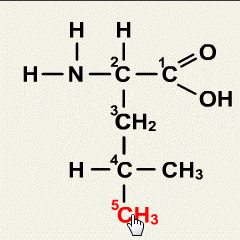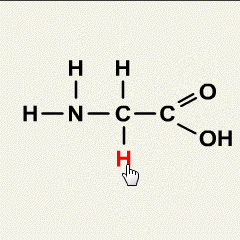
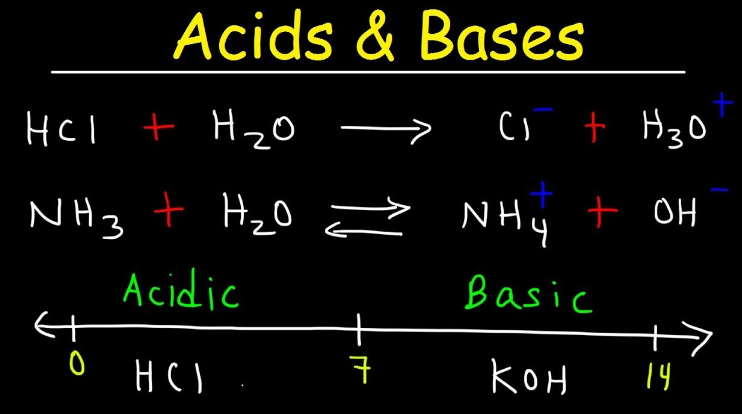
- Acids are substances that donate protons (H⁺ ions) in aqueous solutions, according to the Arrhenius definition. They can also accept electrons in reactions, according to the Lewis definition.
- Bases are substances that donate hydroxide ions (OH⁻ ions) in aqueous solutions, according to the Arrhenius definition. They can also accept protons in reactions, according to the Lewis definition.
- Taste and Feel:
- Acids typically have a sour taste, such as vinegar or citrus fruits.
- Bases typically have a bitter taste, such as soap or baking soda. They may also feel slippery to the touch.
- Electrical Conductivity:
- Acids and bases both conduct electricity when dissolved in water, as they produce ions. However, acids conduct electricity due to the presence of hydrogen ions (H⁺), while bases conduct electricity due to the presence of hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
- pH Levels:
- Acids have pH values less than 7. The lower the pH, the stronger the acid.
- Bases have pH values greater than 7. The higher the pH, the stronger the base.
- A pH of 7 indicates a neutral solution, where the concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions are equal.
- Chemical Reactions:
- Acids react with metals to produce hydrogen gas and with bases to form salts and water in neutralization reactions.
- Bases react with acids to form salts and water in neutralization reactions. They can also react with fats and oils in a process called saponification.
- Indicators:
- Acids turn blue litmus paper red.
- Bases turn red litmus paper blue.
- Examples:
- Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), and citric acid (found in citrus fruits).
- Common examples of bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and ammonia (NH₃).
Understanding the differences between acids and bases is essential in chemistry, as they play vital roles in various chemical reactions and processes, ranging from industrial applications to biological systems.