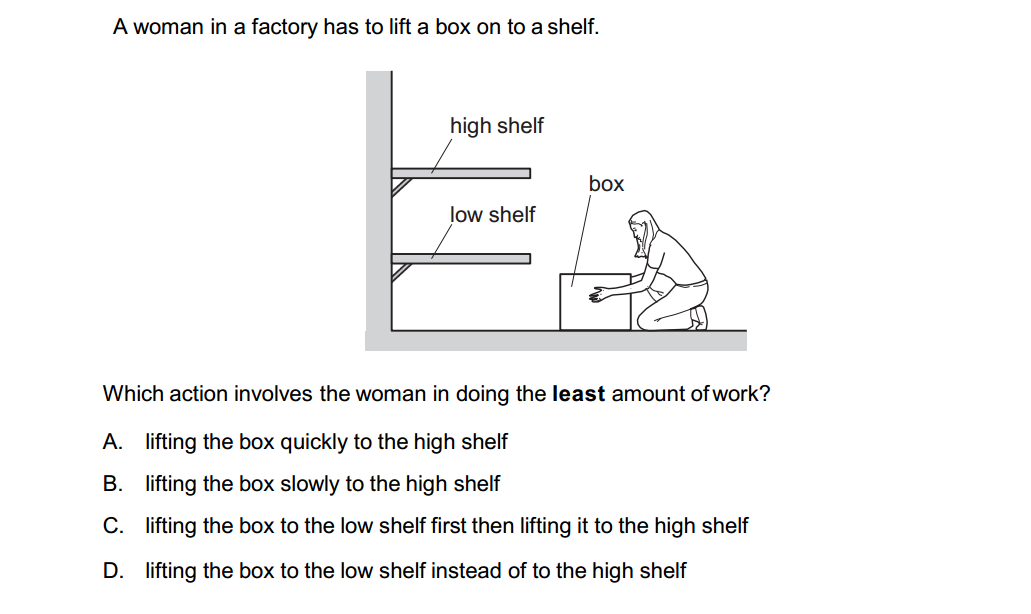
In auditing, various terms are used to describe processes, standards, and concepts related to examining and evaluating financial information. Here are some common terms used in auditing:
- Audit:
- The systematic examination of financial information, transactions, records, and processes to ensure accuracy, reliability, and compliance with applicable standards.
- Auditor:
- A professional who conducts audits and examines financial statements to express an opinion on their fairness and compliance with accounting standards.
- Financial Statements:
- Formal records that present the financial position, performance, and cash flows of an entity. They typically include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
- Internal Audit:
- An independent, objective evaluation of an organization’s internal controls, risk management, and operational processes conducted by internal auditors.
- External Audit:
- An independent examination of financial statements conducted by external auditors to provide assurance to stakeholders regarding their reliability and adherence to accounting principles.
- Materiality:
- The significance or importance of an item or an error in financial statements. Materiality is a key factor in determining the scope and focus of an audit.
- Audit Risk:
- The risk that the auditor may express an inappropriate opinion on financial statements that are materially misstated. It is a combination of inherent risk, control risk, and detection risk.
- Inherent Risk:
- The susceptibility of financial statements to material misstatement before considering internal controls.
- Control Risk:
- The risk that internal controls will not prevent or detect material misstatements in financial statements.
- Detection Risk:
- The risk that auditors’ procedures will fail to detect a material misstatement that exists in the financial statements.
- Sampling:
- The process of selecting a subset of items from a population for examination during an audit. It is often used due to the impracticality of examining every item.
- Segregation of Duties:
- The practice of dividing tasks and responsibilities among different individuals or departments to prevent fraud and errors.
- Substantive Procedures:
- Audit procedures designed to obtain direct evidence about the accuracy and completeness of account balances and transactions.
- Audit Trail:
- A step-by-step record that traces the financial transactions from their source to the final financial statements.
- Going Concern Assumption:
- The assumption that an entity will continue its operations for the foreseeable future. Auditors assess an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern.
- Management Assertion:
- Representations made by management regarding the fairness of financial statements and the effectiveness of internal controls.
- Material Weakness:
- A significant deficiency or combination of deficiencies in internal controls over financial reporting that could lead to a material misstatement.
- Qualified Opinion:
- An audit opinion expressing reservations about certain aspects of the financial statements but not overall fairness.
- Unqualified Opinion:
- An audit opinion expressing no reservations about the fairness of the financial statements.
- Peer Review:
- An external review of an audit firm’s quality control systems and procedures performed by another audit firm.
These terms provide a foundation for understanding the language and concepts used in the field of auditing. They are crucial for auditors, accounting professionals, and stakeholders involved in the financial reporting process.