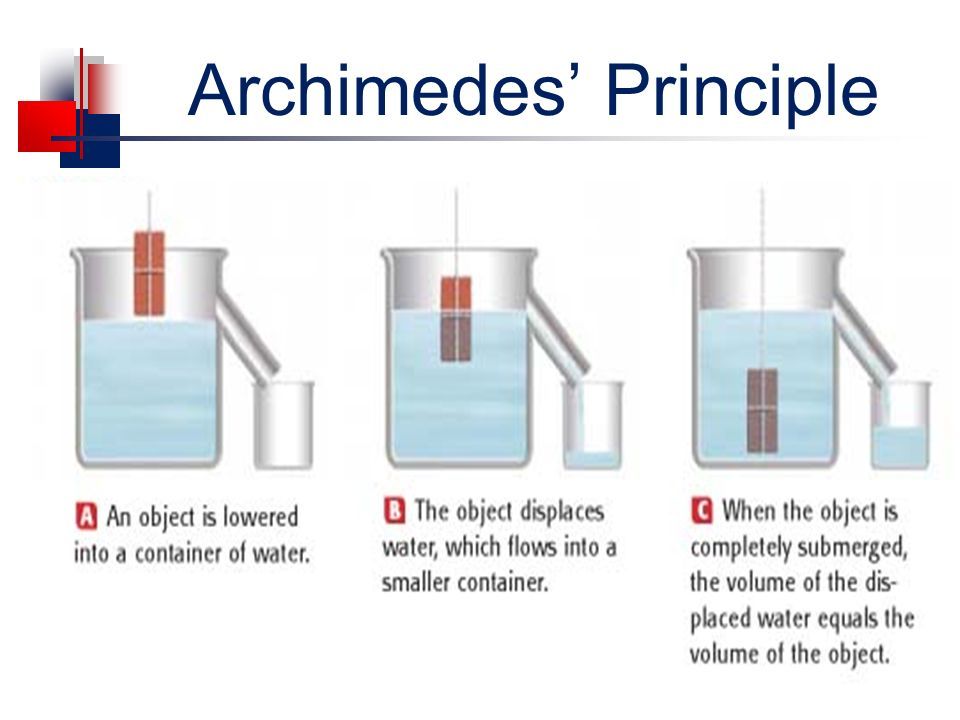
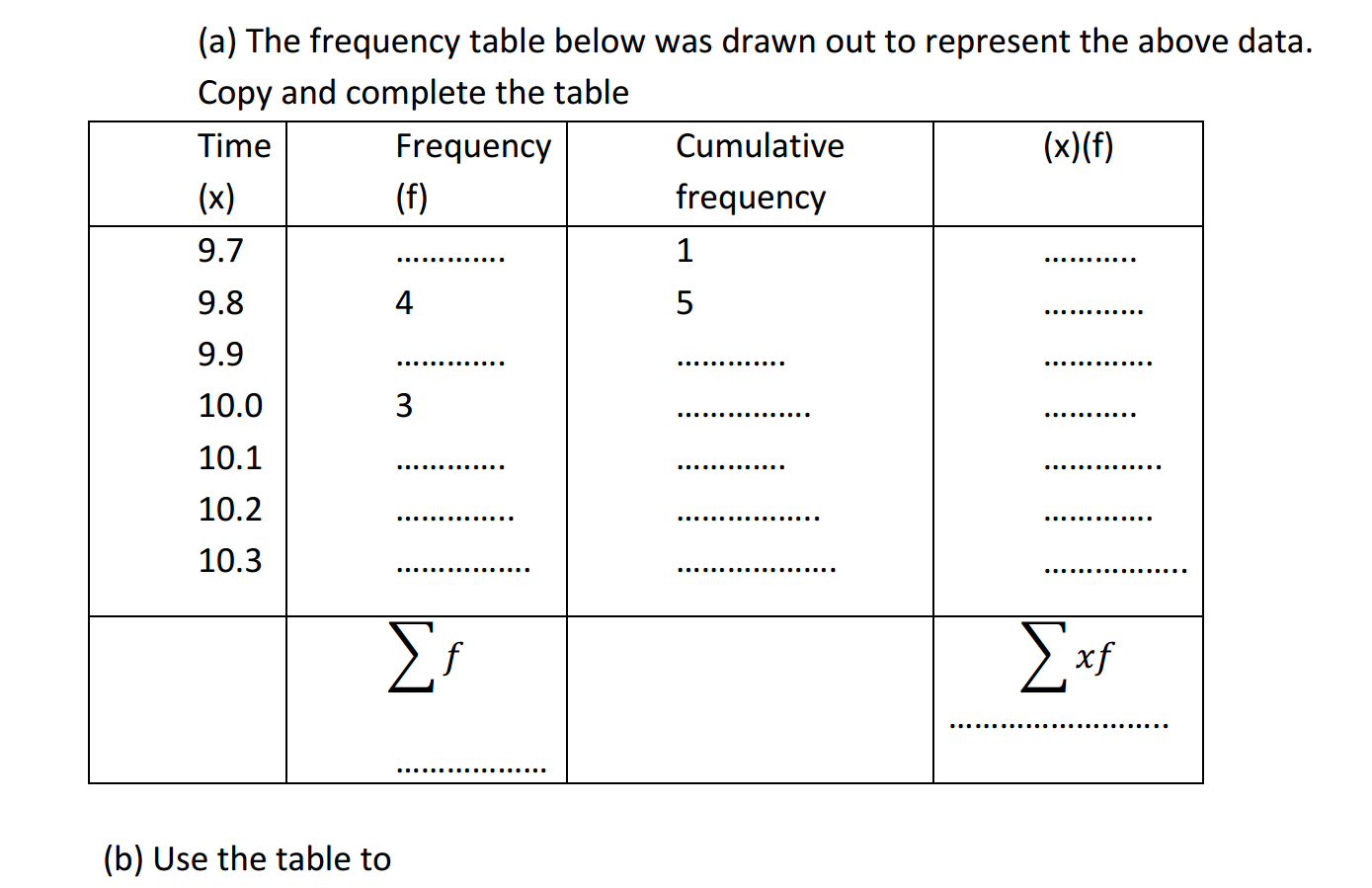
Practicing agriculture in arid or semi-arid areas, where water resources are limited, can be challenging. However, it is possible to implement sustainable farming practices that maximize water efficiency and productivity. Here are some strategies for agriculture in arid regions:
- Drought-Resistant Crop Selection:
- Choose crop varieties that are well-suited to arid conditions. Drought-resistant or drought-tolerant crops are adapted to limited water availability.
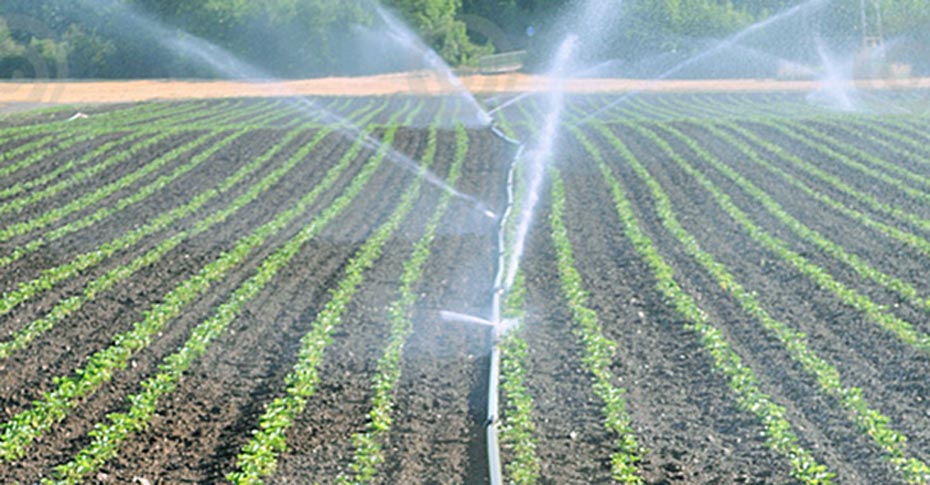
- Improved Irrigation Techniques:
- Implement efficient irrigation methods such as drip irrigation, which delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation.
- Use rainwater harvesting systems to collect and store rainwater for irrigation during dry periods.
- Soil Management:
- Enhance soil fertility and structure through organic matter addition (compost, manure) to improve water retention.
- Practice no-till or reduced tillage to reduce soil moisture loss.
- Mulching:
- Apply mulch (e.g., straw, plastic, or organic material) to the soil surface to reduce evaporation and conserve moisture.
- Crop Rotation and Intercropping:
- Rotate crops to reduce the risk of soil degradation and disease buildup.
- Intercrop drought-tolerant and complementary crops to optimize water and nutrient use.
- Agroforestry:
- Integrate drought-resistant tree species into your farming system to provide shade and improve soil health.
- Desert Farming Techniques:
- Explore innovative desert farming techniques such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and vertical farming to reduce water use and maximize yield.
- Dryland Farming:
- Practice dryland farming techniques suitable for arid regions, like conservation tillage and moisture conservation through terracing and contour farming.
- Improved Seeds and Genetic Engineering:
- Consider the use of drought-resistant crop varieties and genetically modified (GM) crops that are engineered to withstand water stress.
- Salinity Management:
- Implement measures to manage soil salinity, such as leaching and using salt-tolerant crops.
- Smart Water Management:
- Employ water-saving technologies like soil moisture sensors and automated irrigation systems to optimize water use.
- Climate-Adaptive Farming:
- Monitor local climate patterns and adapt farming practices accordingly. Timing of planting and harvesting is crucial in arid regions.
- Livestock Management:
- Practice rotational grazing and provide sufficient water sources for livestock.
- Consider drought-resistant livestock breeds adapted to arid conditions.
- Community Water Management:
- Collaborate with neighboring farmers and communities to manage shared water resources more effectively.
- Diversified Income Sources:
- Consider diversifying your income sources with non-farming activities to mitigate the risks associated with arid agriculture.
- Government Support and Policies:
- Advocate for policies that support sustainable agriculture in arid regions, such as water management and research initiatives.
- Education and Training:
- Stay informed about the latest advancements in arid agriculture through education, training, and knowledge-sharing within your community.
- Investment in Research and Innovation:
- Support research into arid agriculture and explore innovative solutions to address water scarcity and environmental challenges.
Practicing agriculture in arid areas requires a combination of resilient crop choices, efficient water management, and sustainable farming techniques. It’s essential to adapt to local conditions and seek solutions that are environmentally friendly and economically viable. Additionally, collaborating with local agricultural experts and organizations can provide valuable insights and support for successful arid agriculture.