- Which of the following is a mechanical wave?
- A. Light wave
- B. Sound wave
- C. Radio wave
- D. X-ray
- What type of wave requires a medium for propagation?
- A. Electromagnetic wave
- B. Sound wave
- C. Radio wave
- D. X-ray
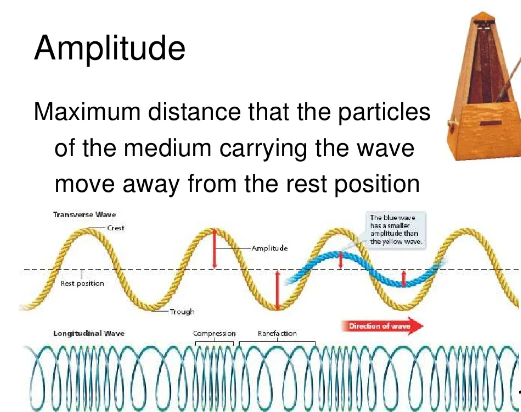
- What is the highest point of a wave called?
- A. Trough
- B. Crest
- C. Amplitude
- D. Wavelength
- What is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave called?
- A. Amplitude
- B. Frequency
- C. Wavelength
- D. Period
- The time taken for one complete oscillation of a wave is called:
- A. Wavelength
- B. Frequency
- C. Amplitude
- D. Period
- Which of the following wave types requires a medium to propagate?
- A. Transverse wave
- B. Longitudinal wave
- C. Electromagnetic wave
- D. Surface wave
- What is the SI unit of frequency?
- A. Meters (m)
- B. Hertz (Hz)
- C. Newton (N)
- D. Joules (J)
- If the frequency of a wave increases, what happens to its wavelength?
- A. Increases
- B. Decreases
- C. Stays the same
- D. Cannot be determined
- The amplitude of a wave is related to its:
- A. Speed
- B. Energy
- C. Wavelength
- D. Frequency
- Which of the following waves can travel through a vacuum?
- A. Sound waves
- B. Water waves
- C. Light waves
- D. Seismic waves
- Which wave property determines the loudness of sound?
- A. Amplitude
- B. Wavelength
- C. Frequency
- D. Speed
- In a longitudinal wave, the particles of the medium move:
- A. Perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation
- B. Parallel to the direction of wave propagation
- C. In a circular motion
- D. In random directions
- What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
- A. 300,000 meters per second
- B. 3 x 10^8 meters per second
- C. 30,000 meters per second
- D. 3 x 10^6 meters per second
- Which of the following waves exhibits refraction?
- A. Sound waves
- B. Light waves
- C. Water waves
- D. Seismic waves
- The distance between two consecutive points in phase in a wave is called:
- A. Amplitude
- B. Frequency
- C. Wavelength
- D. Period
- What happens to the wavelength of a wave if its frequency increases?
- A. Increases
- B. Decreases
- C. Stays the same
- D. Becomes zero
- What type of wave is a water wave?
- A. Transverse wave
- B. Longitudinal wave
- C. Electromagnetic wave
- D. Surface wave
- The number of waves passing a point per unit time is called:
- A. Amplitude
- B. Frequency
- C. Wavelength
- D. Period
- In which medium does sound travel the fastest?
- A. Air
- B. Water
- C. Steel
- D. Vacuum
- Which wave property is directly related to its energy?
- A. Amplitude
- B. Wavelength
- C. Frequency
- D. Period
- What is the unit of wavelength?
- A. Meters (m)
- B. Hertz (Hz)
- C. Newton (N)
- D. Joules (J)
- What happens to the speed of sound as the temperature increases?
- A. Increases
- B. Decreases
- C. Stays the same
- D. Depends on the medium
- What is the phenomenon where two or more waves meet and combine to form a new wave?
- A. Reflection
- B. Refraction
- C. Diffraction
- D. Interference
- What happens to the frequency of a wave if its wavelength decreases?
- A. Increases
- B. Decreases
- C. Stays the same
- D. Cannot be determined
- Which type of wave oscillates perpendicular to the direction of propagation?
- A. Transverse wave
- B. Longitudinal wave
- C. Surface wave
- D. Standing wave
- What is the phenomenon of a wave bending as it passes from one medium to another?
- A. Reflection
- B. Refraction
- C. Diffraction
- D. Interference
- What is the process by which a wave bounces off a surface called?
- A. Reflection
- B. Refraction
- C. Diffraction
- D. Interference
- What happens to the wavelength of a wave if its frequency decreases?
- A. Increases
- B. Decreases
- C. Stays the same
- D. Becomes zero
- What is the phenomenon where a wave spreads out as it passes through an opening or around an obstacle?
- A. Reflection
- B. Refraction
- C. Diffraction
- D. Interference
- What is the relationship between the frequency and period of a wave?
- A. They are inversely proportional
- B. They are directly proportional
- C. They are unrelated
- D. They are exponentially related
Answers to the above Questions. Leave a comment if you find a wrong answer or you have ans=y questions.
1. B. Sound wave 2. B. Sound wave 3. B. Crest 4. C. Wavelength 5. D. Period 6. B. Longitudinal wave 7.B. Hertz (Hz) 8.B. Decreases 9.B. Energy 10.C. Light waves 11.A. Amplitude 12. B. Parallel to the direction of wave propagation 13.B. 3 x 10^8 meters per second 14.C. Water waves 15.C. Wavelength 16.B. Decreases 17.D. Surface wave 18.B. Frequency 19.C. Steel 20.A. Amplitude 21.A. Meters (m) 22.A. Increases 23.D. Interference 24.A. Increases 25.A. Transverse wave 26.B. Refraction 27.A. Reflection 28.A. Increases 29.C. Diffraction 30.A. They are inversely proportional