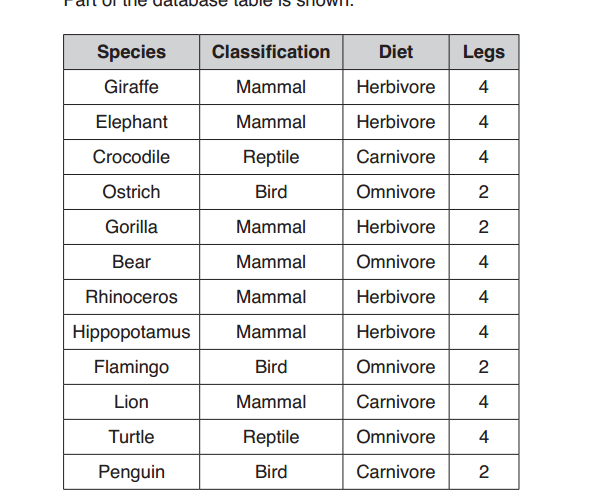
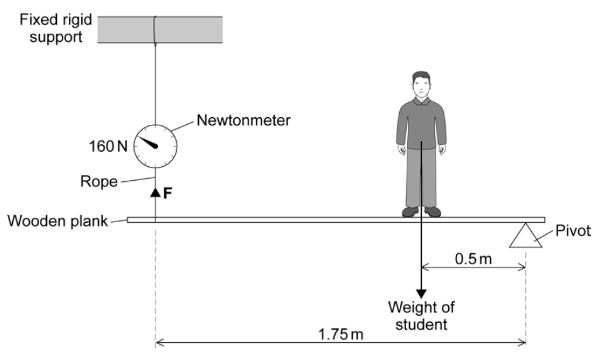
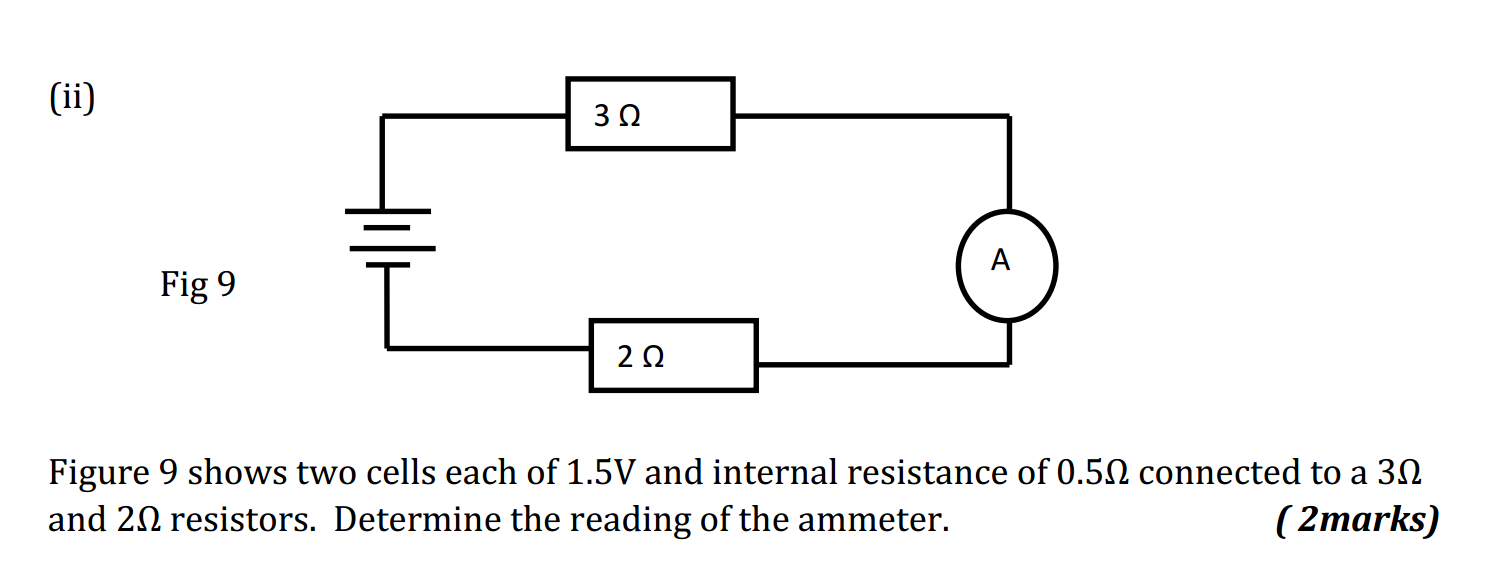
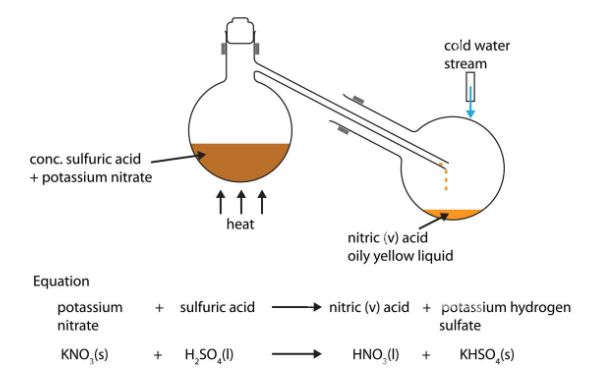
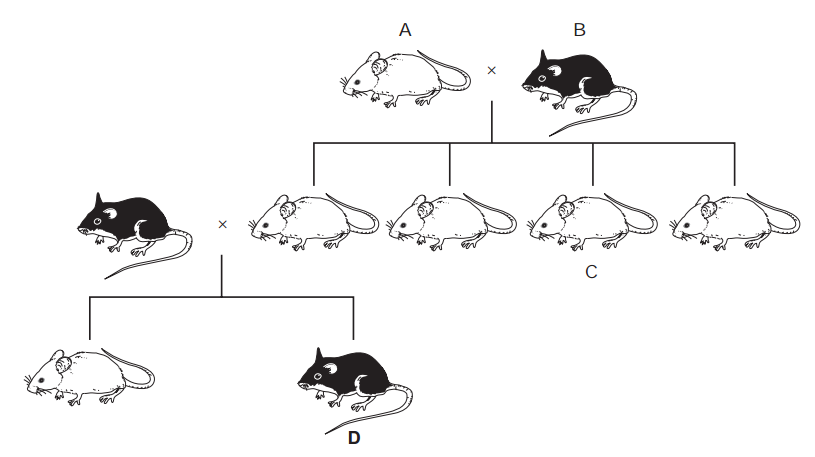
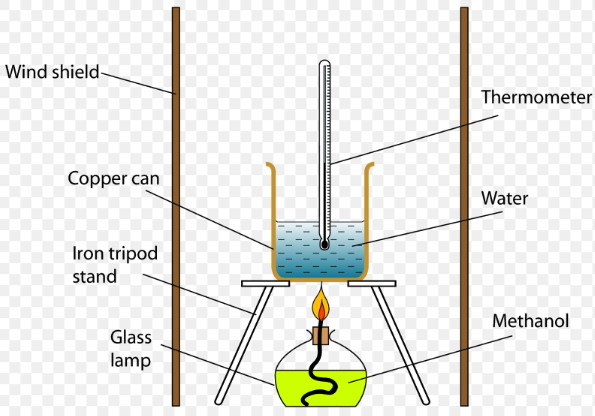
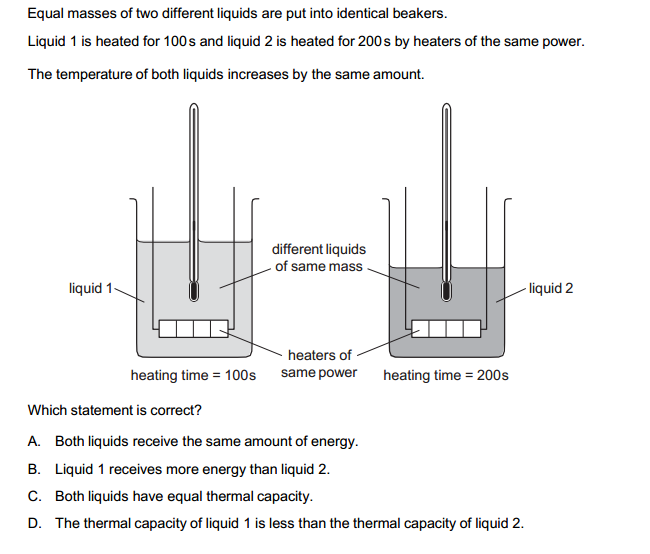
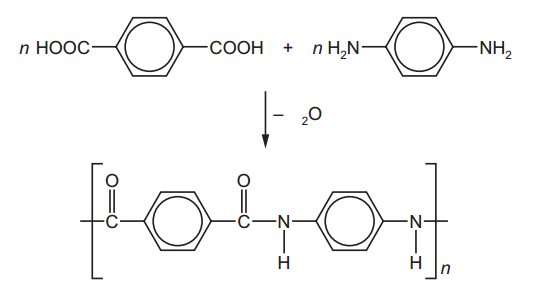
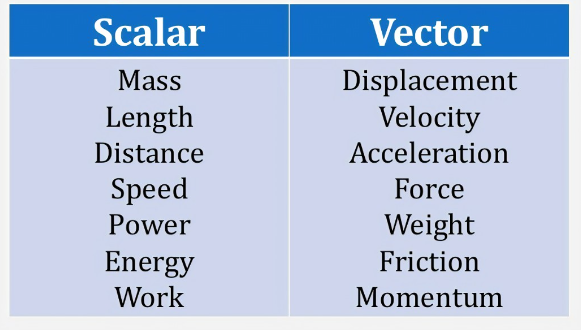
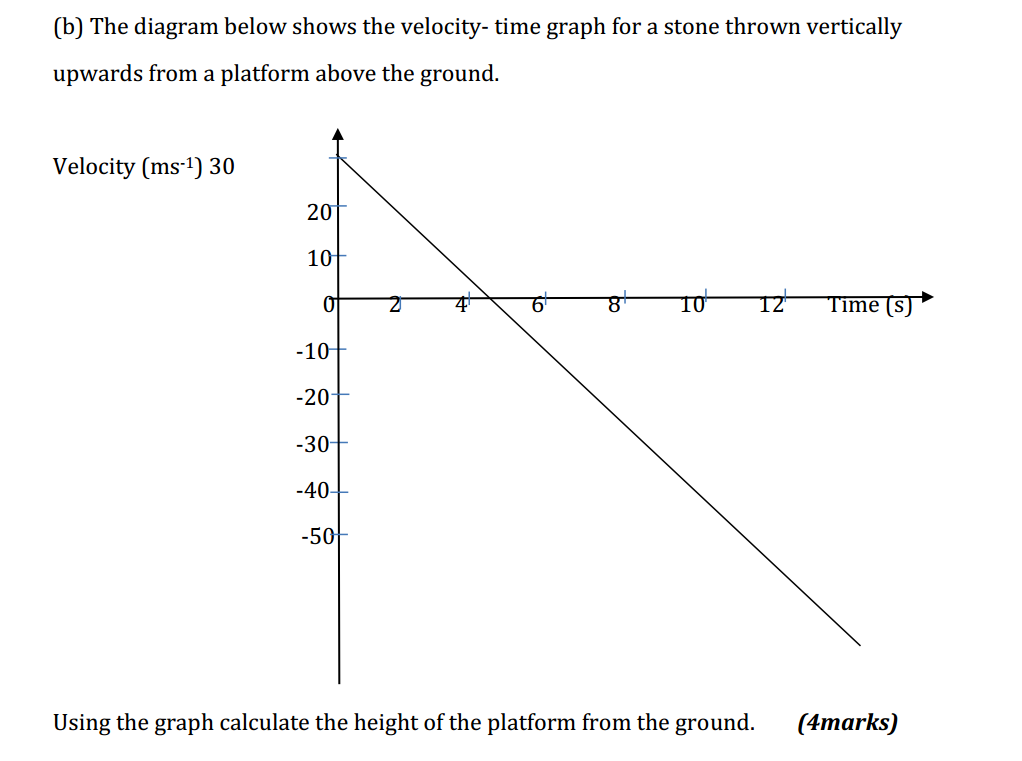
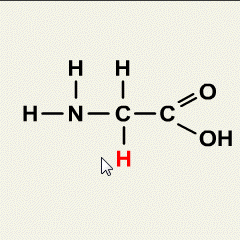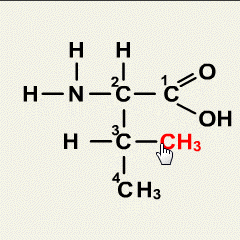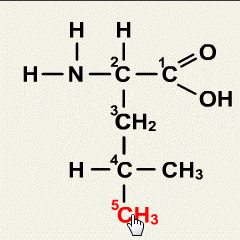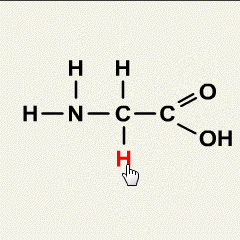
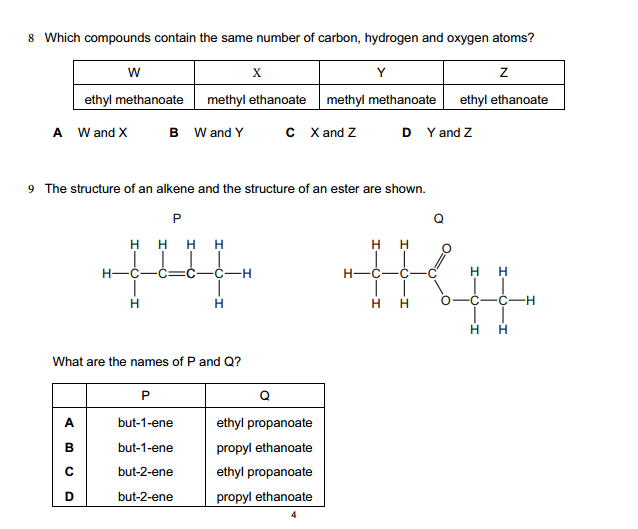
Units of measurement are standardized values used to express various physical quantities. They provide a consistent and universally accepted way to describe the magnitude of different properties. Here are some commonly used units of measurement for various physical quantities:
- Length:
- Meter (m): The base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI).
- Kilometer (km), centimeter (cm), millimeter (mm), and others are derived units.
- Mass:
- Kilogram (kg): The base unit of mass in the SI system.
- Gram (g), milligram (mg), and microgram (μg) are derived units.
- Time:
- Second (s): The base unit of time in the SI system.
- Minute (min), hour (hr), and day (d) are derived units.
- Electric Current:
- Ampere (A): The base unit of electric current in the SI system.
- Temperature:
- Kelvin (K): The base unit of temperature in the SI system.
- Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) are commonly used in some regions, but they are not part of the SI system.
- Amount of Substance:
- Mole (mol): The base unit for the amount of substance in the SI system.
- Luminous Intensity:
- Candela (cd): The base unit for luminous intensity in the SI system.
- Area:
- Square meter (m²): The unit for measuring area.
- Square kilometer (km²), square centimeter (cm²), and others are also used.
- Volume:
- Cubic meter (m³): The unit for measuring volume.
- Liter (L), milliliter (mL), and cubic centimeter (cm³) are commonly used.
- Speed/Velocity:
- Meters per second (m/s): Common unit for speed and velocity.
- Acceleration:
- Meters per second squared (m/s²): The unit for acceleration.
- Force:
- Newton (N): The unit of force in the SI system.
- Pressure:
- Pascal (Pa): The unit of pressure in the SI system.
- Bar, atmosphere (atm), and millimeter of mercury (mmHg) are also used for pressure.
- Energy:
- Joule (J): The unit of energy in the SI system.
- Calorie (cal) and electronvolt (eV) are also used.
- Power:
- Watt (W): The unit of power in the SI system.
- Horsepower (hp) is another unit of power commonly used in some contexts.
- Electric Charge:
- Coulomb (C): The unit of electric charge in the SI system.
- Voltage (Electric Potential):
- Volt (V): The unit of electric potential in the SI system.
- Resistance:
- Ohm (Ω): The unit of electrical resistance in the SI system.
These are just a few examples of units of measurement. Depending on the field of science or engineering, there may be specialized units for specific quantities. It’s important to use the appropriate units to ensure clarity and consistency in scientific and technical communication.