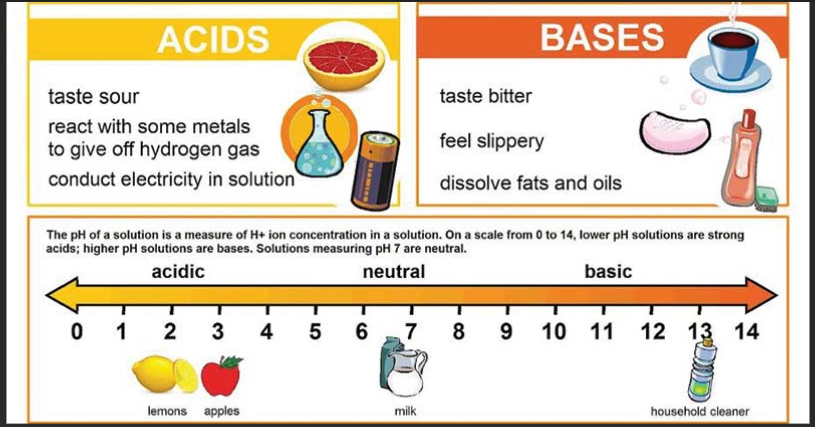
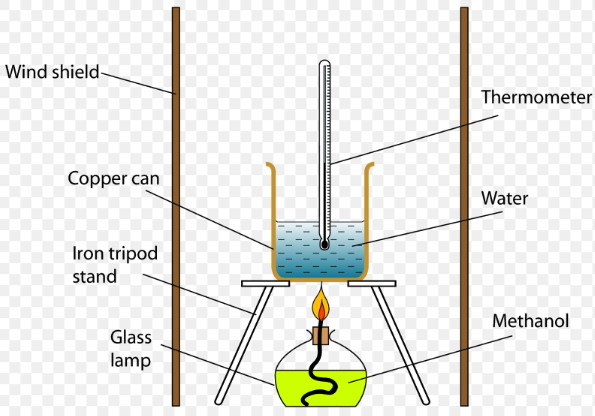
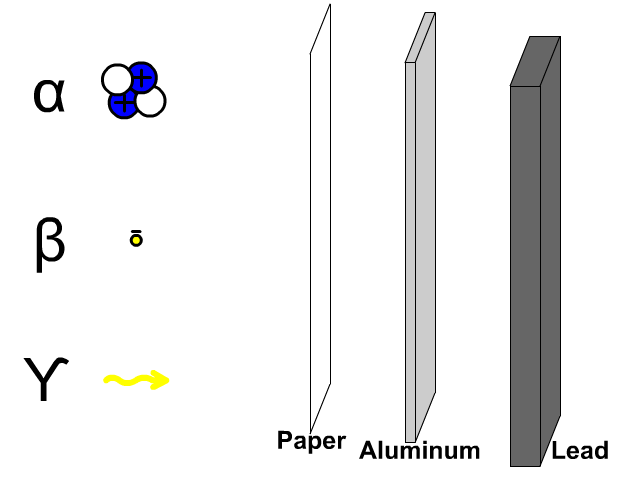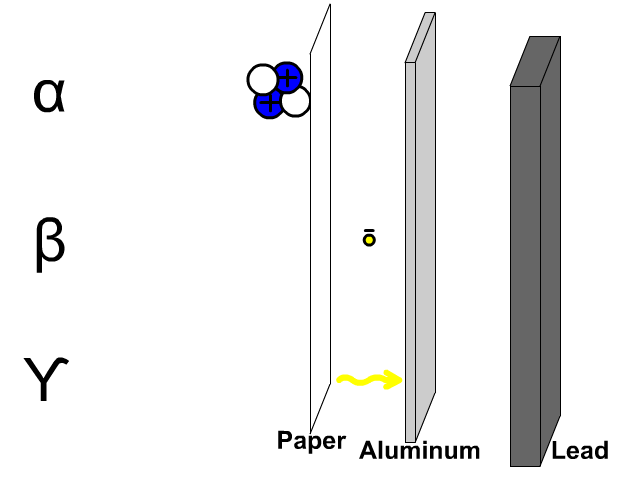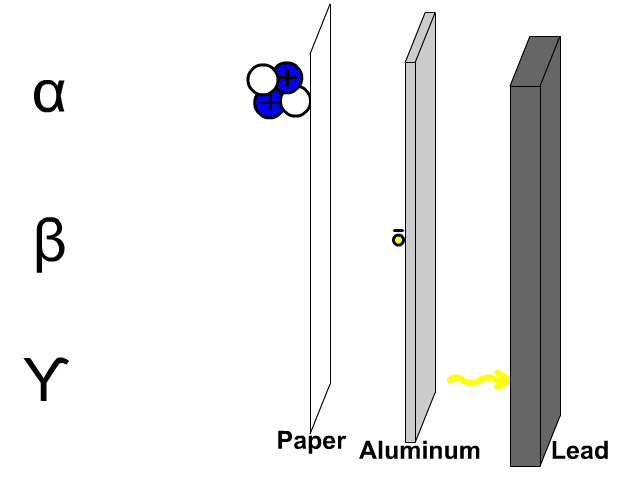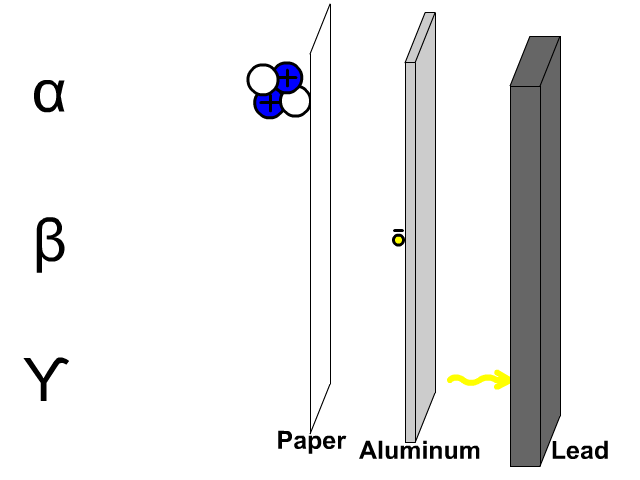
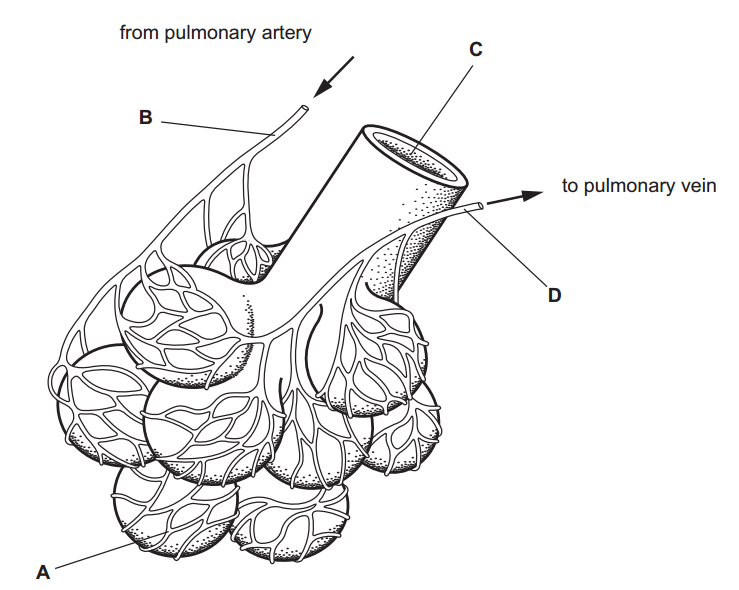
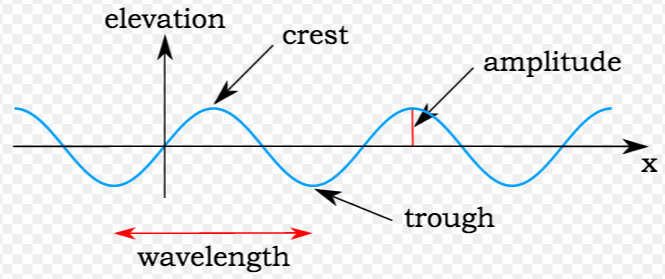
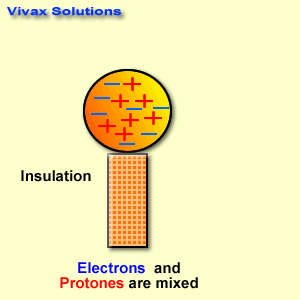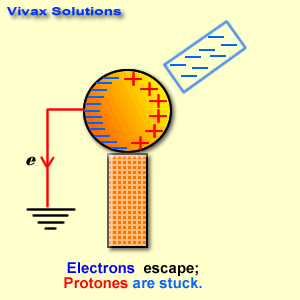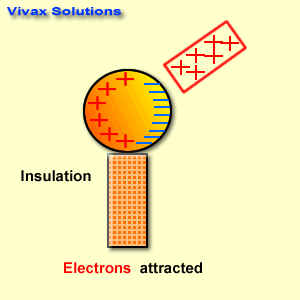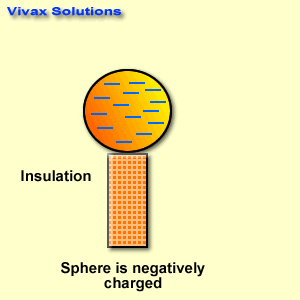
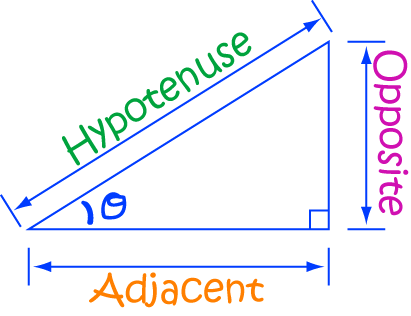
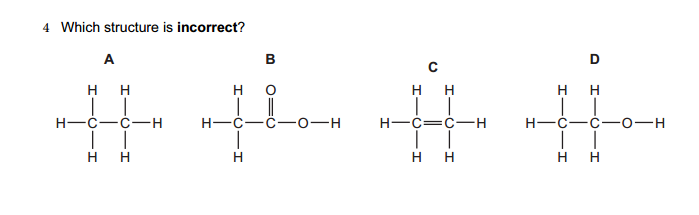
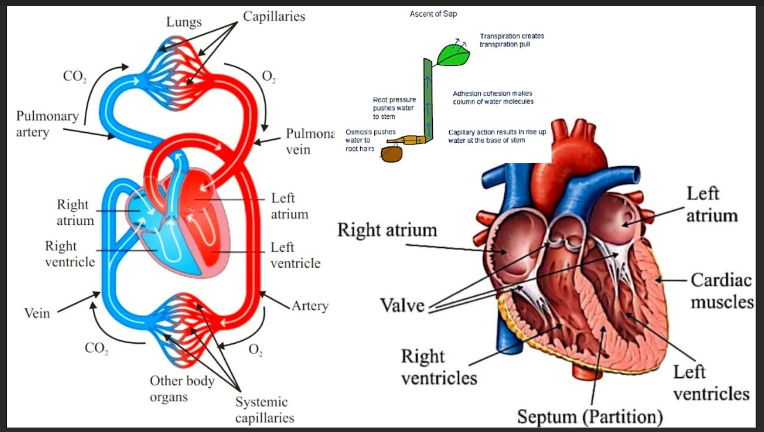
Research is a systematic and methodical investigation carried out to discover new knowledge, validate existing knowledge, or solve specific problems. It involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data to answer research questions or test hypotheses.
There are various research methods that researchers employ based on the nature of the research question, available resources, and the type of data required. Here are some common research methods:
- Experimental Research: This method involves manipulating variables under controlled conditions to establish cause-and-effect relationships. Researchers divide participants into experimental and control groups, apply interventions or treatments to the experimental group, and compare the outcomes with the control group.
- Survey Research: Surveys gather data from a sample of individuals by using questionnaires or interviews. Researchers aim to collect information about opinions, attitudes, behaviors, and characteristics of a particular population. Survey research can be conducted through online surveys, telephone interviews, face-to-face interviews, or mailed questionnaires.
- Observational Research: Observational research involves directly observing and recording behaviors, phenomena, or events in their natural setting without intervening or manipulating variables. Researchers may use structured observation, where specific behaviors are predefined, or unstructured observation, where they observe and record various aspects of the situation.
- Qualitative Research: Qualitative research aims to explore and understand complex phenomena and subjective experiences. It involves in-depth interviews, focus groups, observations, and analysis of textual or visual data. Qualitative research focuses on generating rich, descriptive data to capture the depth and complexity of human experiences and social contexts.
- Quantitative Research: Quantitative research involves the systematic collection and analysis of numerical data. It focuses on measuring variables, establishing patterns, and testing hypotheses using statistical analysis. Surveys, experiments, and large-scale data analysis are common quantitative research methods.
- Case Study Research: Case studies involve in-depth investigation and analysis of a specific individual, group, organization, or event. Researchers gather detailed information through various methods such as interviews, observations, documents, and archival records. Case studies provide an in-depth understanding of specific contexts and can be used to generate hypotheses or theories.
- Literature Review: A literature review is a systematic and critical analysis of existing research and publications on a specific topic. It involves searching, reviewing, and synthesizing relevant literature to identify gaps, contradictions, or areas for further research. Literature reviews are crucial for establishing the context of research and identifying research questions.
- Action Research: Action research involves collaborative and iterative problem-solving within a specific context. It aims to bring about practical change or improvement while simultaneously generating knowledge. Action research typically involves cycles of planning, action, observation, and reflection.
These are just a few examples of research methods used in various disciplines. Researchers often combine multiple methods or adapt them to suit their specific research objectives and the nature of the research question at hand. The choice of research method depends on the research goals, available resources, ethical considerations, and the type of data needed to answer the research question.