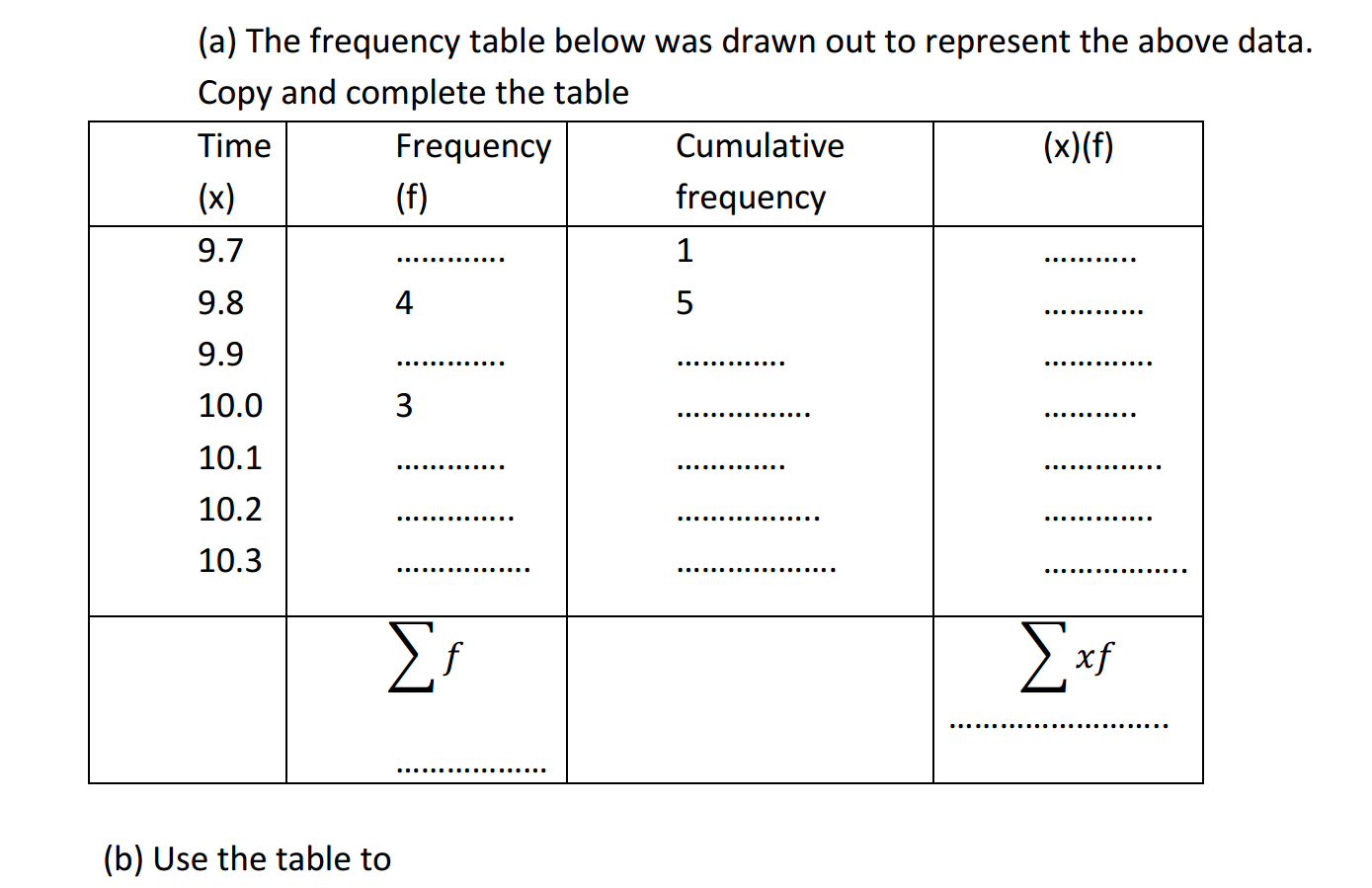
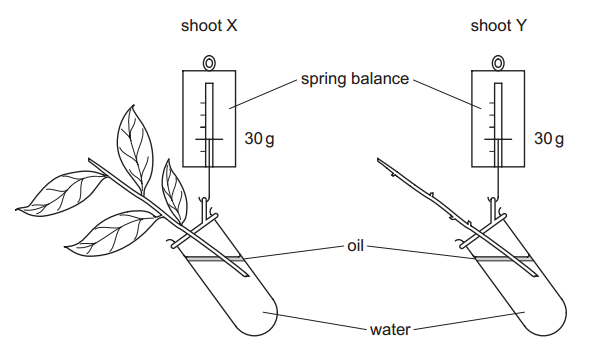
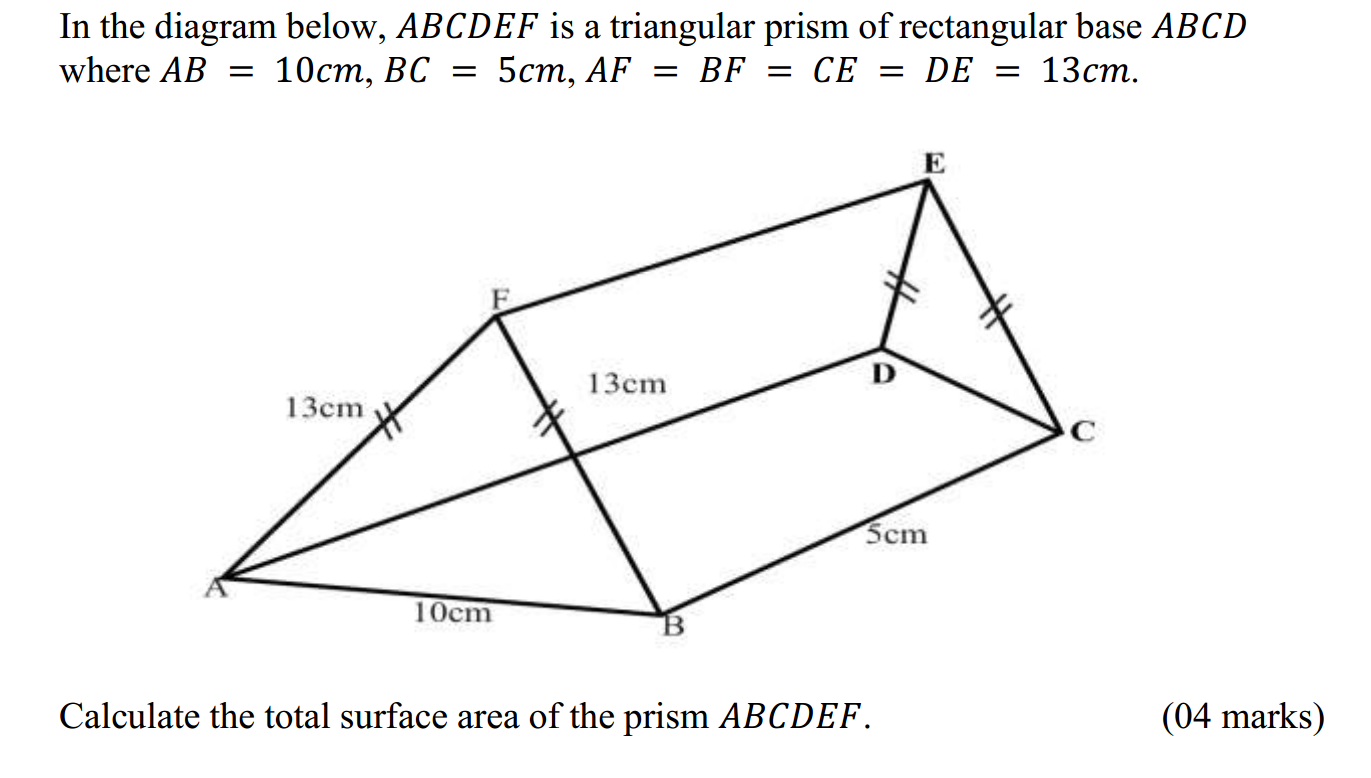
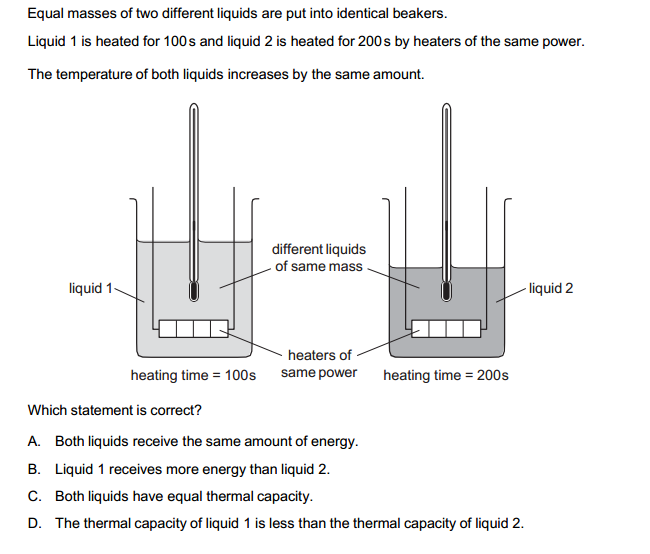
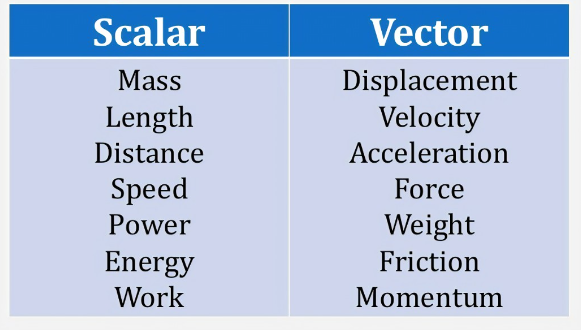
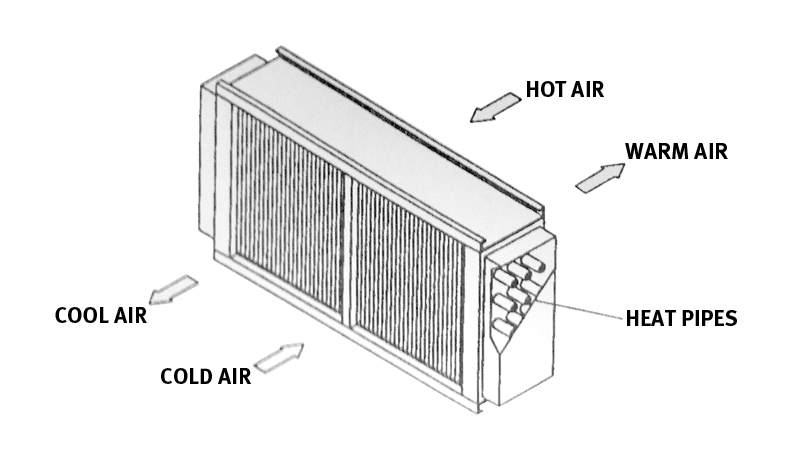
Secondary physics covers a wide range of topics that explore the fundamental principles governing the physical world. These topics delve into the behavior of matter, energy, and the forces that shape our universe. Here’s a brief introduction to some of the key secondary physics topics and their real-world applications:
- Mechanics: Mechanics deals with the motion of objects and the forces that cause that motion. It includes topics like kinematics, dynamics, and statics. Applications include designing vehicles, predicting planetary motion, and understanding the behavior of materials under stress.
- Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics studies the transfer of heat and energy. It explores concepts like temperature, entropy, and heat engines. Applications include designing engines, refrigeration systems, and understanding climate change.
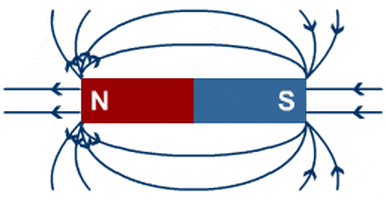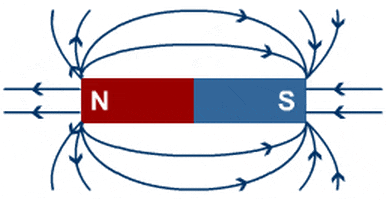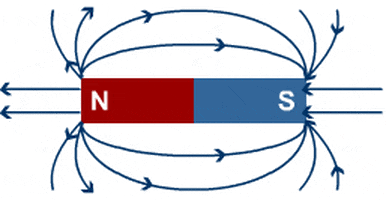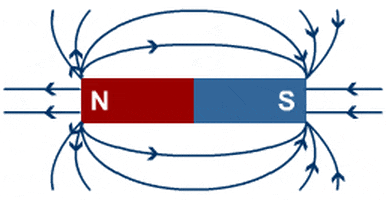
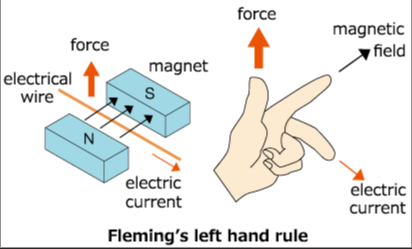
- Electromagnetism: Electromagnetism examines the behavior of electric and magnetic fields. Topics include electrical circuits, electromagnetic waves, and the behavior of charged particles. Applications include electronics, electricity generation, and wireless communication.
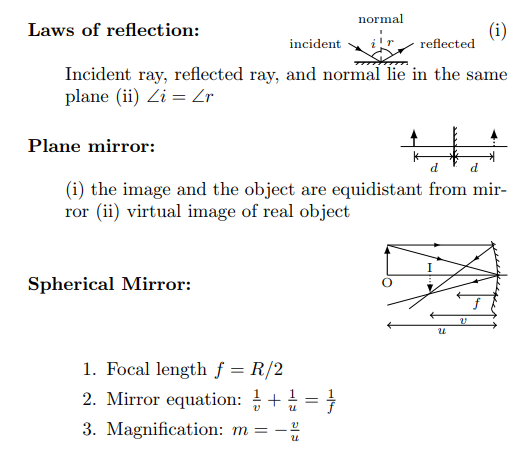
- Optics: Optics is the study of light and its interactions with matter. It covers topics like reflection, refraction, and the properties of lenses and mirrors. Applications include designing optical instruments, eyeglasses, and understanding vision.
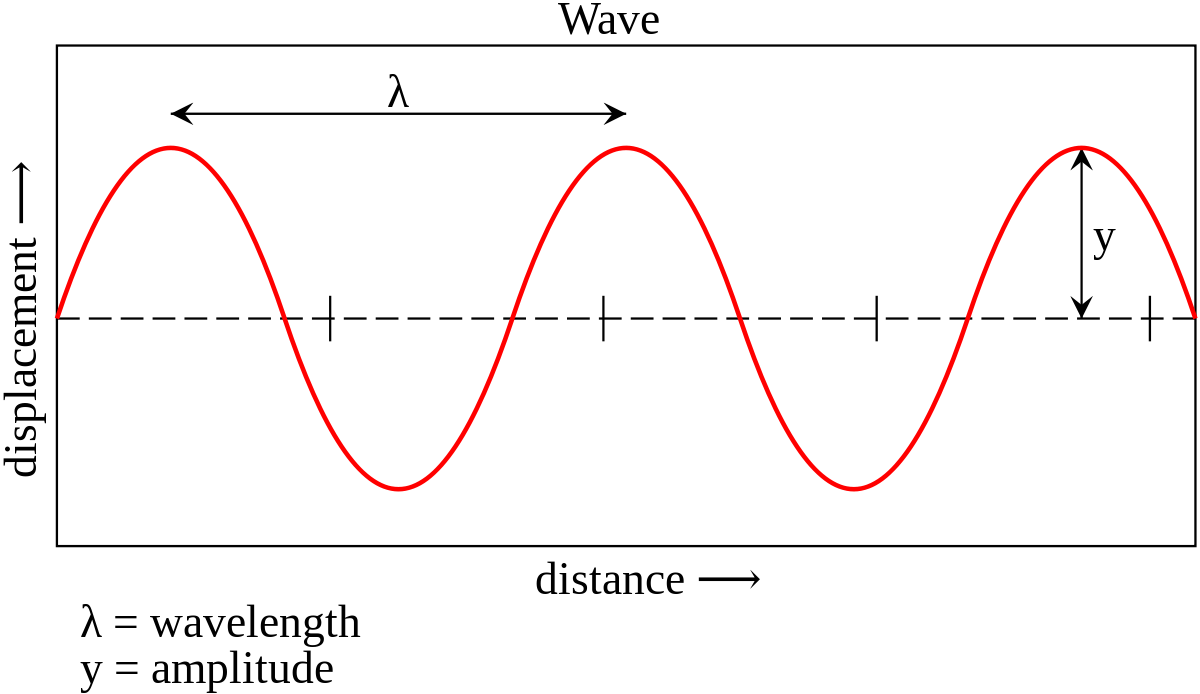
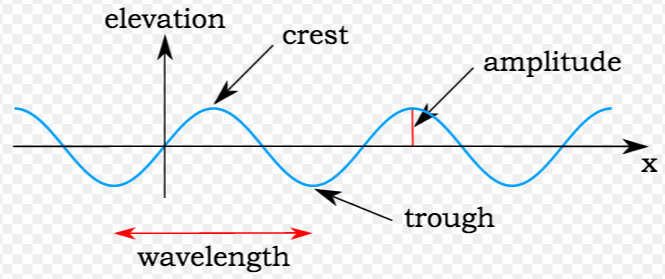
- Waves and Sound: This topic explores the behavior of waves, including sound waves. It includes concepts like wave interference, resonance, and the Doppler effect. Applications include designing musical instruments, sonar systems, and earthquake monitoring.
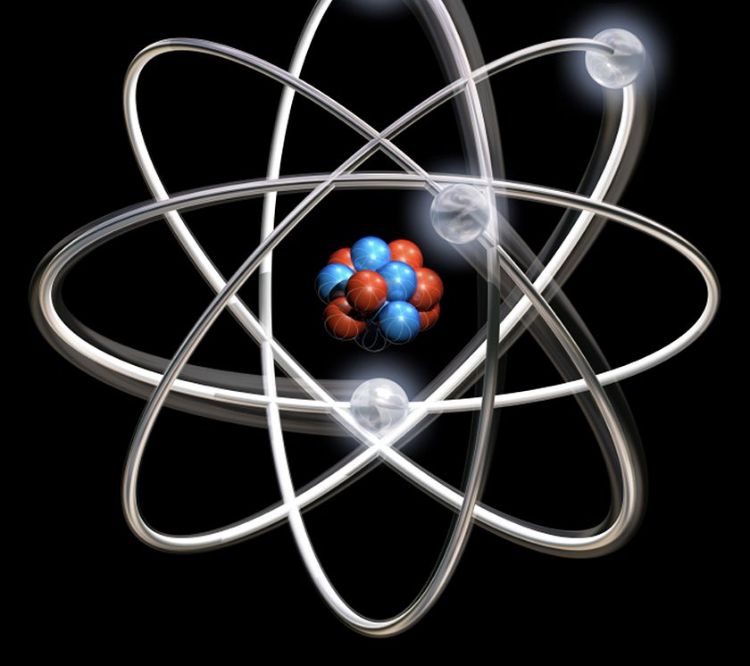
- Modern Physics: Modern physics focuses on the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic level. Topics include quantum mechanics, relativity, and particle physics. Applications include nuclear energy, semiconductors, and medical imaging technologies.
- Nuclear Physics: Nuclear physics deals with the behavior of atomic nuclei and subatomic particles. It includes topics like nuclear reactions, radioactivity, and nuclear decay. Applications include nuclear power generation, radiocarbon dating, and medical treatments.
- Astrophysics: Astrophysics explores the properties and behavior of celestial objects, such as stars, planets, and galaxies. Topics include the life cycles of stars, the Big Bang theory, and cosmic phenomena. Applications include understanding the universe’s origins, predicting astronomical events, and space exploration.
- Fluid Dynamics: Fluid dynamics investigates the behavior of liquids and gases in motion. Topics include fluid flow, turbulence, and aerodynamics. Applications include aircraft design, weather prediction, and the study of ocean currents.
- Geophysics: Geophysics applies physical principles to the study of the Earth’s structure and processes. Topics include seismic waves, magnetism, and gravity. Applications include earthquake monitoring, resource exploration, and understanding the Earth’s magnetic field.
These secondary physics topics have a wide range of practical applications, from designing everyday technologies to advancing our understanding of the natural world and the universe. Physics plays a crucial role in many scientific and engineering disciplines, shaping the way we interact with the world and explore the unknown.