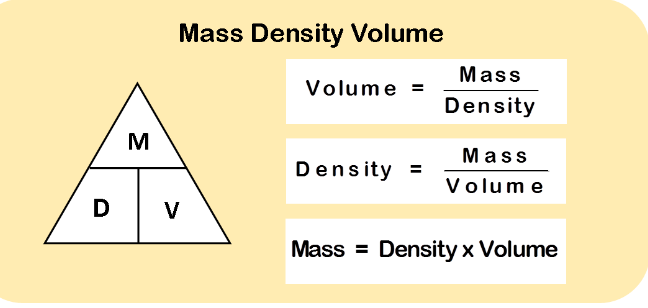
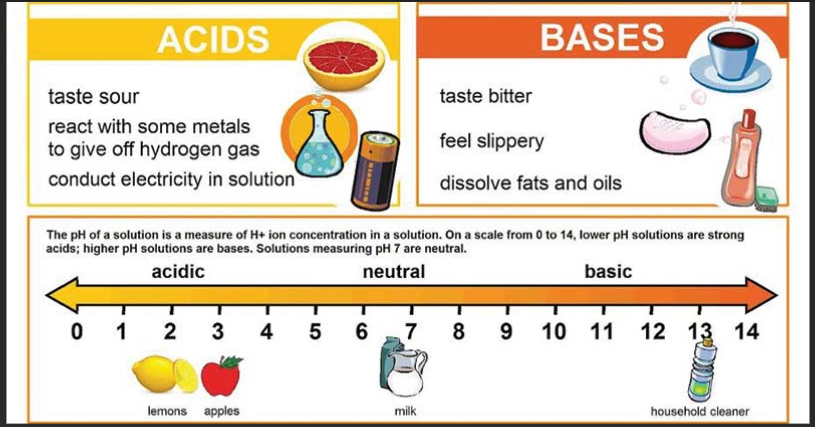
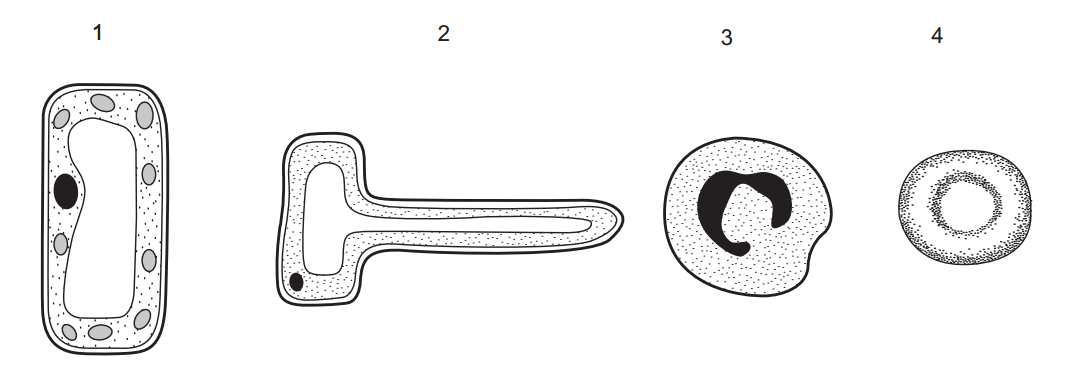
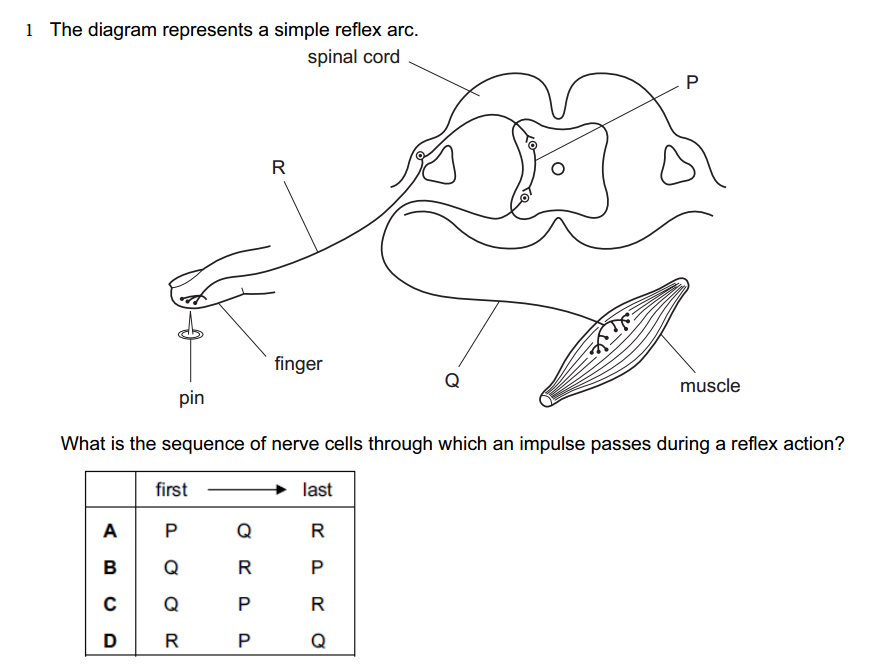
1.What is the study of astrophysics primarily concerned with?
a. The physics of Earth's atmosphere
b. The physics of celestial bodies and the universe
c. The physics of electromagnetic waves
d. The physics of subatomic particles in space
2.Which scientist formulated the theory of general relativity?
a. Isaac Newton
b. Albert Einstein
c. Stephen Hawking
d. Edwin Hubble
3.What is the name given to the massive celestial objects formed from the remnants of a supernova explosion?
a. White dwarfs
b. Neutron stars
c. Black holes
d. Red giants
4.What phenomenon causes the bending of light rays as they pass through a gravitational field?
a. Refraction
b. Reflection
c. Diffraction
d. Gravitational lensing
5.What is the name of the theoretical boundary around a black hole from which no matter or radiation can escape?
a. Event horizon
b. Singularity
c. Photon sphere
d. Ergosphere
6.Which force is primarily responsible for the formation of stars from interstellar gas clouds?
a. Electromagnetic force
b. Strong nuclear force
c. Weak nuclear force
d. Gravitational force
7.What is the term for the explosion of a massive star at the end of its life cycle?
a. Supernova
b. Nova
c. Hypernova
d. Neutron star
8.What is the name of the galaxy that contains our solar system?
a. Andromeda
b. Milky Way
c. Sombrero
d. Pinwheel
9.Which concept describes the universe expanding from a singular point around 13.8 billion years ago?
a. Big Rip
b. Big Bang
c. Big Crunch
d. Big Bounce
10.What is the term for the distortion of space-time caused by the presence of mass?
a. Gravitational wave
b. Space-time curvature
c. Quantum tunneling
d. Cosmic inflation
11.Which type of celestial object emits strong bursts of electromagnetic radiation and is considered the most luminous objects in the universe?
a. Quasars
b. Pulsars
c. Black holes
d. Red giants
12.What is the primary source of energy for stars?
a. Nuclear fusion
b. Nuclear fission
c. Electromagnetic radiation
d. Gravitational potential energy
13.Which astronomical unit of measurement is equal to the distance that light travels in one year?
a. Light-second
b. Light-minute
c. Light-hour
d. Light-year
14.What is the name of the theoretical model that describes how the universe expanded rapidly in its earliest stages?
a. String theory
b. Inflationary model
c. Quantum mechanics
d. Dark matter theory
15.What is the name of the theory proposing that the observable universe is only one of many disconnected universes?
a. Multiverse theory
b. Parallel universe theory
c. Infinite universe theory
d. Omniverse theory
16.Which telescope detects and studies objects primarily by their infrared radiation rather than visible light?
a. Hubble Space Telescope
b. Chandra X-ray Observatory
c. Spitzer Space Telescope
d. James Webb Space Telescope
17.What is the name given to the boundary surrounding a black hole where matter is torn apart by gravitational forces?
a. Event horizon
b. Schwarzschild radius
c. Ergosphere
d. Photon sphere
18.Which law in astrophysics states that the observed redshift in light from distant galaxies increases in proportion to their distance from Earth?
a. Newton's Law of Gravitation
b. Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
c. Hubble's Law
d. Doppler Effect
19.What is the name given to the remnants of a massive star's core after a supernova explosion?
a. Neutron star
b. White dwarf
c. Black hole
d. Red giant
20.What term describes the point in the orbit of a planet or comet when it is farthest from the sun?
a. Aphelion
b. Perihelion
c. Apogee
d. Perigee
21.Which phenomenon occurs when light from a distant object is bent around a massive object in space, creating a distorted or magnified image?
a. Gravitational wave
b. Gravitational redshift
c. Gravitational lensing
d. Gravitational attraction
22.What is the name of the process by which stars convert hydrogen into helium through nuclear reactions in their cores?
a. Nuclear fusion
b. Nuclear fission
c. Nuclear decay
d. Stellar evolution
23.Which concept suggests that the universe will continue expanding indefinitely, becoming increasingly cold and dark over time?
a. Big Rip
b. Big Bang
c. Big Crunch
d. Heat Death
24.What is the term for the curved path followed by a celestial object around a massive body due to gravity?
a. Orbit
b. Trajectory
c. Ellipse
d. Parabola
25.Which unit of measurement is used to express the brightness of stars?
a. Luminosity
b. Magnitude
c. Flux
d. Intensity
26.What is the name of the concept proposing that the universe's expansion is accelerating due to a mysterious force counteracting gravity?
a. Dark energy
b. Dark matter
c. Cosmic inflation
d. Quintessence
27.Which celestial object is a rapidly rotating neutron star that emits beams of radiation, observed as periodic pulses?
a. Quasar
b. Pulsar
c. Black hole
d. Supernova
28.What term describes the shift in the observed wavelength of light caused by the relative motion of the source and observer?
a. Redshift
b. Blueshift
c. Doppler effect
d. Relativistic effect
29.What is the name given to the outermost layer of the sun's atmosphere that is visible during a solar eclipse?
a. Corona
b. Chromosphere
c. Photosphere
d. Heliosphere
30.Which type of radiation has the shortest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum?
a. X-rays
b. Gamma rays
c. Ultraviolet rays
d. Visible light
These questions cover various aspects of astrophysics, including cosmology, celestial bodies, radiation, and astronomical phenomena.
Answers
- b. The physics of celestial bodies and the universe
- b. Albert Einstein
- b. Neutron stars
- d. Gravitational lensing
- a. Event horizon
- d. Gravitational force
- a. Supernova
- b. Milky Way
- b. Big Bang
- b. Space-time curvature
- a. Quasars
- a. Nuclear fusion
- d. Light-year
- b. Inflationary model
- a. Multiverse theory
- c. Spitzer Space Telescope
- a. Event horizon
- c. Hubble’s Law
- a. Neutron star
- a. Aphelion
- c. Gravitational lensing
- a. Nuclear fusion
- d. Heat Death
- a. Orbit
- b. Magnitude
- a. Dark energy
- b. Pulsar
- c. Doppler effect
- a. Corona
- b. Gamma rays
Share love with others on
Like this:
Like Loading...
Related