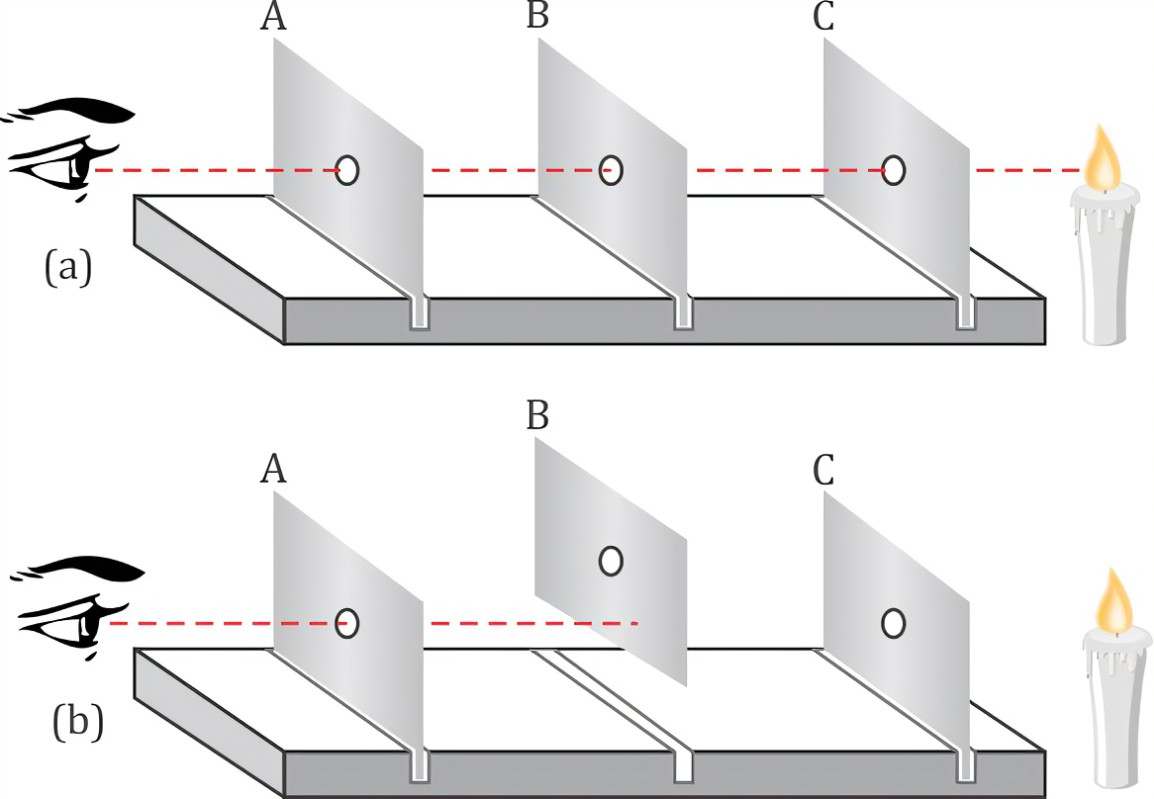
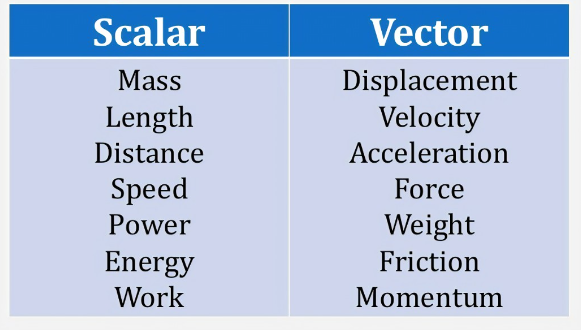
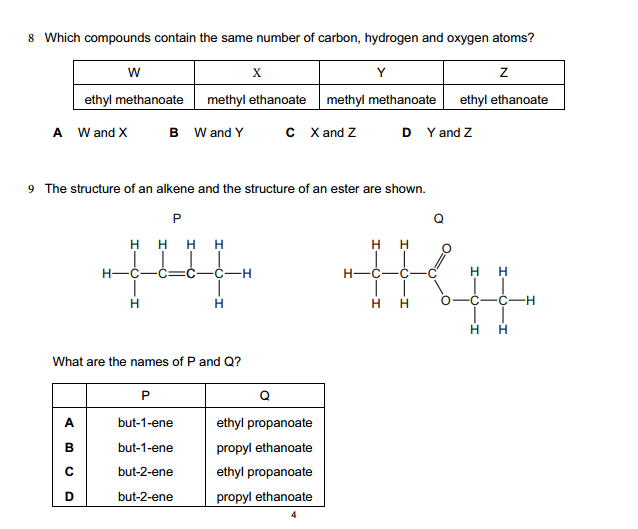
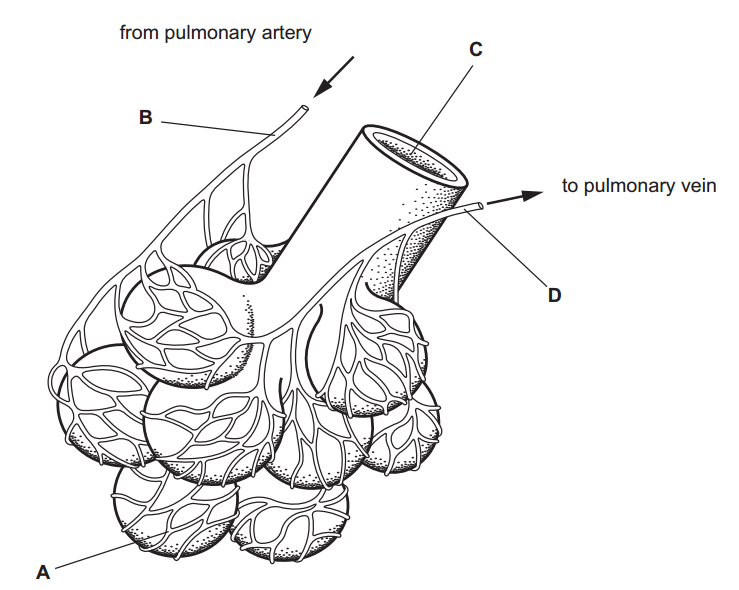
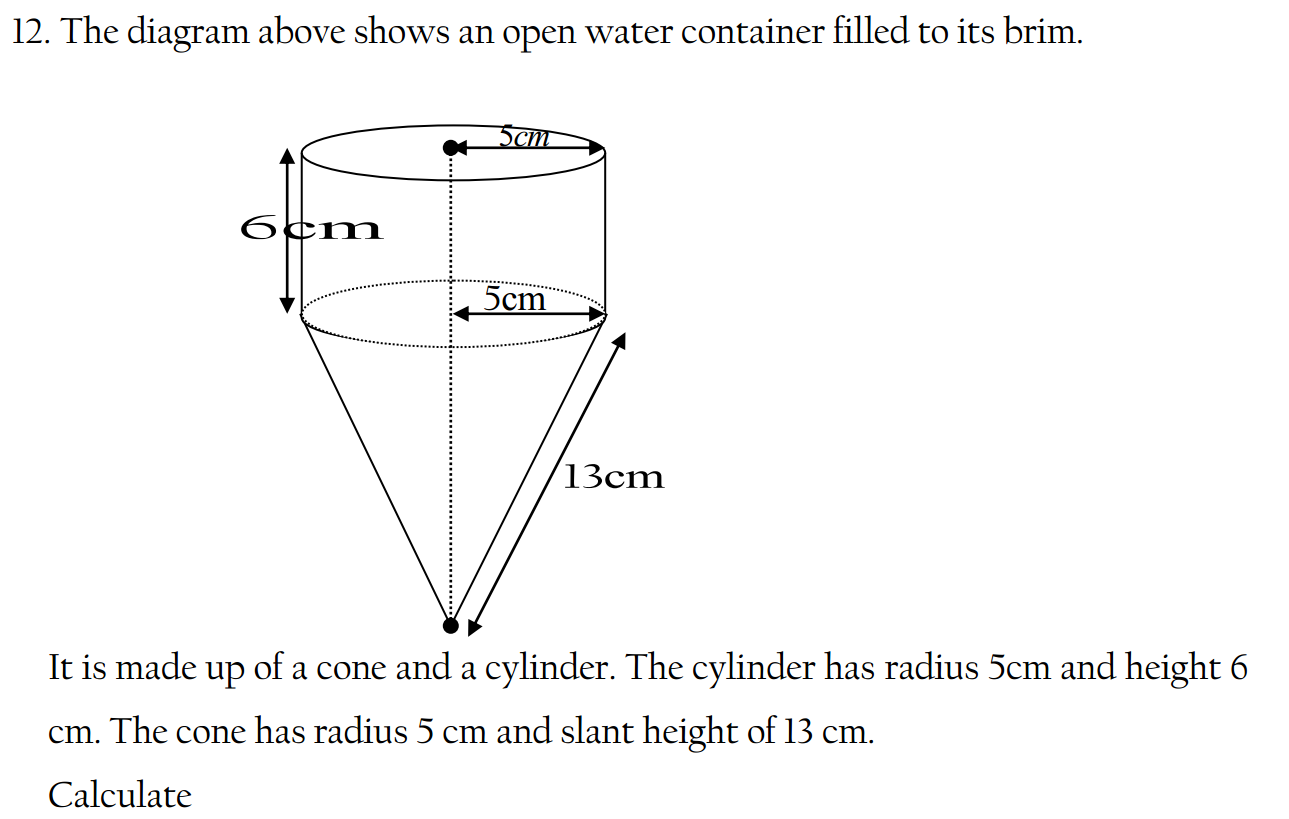
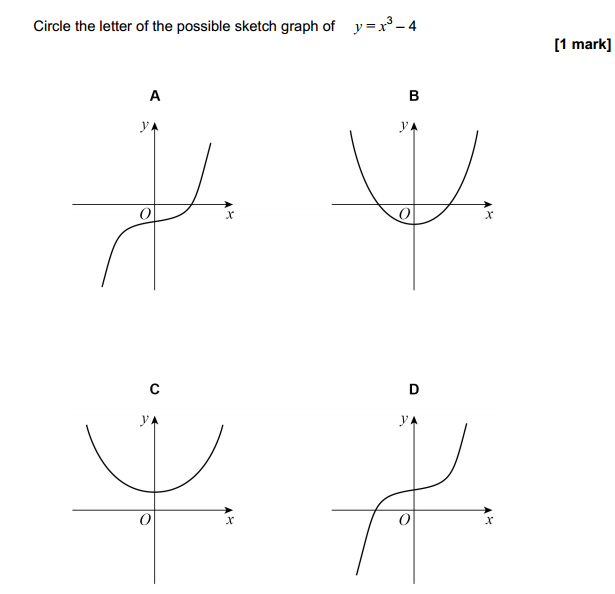
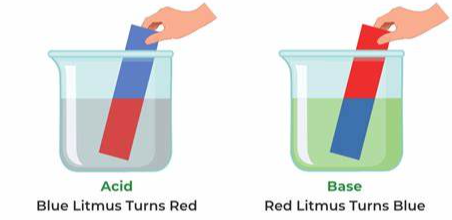
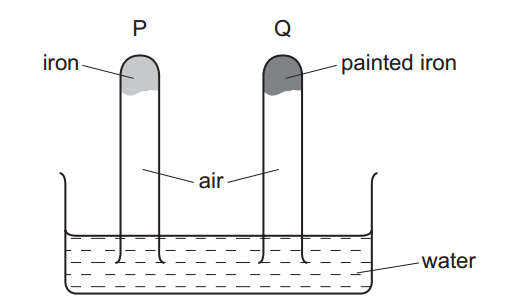
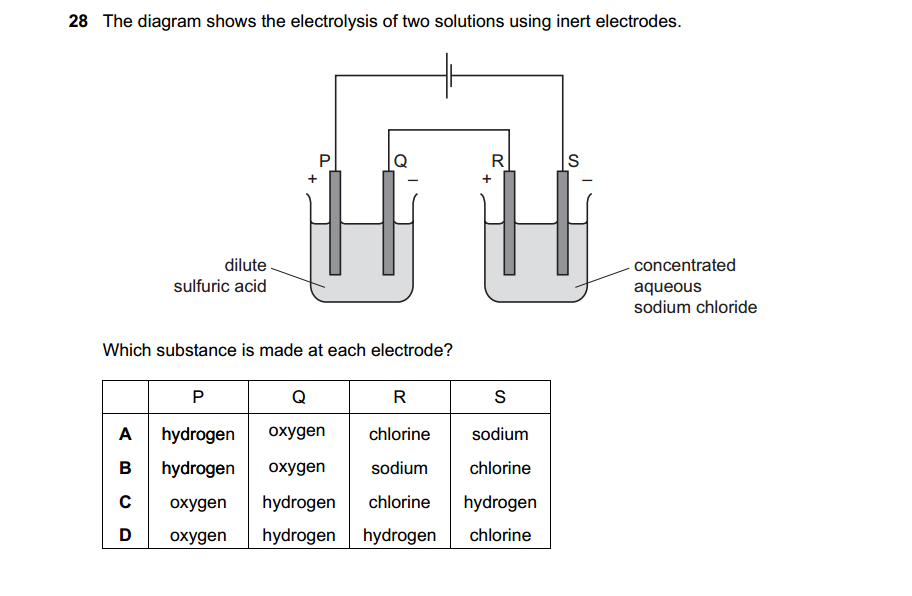
Bases can be prepared through various methods depending on the specific base required and the starting materials available. Here are some common methods for preparing bases:
- Direct Synthesis:
- Some bases can be prepared directly by combining the appropriate elements or compounds. For example:
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) can be prepared by reacting sodium metal with water.
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) can be prepared by reacting potassium metal with water.
- Some bases can be prepared directly by combining the appropriate elements or compounds. For example:
- Neutralization Reactions:
- Bases can be prepared by neutralizing acidic solutions with appropriate alkalis. For example:
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) can be prepared by neutralizing sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃) with calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)₂].
- Ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH) can be prepared by reacting ammonia (NH₃) with water.
- Bases can be prepared by neutralizing acidic solutions with appropriate alkalis. For example:
- Hydrolysis of Salts:
- Some bases can be prepared by the hydrolysis of their corresponding salts. For example:
- Calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)₂] can be prepared by the hydrolysis of calcium oxide (CaO) in water.
- Magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)₂] can be prepared by the hydrolysis of magnesium chloride (MgCl₂) in water.
- Some bases can be prepared by the hydrolysis of their corresponding salts. For example:
- Biological Processes:
- Some bases can be produced through biological processes. For example:
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) can be produced by the electrolysis of potassium chloride (KCl) extracted from seawater.
- Some bases can be produced through biological processes. For example:
- Extraction from Natural Sources:
- Some bases can be extracted from natural sources. For example:
- Calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)₂], also known as slaked lime, can be produced by adding water to quicklime (calcium oxide, CaO), which is obtained from limestone.
- Some bases can be extracted from natural sources. For example:
- Ammonia Synthesis:
- Ammonia (NH₃) is a weak base and can be synthesized through the Haber process, which involves the reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen gases in the presence of a catalyst.
These are just a few methods for preparing bases. The choice of method depends on factors such as the desired base, availability of starting materials, and scale of production. It’s important to follow proper safety precautions and procedures when working with bases, as they can be corrosive and hazardous.