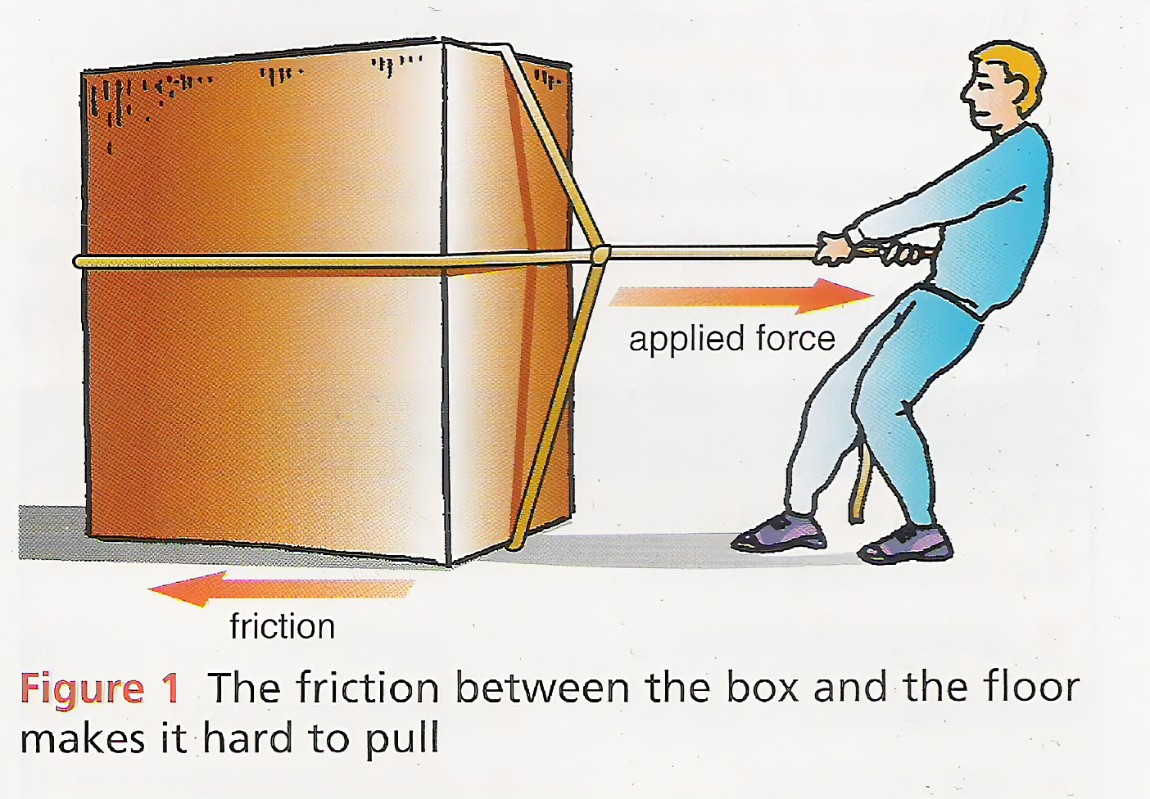
Workshop safety refers to the measures and practices implemented to ensure the well-being and protection of individuals working in a workshop environment. It involves identifying and mitigating potential hazards, promoting safe work practices, and maintaining a secure and healthy workspace. Here are some key aspects of workshop safety:
- Hazard identification and risk assessment: Regularly inspect the workshop to identify potential hazards such as sharp tools, heavy machinery, electrical equipment, chemicals, and flammable materials. Assess the risks associated with each hazard and take appropriate measures to control or eliminate them.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Provide and enforce the use of suitable PPE, such as safety goggles, ear protection, gloves, aprons, and safety shoes. The type of PPE required depends on the specific tasks and potential hazards present in the workshop.
- Machinery and equipment safety: Ensure that all machinery and equipment in the workshop are properly maintained, inspected, and used correctly. Train employees on the safe operation of machinery, including lockout/tagout procedures, emergency stops, and guarding mechanisms.
- Electrical safety: Regularly inspect electrical systems, cords, and outlets for any damage or hazards. Avoid overloading circuits and ensure proper grounding. Encourage employees to report any electrical issues promptly.
- Fire safety: Maintain clear access to fire exits, fire extinguishers, and fire alarms. Implement fire prevention measures, such as proper storage of flammable materials, regular cleaning, and the availability of appropriate firefighting equipment.
- Chemical safety: Store and handle chemicals properly, following guidelines and safety data sheets (SDS). Provide adequate ventilation in areas where chemicals are used, and train employees on safe handling, storage, and disposal practices.
- Ergonomics: Arrange workstations to promote ergonomic principles, ensuring that employees have proper posture, suitable seating, and adequate lighting. Encourage regular breaks and stretching exercises to minimize the risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
- Training and education: Conduct comprehensive safety training programs for all workshop employees. Train them on proper equipment use, emergency procedures, hazard recognition, and the importance of following safety protocols.
- Housekeeping: Maintain a clean and organized workshop environment. Regularly remove debris, spills, and clutter to prevent slip and trip hazards. Properly store tools and equipment when not in use.
- Emergency preparedness: Develop and communicate emergency response plans, including procedures for accidents, injuries, fires, and evacuation. Conduct drills periodically to ensure employees are familiar with the protocols.
Regular safety audits, feedback from employees, and continuous improvement efforts are essential to maintaining a safe workshop environment. It is crucial to promote a culture of safety where all employees actively participate in identifying and addressing potential hazards.
- What is the importance of workplace safety?
- Why is it important to wear personal protective equipment (PPE)?
- What are the main causes of slips, trips, and falls in the workplace?
- How can you prevent ergonomic injuries in the office?
- What are the risks associated with working at heights, and how can they be mitigated?
- How should you handle and store hazardous chemicals safely?
- What are the fire safety procedures in the workplace?
- What should you do if you discover a fire in the building?
- What are the risks of using electrical equipment improperly?
- How can you prevent repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) in the workplace?
- What are the dangers of working with machinery, and how can they be minimized?
- How should you respond to a workplace accident or injury?
- What are the safety precautions for working with ladders and scaffolding?
- How can you prevent back injuries when lifting heavy objects?
- What are the dangers of working in confined spaces, and what safety measures should be taken?
- What should you do in case of a chemical spill or leak?
- What are the risks associated with working in extreme temperatures, and how can they be managed?
- How can you prevent exposure to harmful fumes, dust, or other airborne substances?
- What is the importance of regular equipment inspections and maintenance?
- How can you prevent accidents caused by distracted driving or walking?
- What are the safety procedures for working with power tools?
- How should you handle and dispose of sharp objects, such as needles or broken glass?
- What are the risks associated with working alone, and how can they be mitigated?
- What are the safety precautions for using and storing compressed gas cylinders?
- How can you prevent accidents caused by improper storage or handling of materials?
- What are the safety protocols for working in a laboratory environment?
- How should you respond to a workplace emergency, such as a natural disaster?
- What are the risks of exposure to excessive noise, and how can they be controlled?
- How should you properly secure and lockout/tagout equipment during maintenance or repairs?
- What are the safety precautions for working with corrosive substances?
- How can you prevent accidents caused by inadequate lighting in the workplace?
- What are the risks of working with vibrating tools or equipment, and how can they be minimized?
- How should you respond to a workplace violence incident?
- What are the safety procedures for handling and storing flammable materials?
- How can you prevent accidents caused by unguarded machinery or moving parts?
- What are the safety measures for preventing falls from ladders or elevated platforms?
- How should you respond to a medical emergency in the workplace?
- What are the risks of exposure to radiation, and how can they be managed?
- How can you prevent accidents caused by improper use or maintenance of fire extinguishers?
- What are the safety protocols for working in outdoor environments with extreme weather conditions?
These questions cover a variety of safety topics and can be used for training, discussions, or assessments to promote safety awareness and knowledge in the workplace.
Answers to the Above questions are next….
- Workplace safety is important to protect employees from accidents, injuries, and illnesses, ensuring their well-being and promoting a productive work environment.
- Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) is important because it provides a physical barrier and safeguards against workplace hazards, such as chemicals, flying objects, noise, and impacts.
- The main causes of slips, trips, and falls in the workplace include wet or slippery surfaces, uneven flooring, cluttered walkways, and improper footwear.
- Ergonomic injuries in the office can be prevented by using ergonomic furniture and equipment, maintaining proper posture, taking regular breaks, and incorporating stretching exercises.
- Working at heights poses risks of falling. Mitigation measures include using fall protection equipment, such as harnesses and guardrails, and implementing proper training and procedures.
- Hazardous chemicals should be handled and stored safely by following proper labeling, using appropriate containers, ensuring proper ventilation, and having clear procedures for spills and leaks.
- Fire safety procedures in the workplace include having fire alarms, clear escape routes, fire extinguishers, and conducting fire drills. Employees should know how to evacuate safely and raise the alarm.
- In case of a fire, the priority is to ensure everyone’s safety by evacuating the building and calling emergency services. If it’s safe to do so, attempt to extinguish the fire using appropriate equipment.
- Improper use of electrical equipment can lead to electrical shocks or fires. Safety measures include proper grounding, avoiding overloading circuits, and using insulated tools and equipment.
- Repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) can be prevented by practicing good ergonomics, taking regular breaks, using proper posture, and using ergonomic tools and equipment.
- Dangers associated with machinery can include entanglement, crushing, and impact hazards. Minimize risks by providing proper training, using guarding mechanisms, and following lockout/tagout procedures.
- In case of a workplace accident or injury, the response should include providing immediate medical attention, securing the area, documenting the incident, and conducting an investigation to prevent future occurrences.
- Safety precautions for working with ladders and scaffolding include proper setup, regular inspection, maintaining three points of contact, and using fall protection equipment.
- To prevent back injuries when lifting heavy objects, use proper lifting techniques, such as bending at the knees and using leg muscles, seeking assistance when needed, and using mechanical aids.
- Working in confined spaces can be hazardous due to lack of ventilation, toxic gases, or the potential for entrapment. Safety measures include proper training, proper air monitoring, and following entry procedures.
- In case of a chemical spill or leak, follow proper spill response procedures, which may include evacuating the area, containing the spill, and contacting specialized personnel for cleanup.
- Risks associated with working in extreme temperatures include heat exhaustion, heatstroke, hypothermia, and frostbite. Manage risks by providing suitable clothing, breaks, hydration, and temperature control measures.
- To prevent exposure to harmful fumes, dust, or other airborne substances, use ventilation systems, wear appropriate respiratory protection, and follow proper handling and storage procedures.
- Regular equipment inspections and maintenance help identify and address potential hazards, prevent equipment failures, and ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Accidents caused by distracted driving or walking can be prevented by eliminating distractions, such as using mobile devices, and practicing situational awareness and safe behavior.
- Safety procedures for working with power tools include wearing appropriate PPE, ensuring proper grounding, using the tools correctly, and disconnecting power before making adjustments.
- Handle and dispose of sharp objects safely by using proper containers, using tools to pick them up, and disposing of them in designated sharps containers.
- Risks associated with working alone include accidents, medical emergencies, and security incidents. Mitigate risks by implementing check-in procedures, emergency protocols, and providing training.
- Safety precautions for using and storing compressed gas cylinders include proper handling, storage in well-ventilated areas, securing cylinders, and regular inspections.
- Accidents caused by improper storage or handling of materials can be prevented by proper labeling, appropriate storage containers, organizing materials, and following storage guidelines.
- Safety protocols for working in a laboratory environment include proper handling of chemicals, wearing appropriate PPE, maintaining good hygiene practices, and following specific procedures for experiments.
- In case of a workplace emergency, such as a natural disaster, follow established emergency response plans, evacuate if necessary, and seek safety in designated areas.
- Risks of exposure to excessive noise include hearing loss and other health issues. Control noise levels through engineering controls, wearing hearing protection, and implementing a hearing conservation program.
- Properly secure and lockout/tagout equipment during maintenance or repairs by following established procedures to prevent unexpected startup and protect workers from hazardous energy.
- Safety precautions for working with corrosive substances include using appropriate PPE, ensuring proper ventilation, storing substances in compatible containers, and following safe handling procedures.
- Accidents caused by inadequate lighting can be prevented by ensuring proper lighting levels, especially in areas with potential hazards or tasks that require visual acuity.
- Risks of working with vibrating tools or equipment include hand-arm vibration syndrome (HAVS). Minimize risks by using anti-vibration gloves, taking regular breaks, and using tools with lower vibration levels.
- In case of a workplace violence incident, prioritize personal safety by removing yourself from the situation and contacting security or law enforcement as appropriate.
- Safety procedures for handling and storing flammable materials include proper labeling, storing in approved containers and areas, using proper ventilation, and following fire safety protocols.
- Accidents caused by unguarded machinery or moving parts can be prevented by installing guards, implementing proper training, and following lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance.
- Safety measures for preventing falls from ladders or elevated platforms include using proper fall protection equipment, maintaining three points of contact, and securing the ladder or platform.
- In case of a medical emergency in the workplace, call for medical assistance, provide first aid if trained to do so, and follow established emergency procedures.
- Risks of exposure to radiation depend on the type and level of radiation. Manage risks through proper shielding, limiting exposure time, and following radiation safety protocols.
- Prevent accidents caused by improper use or maintenance of fire extinguishers by ensuring they are inspected regularly, properly charged, accessible, and employees are trained on their use.
- Safety protocols for working in outdoor environments with extreme weather conditions include monitoring weather forecasts, providing suitable clothing and protection, and having appropriate emergency response plans.