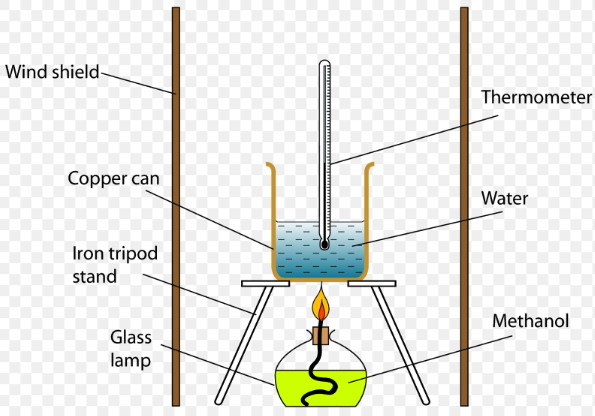
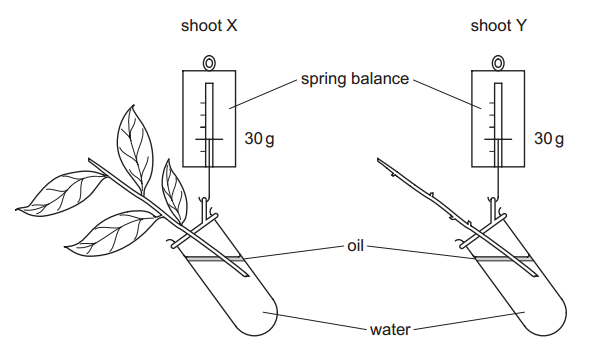
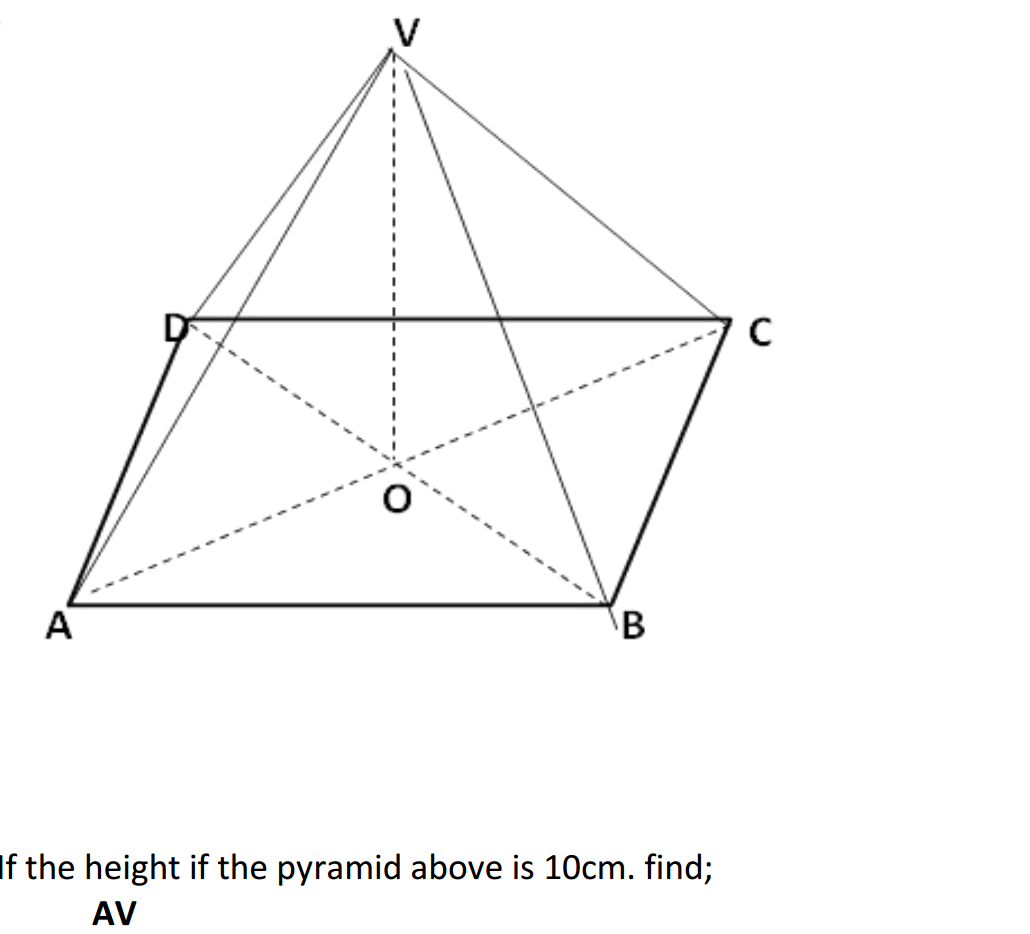
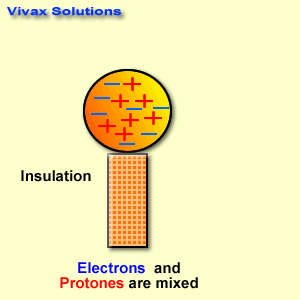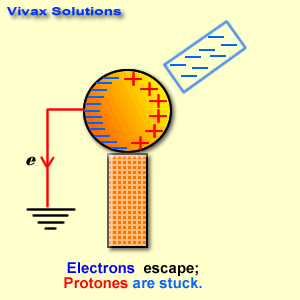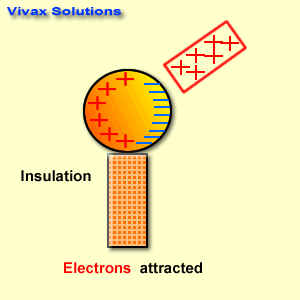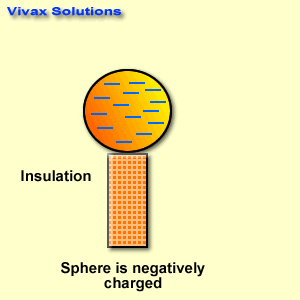
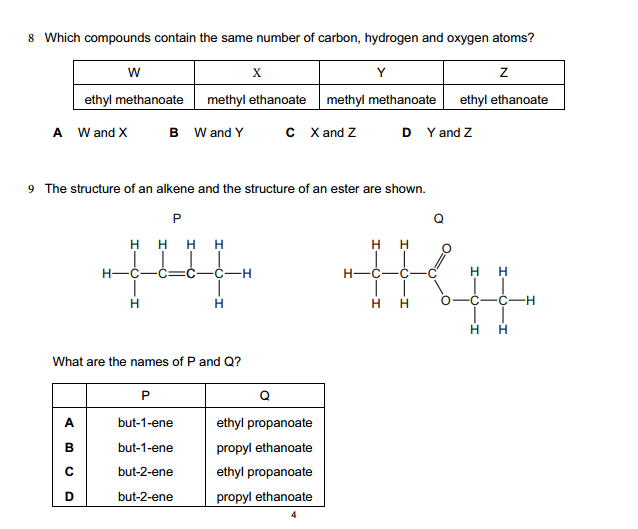
Find below the main terms used in secondary-level chemistry and their definitions:
- Element: An element is a pure substance composed of only one type of atom. Elements are listed on the periodic table.
- Compound: A compound is a substance composed of two or more different elements chemically combined in fixed proportions.
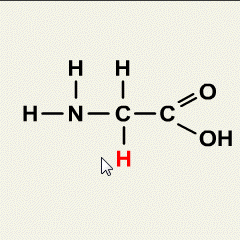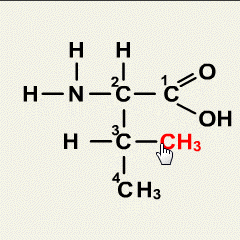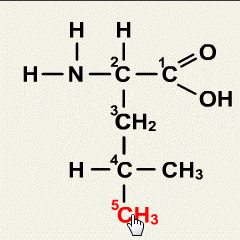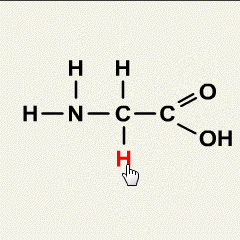
- Molecule: A molecule is the smallest unit of a compound that retains the chemical properties of that compound. It is formed when two or more atoms bond together.
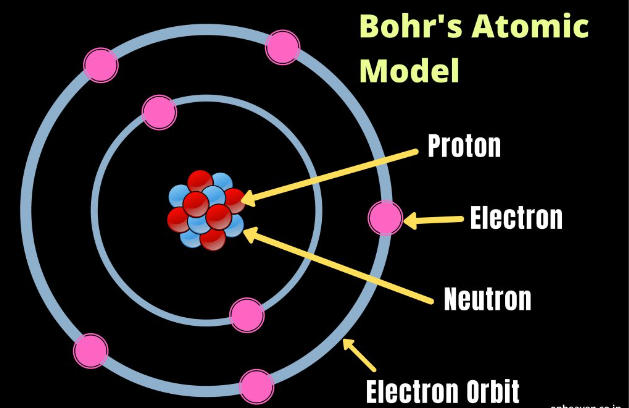
- Atom: An atom is the basic unit of matter, consisting of a nucleus (protons and neutrons) and electrons orbiting the nucleus.
- Chemical Reaction: A chemical reaction is a process that results in the conversion of one or more substances (reactants) into different substances (products) with new chemical properties.
- Chemical Formula: A chemical formula is a concise way to represent the composition of a chemical compound using symbols for the elements and subscripts to indicate the number of atoms of each element.
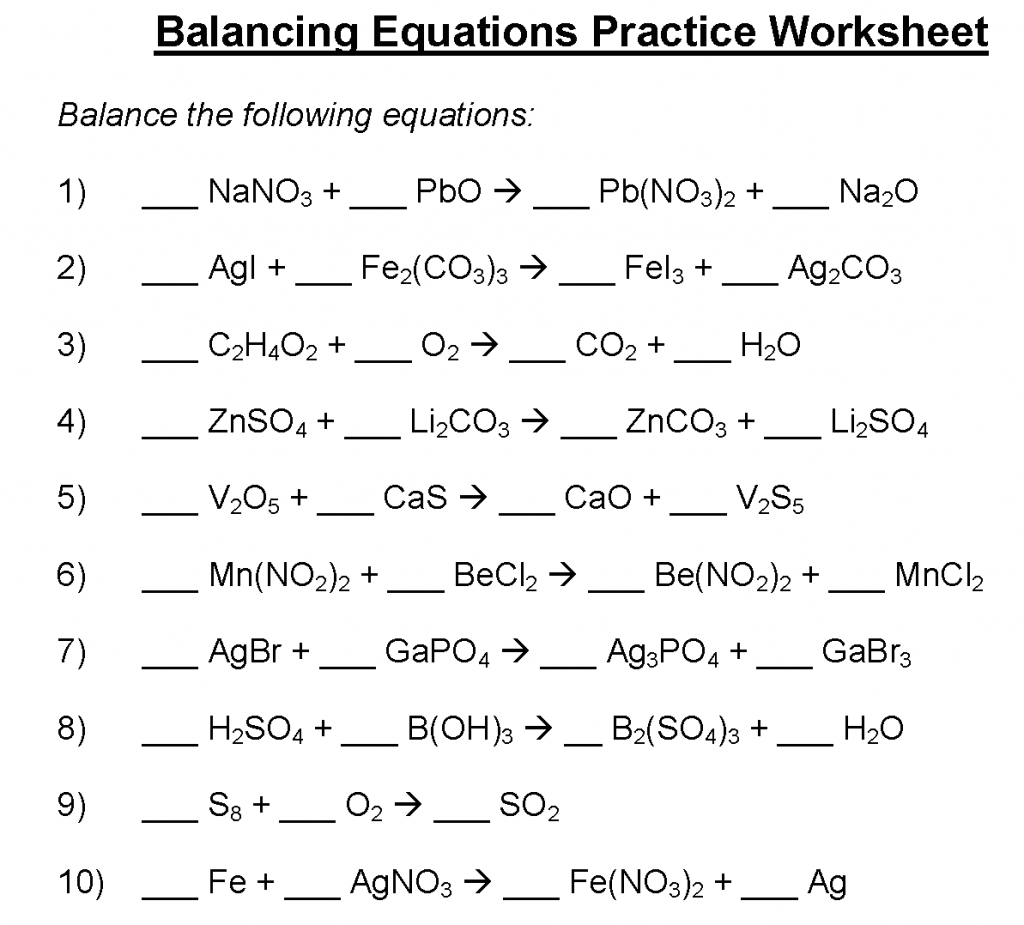
- Chemical Equation: A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction, showing the reactants and products with their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
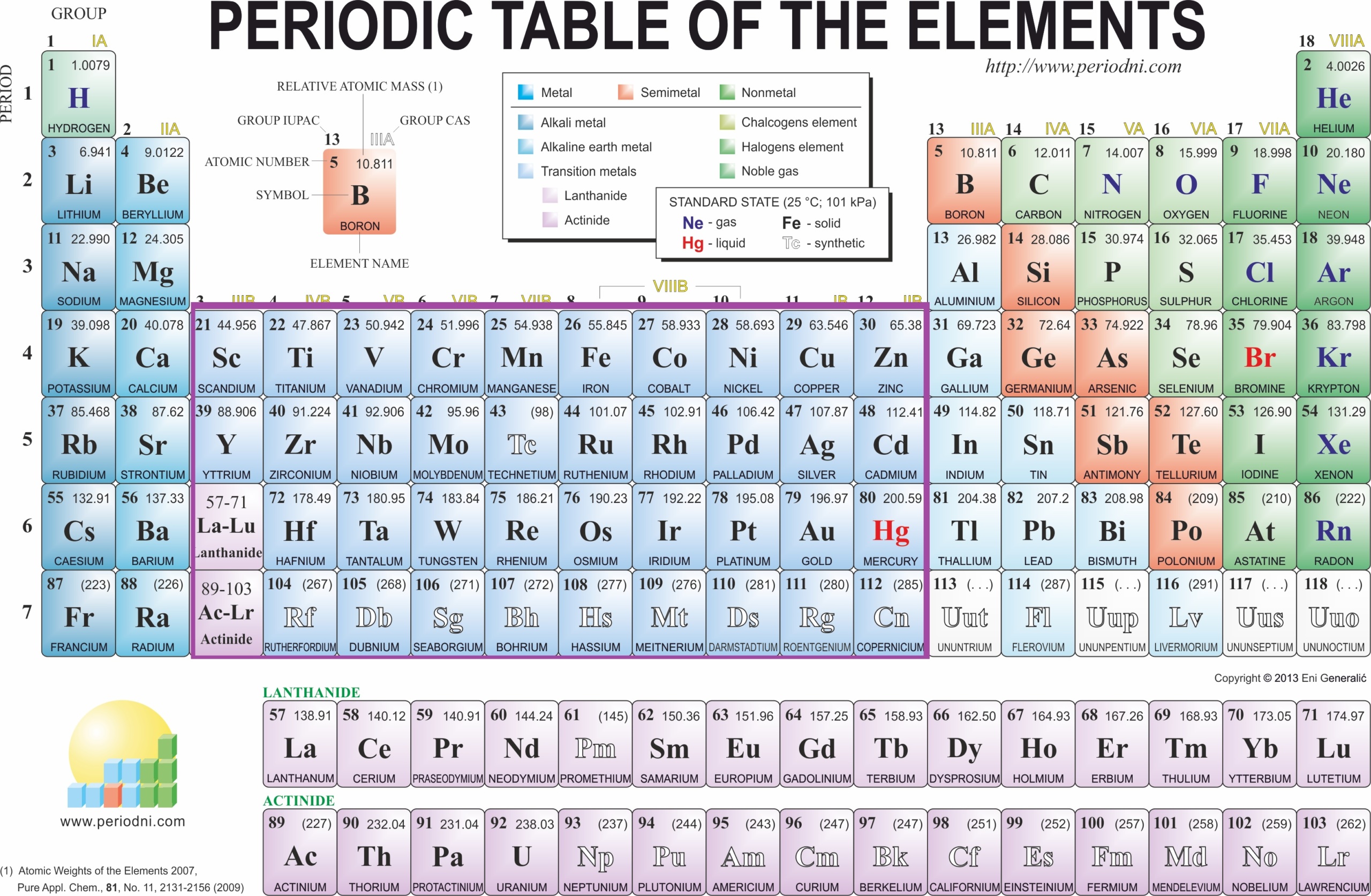
- Periodic Table: The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements, organized by their atomic number and chemical properties.
- Atomic Number: The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. It determines an element’s identity on the periodic table.
- Atomic Mass: Atomic mass is the average mass of the isotopes of an element, measured in atomic mass units (amu).
- Mole: A mole is a unit used to quantify the number of particles in a substance. One mole contains approximately 6.022 x 10^23 particles (Avogadro’s number).
- Chemical Bond: A chemical bond is the force that holds two or more atoms together in a molecule or compound. Common types include covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds.
- Ionic Compound: An ionic compound is a compound formed by the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions.
- Covalent Compound: A covalent compound is a compound formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of molecules.
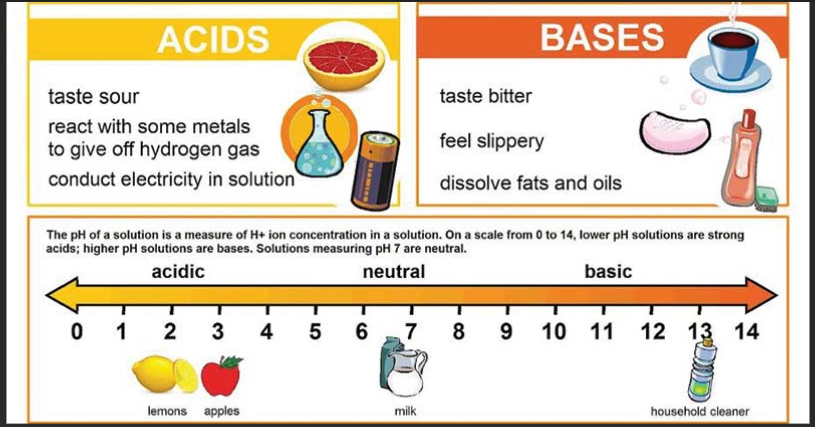
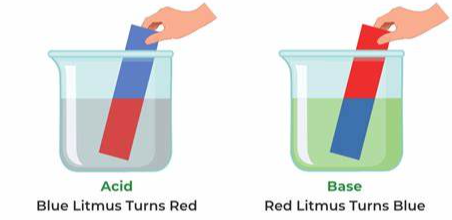
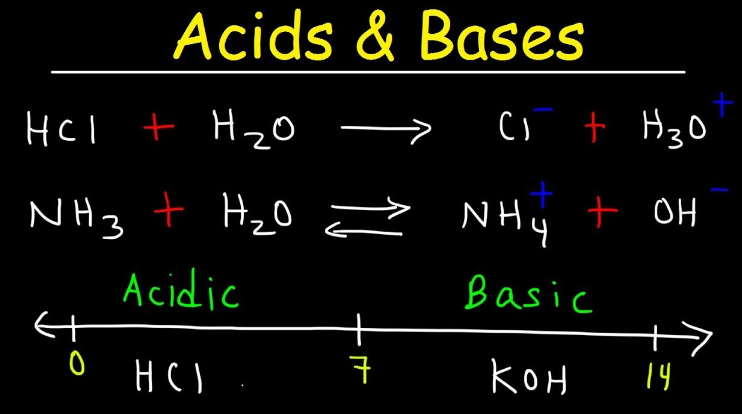
- Acid: An acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, produces hydrogen ions (H+). Acids have a pH less than 7.
- Base: A base is a substance that, when dissolved in water, produces hydroxide ions (OH-). Bases have a pH greater than 7.
- pH: pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It is based on the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution, with a scale from 0 (acidic) to 14 (alkaline).
- Chemical Reaction Rate: The chemical reaction rate is the speed at which a chemical reaction occurs. It can be influenced by factors such as temperature, concentration, and catalysts.
- Catalyst: A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process.
- Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reaction: A redox reaction is a chemical reaction in which there is a transfer of electrons from one substance (oxidation) to another (reduction).
These are some fundamental terms in secondary-level chemistry, and understanding them is essential for grasping the basics of the subject. Keep in mind that the field of chemistry is vast, and there are many more specialized terms and concepts to explore as you progress in your studies.