These values of physical quantities may be useful to you:
Acceleration due to gravity = 10ms -2.
Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 Jkg -1 k-1.
Specific heat capacity of copper = 400 Jkg-1 K-1
Specific latent heat of fusion of water = 340000 Jkg -1
Speed of sound in air = 320 ms -1.
Velocity of electromagnetic waves = 3.0 x 10 8 ms -1.
The above information maybe useful to you.
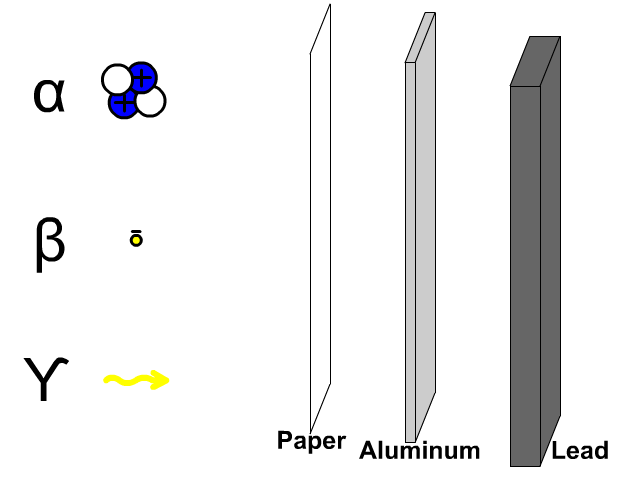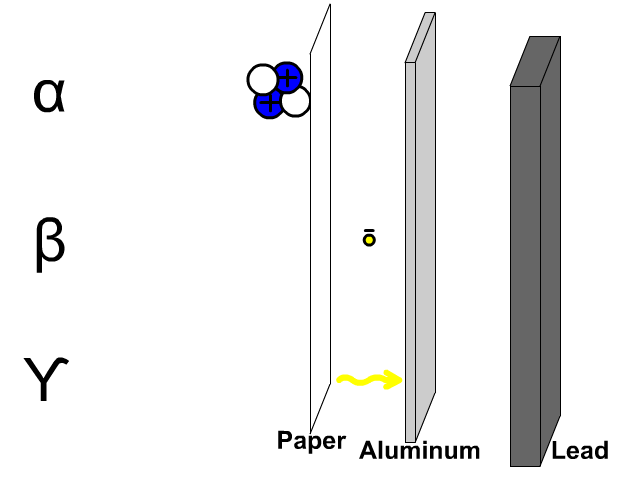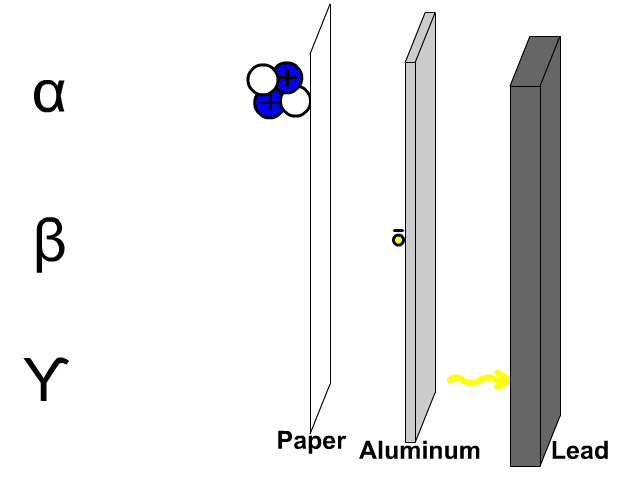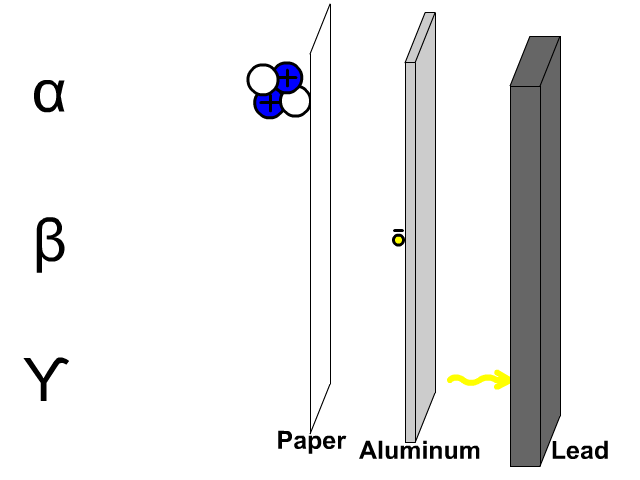
1. (a) State any three differences between cathode rays and X-rays.
(b) (i) Draw a labeled diagram showing the main parts of a cathode ray oscilloscope.
(ii) State any two uses of cathode ray oscilloscope.
(c) (i) Describe energy changes that take place in an X – ray tube from the point of
production of electrons to the cathode.
(ii) Explain how the strength of the X-rays produced can be increased.
(d) What is meant by
(i) Radioactivity?
(ii) Nuclear fission?
2 (a) State Charles’ Law.
(b) Describe an experiment to verify Charles’ Law.
(c) When 80 cm3 of air at 100 Kpa and at a temperature of 7 oc, What is the pressure of the
compressed air?
(d) Using simple kinetic theory, explain why there is no increase in temperature of boiling
water even when more heat is supplied to the water. (e) (i) what is meant by saturated vapour?
(ii) Explain why food in a covered saucepan takes a shorter time to cook.
3.(a) State any three differences between cathode rays and X-rays.
(b) (i) Draw a labeled diagram showing the main parts of a cathode ray oscilloscope.
(ii) State any two uses of cathode ray oscilloscope.
(c) (i) Describe energy changes that take place in an X – ray tube from the point of
production of electrons to the cathode.
(ii) Explain how the strength of the X-rays produced can be increased.
(d) What is meant by
(i) Radioactivity?
(ii) Nuclear fission?
4 (a)(i) What is meant by refractive index of a given medium?
(ii)Define critical angle.
(iv) State the conditions for total internal reflection to occur.
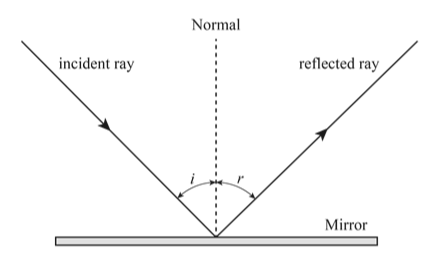
(b)Figure 2 shows rays of light incident on semi – circular glass block.
Ray SP is refracted along PQ.

Explain
(i) Why rays RP and SP are not refracted at the points of incidence on the glass block.
(ii) With the aid of the diagram what happens to a ray RP.
(c) With the aid of a labeled diagram, explain why a pond with clear water appears shallower
than it actually is.
(d) Calculate the critical angle for a glass of refractive index 1.50.
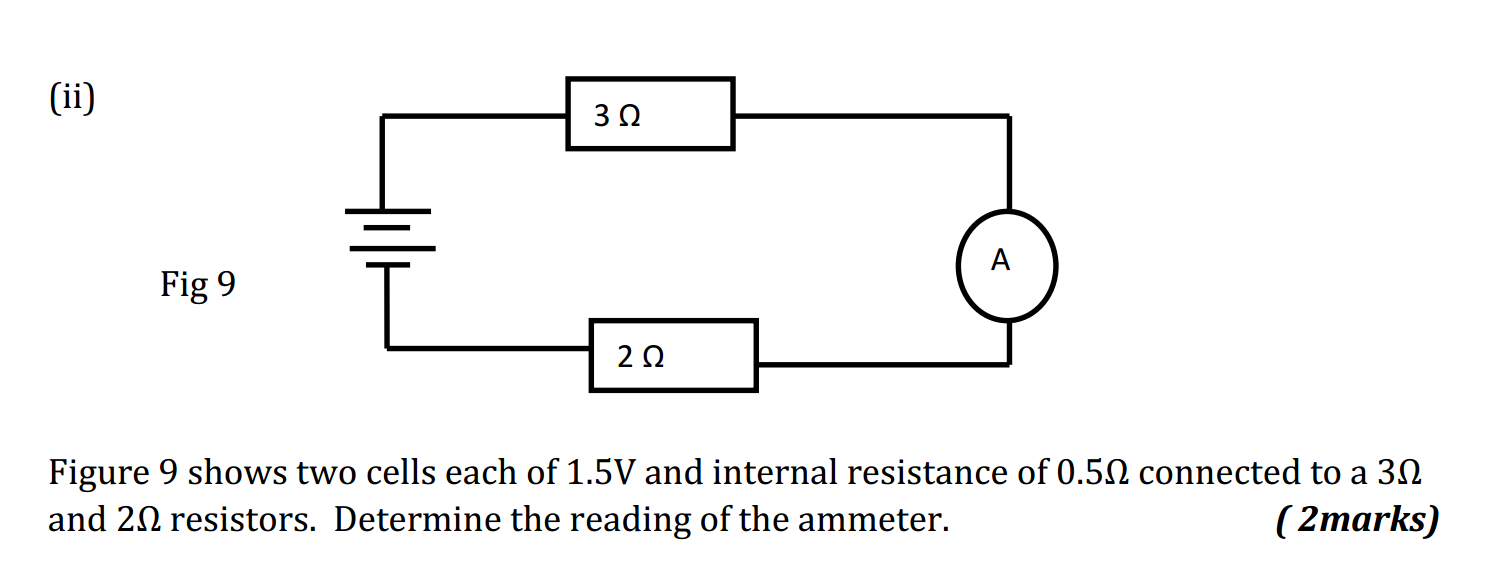
5.(a) (i) State the law of electrostatics.
(ii) Explain how the nature of charge on a body may be determined using a gold leaf
electroscope.
(b) Explain why power cables for cookers are thicker than the ones for lighting.
(c)(i) Explain why voltage is first stepped up before transmission.
(II) Five equal electric bulbs are switched on for 8h a day for thirty days. If each unit costs
Shs600 and the total monthly bill is Shs 43,200, find the power rating of each bulb.
6.(a) (i) what is meant by centre of gravity of a body?
(ii) Given a uniform metre rule, a known mass Mo, a Knife edge and a piece of thread,
describe how the mass of the metre rule can be determined.
(b)(i) State the conditions for a body to be in equilibrium.
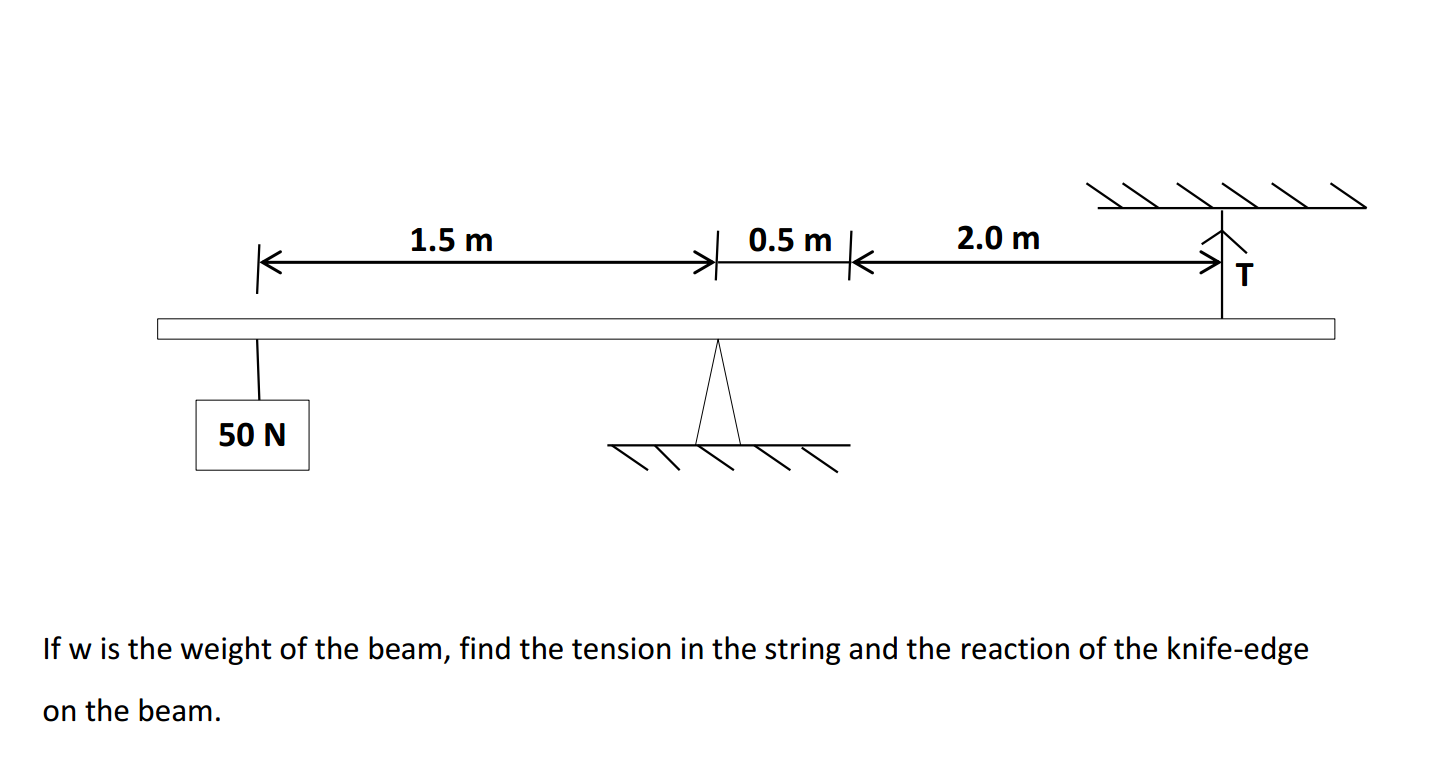
(ii) A uniform beam of weight 500 N is made to balance horizontally on a knife edge by a
string tied near one end and a weight of 50 N hanged near the other end as shown in figure below.

If w is the weight of the beam, find the tension in the string and the reaction of the knife-edge
on the beam.
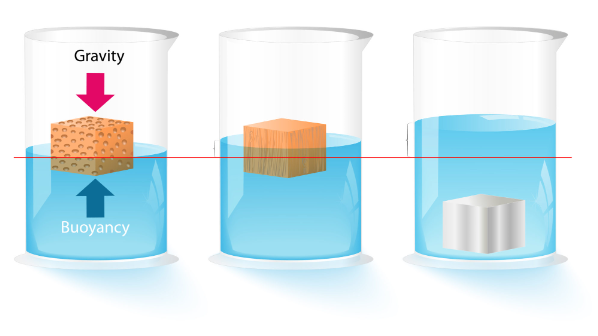
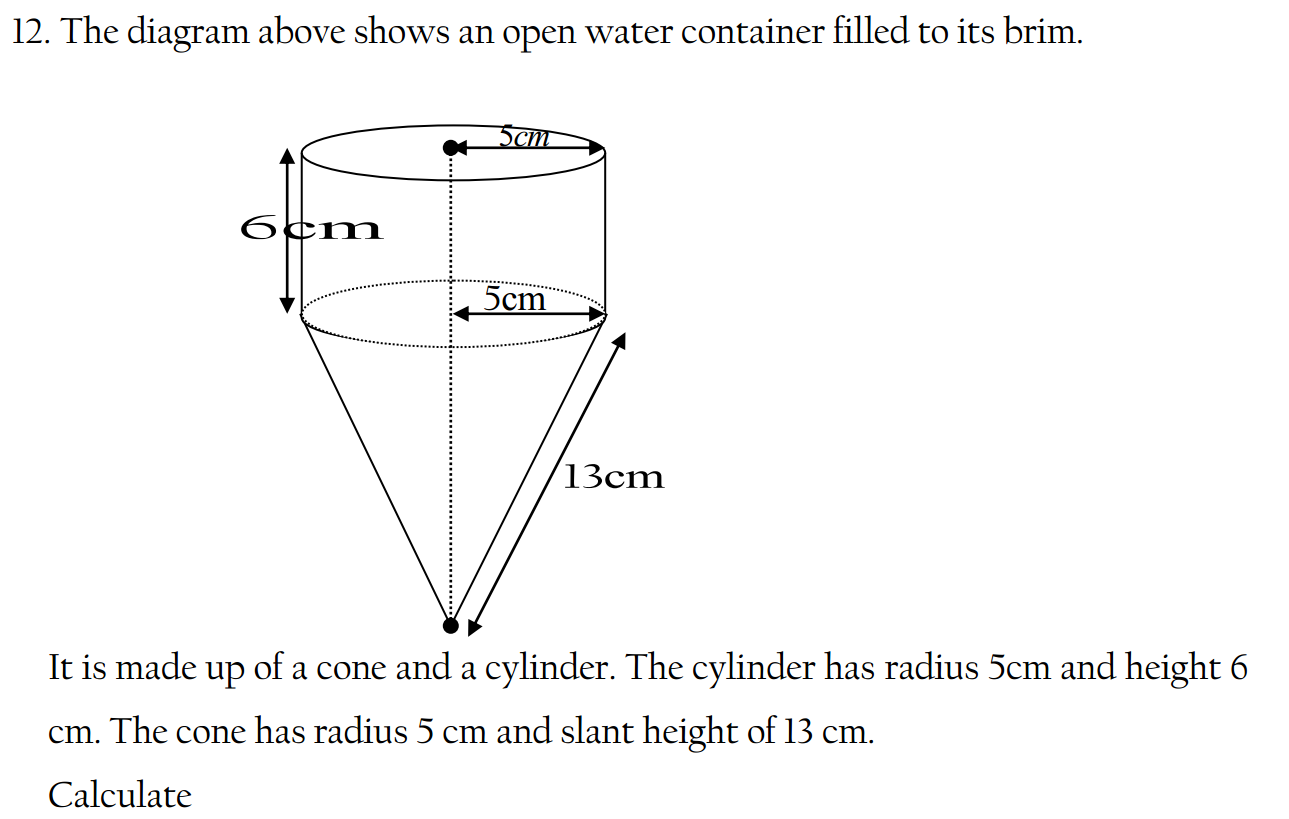
(c) (i) State the law of floatation.
(ii) A solid of volume 10 -5 m3 floats in water of density 10 3 kgm -3 with four – fifths of its
volume submerged. Find the mass of the solid.
(d) State one application of the law of floatation.
(ii) A solid of volume 10 -5 m 3 floats in water of density 103 kgm -3 with four – fifths of its
volume submerged. Find the mass of the solid.
(d) State one application of the law of floatation.
7.(a) (i) what is meant by resonance as applied to sound?
(ii) How are stationary waves formed?
(iii) Describe an experiment to demonstrate resonance in sound.
(b) (i) sketch the standing wave in a closed tube corresponding in sound.
(ii) if the frequency of the fundamental note in
(b) (i) is 110 Hz, find the length of the air
column in the tube. (Take speed of sound = 330 ms -1)
(c)(i) What are electromagnetic waves?
(ii) Infrared radiation and ultraviolet radiation are both electromagnetic. State one common
property and one difference between infrared radiation and ultraviolet radiation
(d) why are radio signals clearer at night than during the day?
8.(a) What is meant by the following as applied to machines?
(i) Velocity ratio.
(ii) Efficiency.
(b) Figure below shows a mass of 30 kg being raised to the top of the incline.

If the effort applied is 160 N, calculate the
(i) Efficiency of the machine.
(ii) Friction
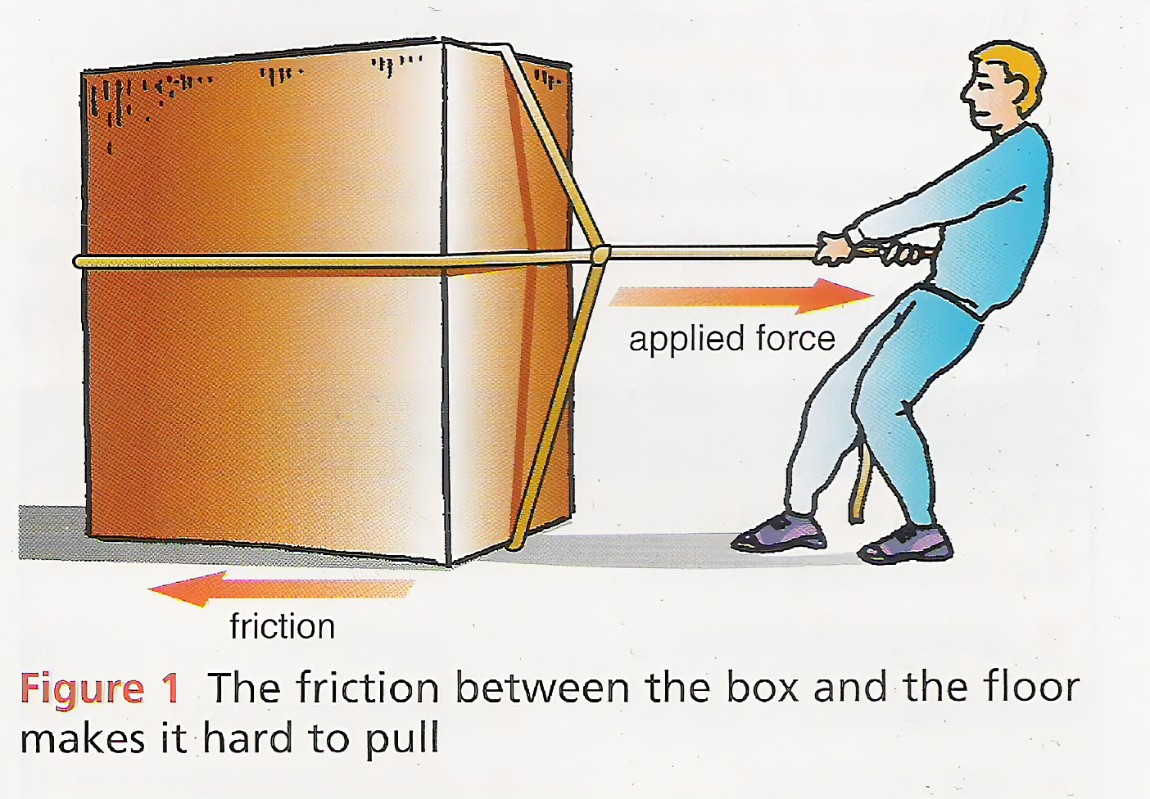
(c) (i) Define static friction
(ii) Describe an experiment to determine static friction between a wooden block and a table.
(iii) State two advantages of friction.