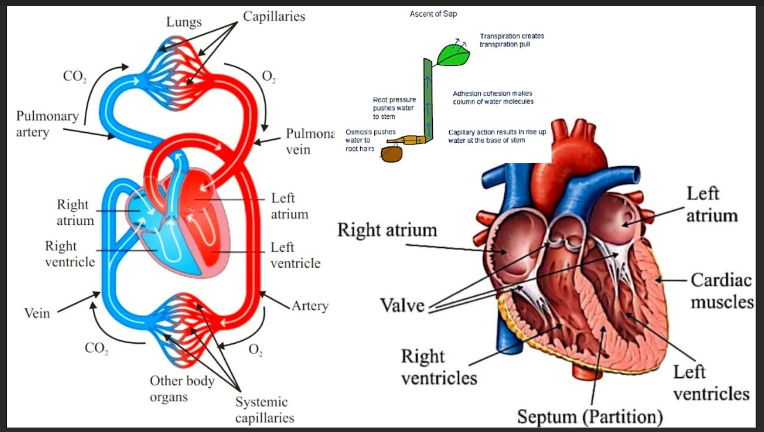
Transport in plants refers to the movement of water, nutrients, sugars, and other substances within a plant’s body. There are two main types of transport in plants:
- Water and mineral transport: This type of transport is known as the ascent of sap and occurs in the xylem tissue. It involves the movement of water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. The process is driven by transpiration, which is the loss of water vapor through small openings called stomata on the leaves. As water evaporates from the leaves, it creates a negative pressure that pulls water up through the xylem vessels. Adhesion and cohesion forces also play a role in the upward movement of water. Mineral ions are absorbed by the roots and transported along with water through the xylem to reach the various parts of the plant.
- Organic nutrient transport: This type of transport is known as the translocation of sap and occurs in the phloem tissue. It involves the movement of sugars, amino acids, hormones, and other organic compounds from sources (such as mature leaves and storage organs) to sinks (such as growing tissues, developing fruits, and roots). The movement of sap in the phloem occurs through specialized cells called sieve tubes, which are connected end-to-end to form a continuous system. The process is driven by osmotic pressure gradients. Sugars produced during photosynthesis are loaded into the phloem at the source, creating a high concentration of solutes. This causes water to enter the phloem through osmosis, creating a positive pressure that pushes the sap toward the sinks where sugars are unloaded.
Overall, the transport system in plants allows for the distribution of water, nutrients, and other essential substances to support various physiological processes, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Here are 20 objective questions on transport in plants and Answers
- Which tissue in plants is responsible for the transport of water and minerals? a) Phloem b) Epidermis c) Xylem d) Parenchyma
- What is the main driving force for water movement in plants? a) Active transport b) Osmosis c) Transpiration d) Photosynthesis
- Water enters the plant through which structure? a) Stomata b) Xylem vessels c) Phloem tubes d) Root hairs
- Which process is responsible for the movement of sugars in plants? a) Osmosis b) Transpiration c) Translocation d) Respiration
- Which tissue is responsible for the transport of sugars in plants? a) Xylem b) Phloem c) Epidermis d) Parenchyma
- What is the primary source of sugars in plants? a) Roots b) Stem c) Leaves d) Flowers
- What is the main force driving the movement of sap in the phloem? a) Transpiration b) Active transport c) Cohesion d) Osmotic pressure
- Which type of cells are involved in the transport of water in xylem? a) Sieve tubes b) Companion cells c) Tracheids and vessels d) Collenchyma cells
- How are mineral ions transported in plants? a) Through diffusion b) Active transport c) Osmosis d) Transpiration
- Which part of the plant is responsible for the absorption of water and minerals? a) Leaves b) Flowers c) Stems d) Roots
- What is the role of stomata in transport? a) Absorption of sunlight b) Exchange of gases c) Movement of sugars d) Water storage
- What is the function of the casparian strip in roots? a) Regulating water loss b) Facilitating gas exchange c) Preventing backflow of water d) Assisting in nutrient absorption
- What is the process by which water vapor is lost through leaf stomata? a) Osmosis b) Respiration c) Transpiration d) Evaporation
- What is the term used to describe the loss of water from plant leaves? a) Photosynthesis b) Osmosis c) Transpiration d) Respiration
- What is the role of transpiration in the ascent of sap? a) It creates a positive pressure in the xylem. b) It pulls water up through the xylem. c) It helps in the transport of sugars. d) It regulates the opening and closing of stomata.
- What is the function of phloem sieve tubes in plants? a) Transporting water and minerals b) Conducting photosynthesis c) Transporting sugars and other organic compounds d) Providing mechanical support
- Which of the following is not a factor affecting the rate of transpiration? a) Temperature b) Humidity c) Wind speed d) Root pressure
- What is the term for the process of loading sugars into the phloem at the source? a) Translocation b) Transpiration c) Transpiration pull d) Phloem loading
- What is the primary function of the root hairs in plants? a) Absorbing water and nutrients b) Storing carbohydrates c) Producing hormones d) Anchoring the plant in the soil
- What is the movement of sugars from the phloem to the sink tissues called? a) Transpiration b) Translocation c) Photosynthesis d) Osmosis
Answers:
- c) Xylem
- c) Transpiration
- d) Root hairs
- c) Translocation
- b) Phloem
- c) Leaves
- d) Osmotic pressure
- c) Tracheids and vessels
- b) Active transport
- d) Roots
- b) Exchange of gases
- c) Preventing backflow of water
- c) Transpiration
- c) Transpiration
- b) It pulls water up through the xylem.
- c) Transporting sugars and other organic compounds
- d) Root pressure
- d) Phloem loading
- a) Absorbing water and nutrients
- b) Translocation